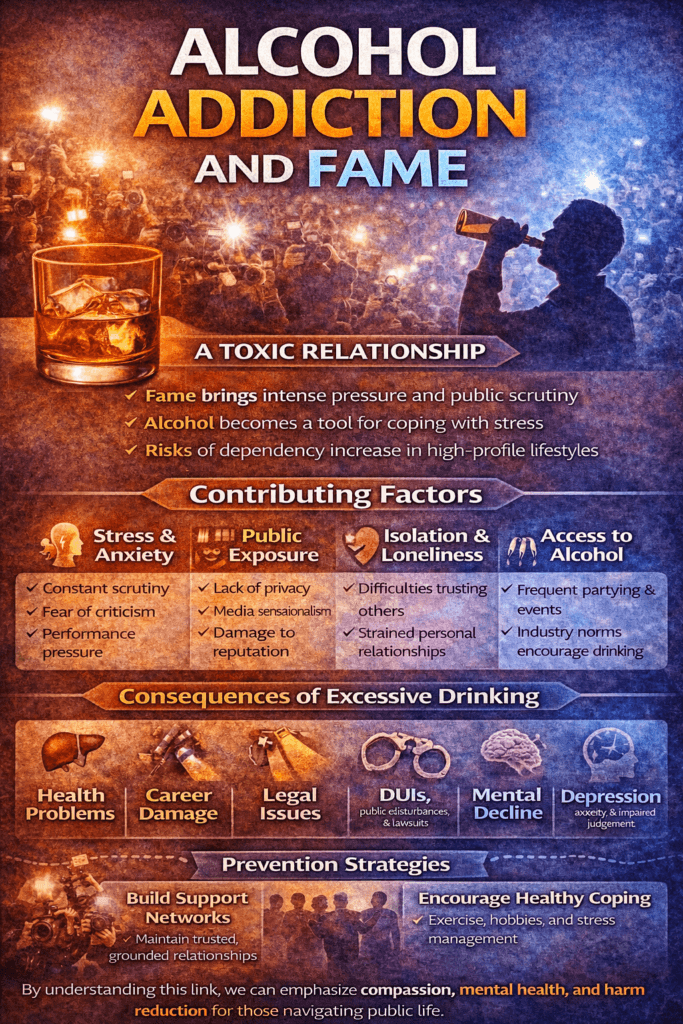
The intersection of alcohol addiction and fame reveals a complex relationship shaped by pressure, visibility, and environment. While public success is often associated with privilege and admiration, individuals in high-profile roles frequently face intense scrutiny, demanding schedules, and social settings where alcohol is normalized. These factors can increase vulnerability to unhealthy coping habits, particularly when stress, isolation, or performance expectations become overwhelming. Understanding how fame can influence drinking behaviors helps shift the conversation away from judgment and toward awareness of the psychological and environmental factors that contribute to alcohol misuse.
Alcoholism and Fame: A Toxic Relationship Exposed
Fame is often associated with glamour, success, and admiration—but beneath the spotlight, many public figures face intense psychological pressures that can increase vulnerability to substance misuse, including alcohol dependence. The relationship between fame and alcoholism is complex and often misunderstood. While fame itself does not cause addiction, the environment surrounding celebrity life can create conditions that heighten risk, blur boundaries, and make harmful habits easier to develop and harder to stop.
The Psychological Pressure of Public Life
Public figures frequently live under constant scrutiny. Every decision, mistake, or emotional reaction can be magnified by media attention and public commentary. This persistent pressure can lead to chronic stress, anxiety, and emotional exhaustion. Alcohol may become a coping mechanism—initially used to relax or manage social demands, but gradually relied upon to escape stress or numb emotional strain.
Access, Opportunity, and Social Norms
Fame often brings wealth, travel, exclusive events, and social environments where alcohol is readily available and culturally normalized. Industry events, parties, and networking functions may revolve around drinking, creating an environment where excessive alcohol use is not only accepted but sometimes encouraged. This constant exposure can make moderation difficult and conceal early warning signs of dependency.
Isolation Behind the Spotlight
Despite being surrounded by people, many famous individuals experience profound loneliness. Trust can become difficult when relationships may be influenced by status or financial interests. This isolation can intensify emotional distress, and alcohol may become a substitute for genuine connection or emotional support.
