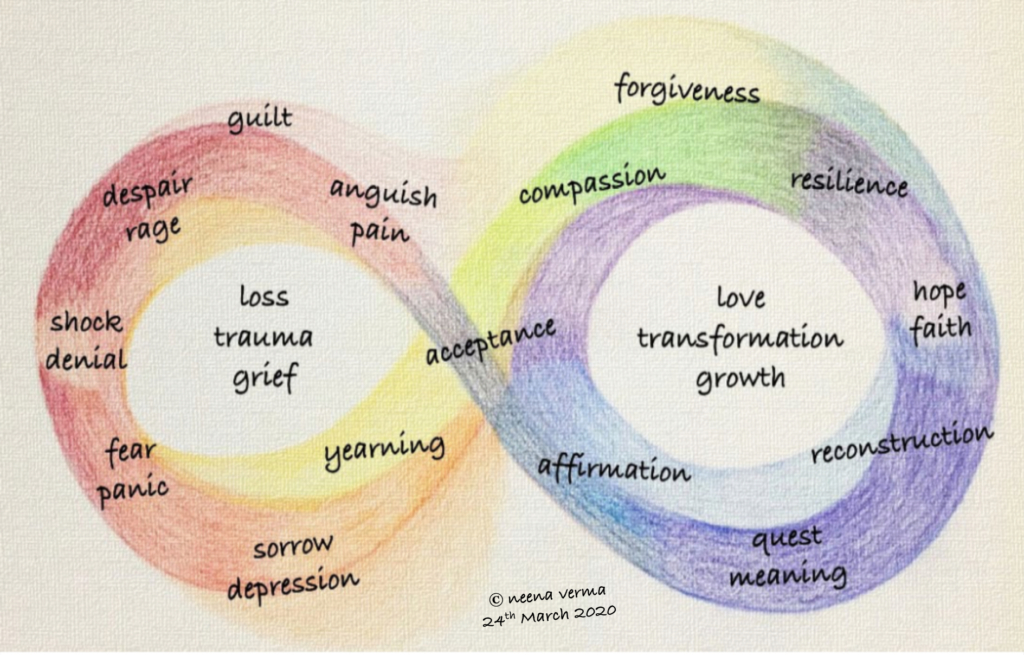
Transforming Pain into Purpose
Pain and struggle often come hand in hand with addiction recovery. But pain can pave the way to some of the most powerful changes in our lives. I’ve learned that real progress happens not by avoiding pain, but by learning how to use it for something that gives us meaning and direction. In this guide, … Read more