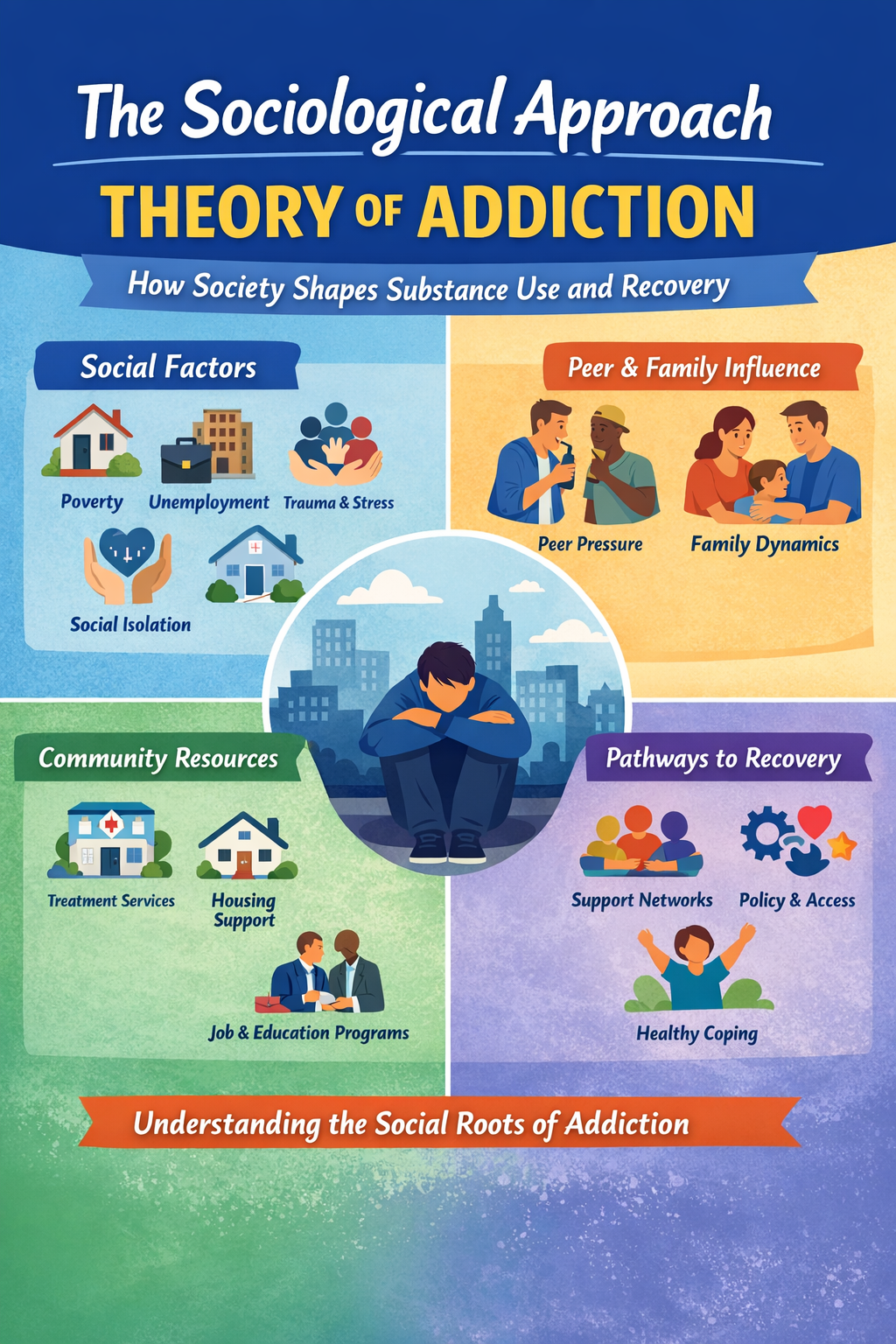
The Three-Fold Disease Of Addiction
Addiction can be a tough and confusing topic to understand because it isn’t just about what someone is using or doing too much. It’s about what’s happening inside a person on different levels. When people talk about the “threefold disease of addiction,” they’re pointing to a way of understanding addiction that covers the body, mind, … Read more