The Reinforcement Loop
Alcohol can temporarily reduce stress and social anxiety, reinforcing its use. For someone in the public eye, this reinforcement can be especially powerful:
- Alcohol eases performance pressure
- It reduces social inhibition
- It dulls criticism or negative press
Over time, this cycle can create psychological and physiological dependence, making it increasingly difficult to function without drinking.
Barriers to Seeking Help
Ironically, fame can make recovery harder. Public figures may fear:
- Damage to reputation or career
- Media exposure of treatment
- Judgment from fans or sponsors
These concerns can delay treatment, allowing alcohol misuse to progress further before intervention occurs.
Why This Issue Matters Beyond Celebrities
Although fame creates unique pressures, the underlying dynamics—stress, isolation, access, and coping patterns—exist in many high-pressure professions and lifestyles. Understanding how these factors interact helps broaden awareness that addiction is rarely about weakness; it is often about environment, stress load, and coping resources.
A Healthier Perspective
Recognizing the link between fame and alcoholism highlights the importance of:
- Mental health support systems
- Healthy coping strategies
- Boundaries with work and public exposure
- Access to confidential treatment
When these supports are in place, the risk of substance misuse can be significantly reduced.
Conclusion
The intersection of alcoholism and fame reveals a powerful truth: success and visibility do not protect against addiction—in some cases, they may increase vulnerability. The pressures of public life, combined with access and isolation, can create a perfect storm that fuels unhealthy coping behaviors. By understanding this toxic relationship, society can move beyond judgment and toward compassion, emphasizing prevention, mental health support, and recovery for anyone navigating life under pressure—whether in the spotlight or not.
Self-Management Strategies to Prevent the Consequences of Alcohol Addiction and Fame
Fame can amplify both success and vulnerability. Public recognition often brings intense pressure, constant scrutiny, and social environments where alcohol is easily accessible and normalized. For individuals in high-visibility roles—whether celebrities, influencers, performers, or public leaders—these conditions can increase the risk of unhealthy coping behaviors. Self-management strategies are essential tools for maintaining emotional balance, protecting health, and preventing the negative consequences of alcohol misuse while navigating public life.
1. Develop Emotional Awareness
One of the strongest protective skills is recognizing emotional triggers. Stress, criticism, loneliness, performance anxiety, and fatigue can all increase the urge to drink. Practicing emotional check-ins—asking “What am I feeling right now?”—helps separate emotional needs from impulsive reactions. Journaling, mindfulness exercises, or brief self-reflection routines can increase awareness and reduce automatic coping behaviors.
2. Set Clear Personal Limits
Establishing boundaries around alcohol use before entering high-risk environments is a powerful preventive strategy. Examples include:
- Predetermining drink limits
- Scheduling alcohol-free days
- Alternating alcoholic and nonalcoholic drinks
- Choosing events selectively
Pre-planned limits reduce decision fatigue in social situations and reinforce self-control.
3. Create Structured Routines
Fame often disrupts normal schedules through travel, performances, media appearances, and irregular sleep. Structured routines—consistent sleep times, exercise habits, meals, and work blocks—help stabilize mood and stress levels. Predictable routines support neurological regulation, reducing the likelihood of impulsive drinking.
4. Build a Trusted Inner Circle
Isolation is a major risk factor for addiction, even for people constantly surrounded by others. Maintaining a small circle of trusted friends, mentors, or professionals who provide honest feedback can counteract the artificial environment that fame sometimes creates. These individuals can help detect early warning signs and provide a grounded perspective.
5. Replace Alcohol With Healthier Coping Tools
Alcohol is often used to reduce anxiety or unwind after public appearances. Replacing it with healthier alternatives—such as exercise, creative outlets, meditation, therapy, or relaxation techniques—can meet the same emotional needs without harmful consequences. The key is identifying which coping tools genuinely restore energy rather than temporarily numbing discomfort.
6. Monitor Early Warning Signs
Self-monitoring helps identify when drinking patterns may be shifting. Warning signs may include:
- Drinking to manage stress or emotions
- Increasing tolerance
- Needing alcohol to socialize
- Difficulty stopping once started
- Drinking despite negative consequences
Recognizing these signs early allows for quick course correction before patterns escalate.
7. Protect Privacy and Seek Support Early
High-profile individuals sometimes delay help due to fear of public exposure or stigma. However, early professional support—such as counseling, coaching, or medical consultation—can prevent small concerns from becoming serious problems. Seeking help early is a proactive strength, not a failure.
Why Self-Management Matters in High-Visibility Lives
Fame magnifies both positive and negative behaviors. Healthy habits become powerful stabilizers, while unhealthy ones can escalate quickly under public pressure. Self-management creates internal structure when external environments are unpredictable. It also reinforces autonomy, ensuring that decisions about alcohol remain intentional rather than reactive.
Conclusion
Navigating fame while maintaining well-being requires intentional self-leadership. By developing emotional awareness, setting boundaries, maintaining routines, building trusted relationships, and monitoring personal patterns, individuals can reduce the risk of alcohol-related consequences despite high-pressure environments. Ultimately, success is not defined only by public recognition but by the ability to sustain health, clarity, and control behind the spotlight. Prevention through self-management allows individuals to thrive professionally without sacrificing personal stability.
Family Support Strategies to Prevent the Consequences of Alcohol Addiction and Fame
Fame can bring opportunity, admiration, and influence—but it can also introduce stress, isolation, and environments where alcohol is easily accessible and socially normalized. For individuals living in the public eye, family support often becomes the most stabilizing force protecting them from unhealthy coping patterns. Strong family systems can act as emotional anchors, helping loved ones maintain perspective, manage pressure, and recognize early signs of alcohol misuse before serious consequences develop. When families understand how fame and stress interact, they can provide proactive support that protects both well-being and long-term success.
1. Maintain Grounded Communication
Open, honest communication is one of the most effective protective tools families can offer. Loved ones should create safe spaces for conversation where the person can speak freely about stress, criticism, or pressure without fear of judgment. When individuals feel emotionally understood, they are less likely to turn to alcohol as a coping mechanism.
2. Reinforce Identity Beyond Fame
Public recognition can sometimes blur personal identity, making success or failure feel tied solely to public approval. Families can help by consistently affirming the person’s worth outside of their achievements, status, or image. This grounding reminder—that they are valued for who they are, not what they produce—reduces anxiety and performance pressure that can trigger substance use.
3. Watch for Early Behavioral Changes
Families are often the first to notice subtle shifts that others miss. Early warning signs may include:
- Increased irritability or mood swings
- Social withdrawal or secrecy
- Changes in sleep or appetite
- Escalating alcohol use at events
- Avoidance of responsibilities
Recognizing these signs early allows for supportive intervention before patterns intensify.
4. Establish Healthy Boundaries
Support does not mean enabling. Families can set compassionate but firm boundaries, such as refusing to cover up missed commitments, legal issues, or consequences related to drinking. Clear expectations help maintain accountability while still communicating love and concern. Balanced boundaries reinforce responsibility without shame.
5. Encourage Healthy Coping Alternatives
Families can model and promote healthier stress-management strategies, such as exercise, creative hobbies, time outdoors, relaxation techniques, or therapy. Engaging in these activities together strengthens connection and demonstrates that emotional relief can come from constructive outlets rather than alcohol.
6. Protect Privacy and Promote Safe Help-Seeking
Individuals in high-visibility roles may fear seeking help because of media exposure or public judgment. Families can play a key role by researching confidential treatment options, supporting discreet counseling, or accompanying loved ones to appointments. Knowing support is available without publicity can make seeking help feel safer.
7. Build a Stable Home Environment
While public life may be unpredictable, a stable home environment offers emotional consistency. Predictable routines, shared meals, traditions, and regular check-ins provide psychological security. This stability counterbalances the volatility of public attention and reduces reliance on substances for comfort.
Why Family Support Is So Powerful
Fame can amplify both strengths and vulnerabilities. Public praise can be intense—but so can criticism. Families serve as emotional regulators, offering perspective when external feedback becomes overwhelming. Their presence helps individuals remain grounded, self-aware, and resilient under pressure.
Conclusion
The intersection of fame and alcohol risk highlights the importance of strong family support systems. Through communication, boundaries, encouragement, and early awareness, families can help protect loved ones from the negative consequences of alcohol misuse while navigating high-pressure environments. Fame may shape a public identity, but family provides the foundation that sustains personal well-being. When families act with compassion, consistency, and insight, they become one of the most powerful protective factors against addiction and its long-term effects.
Community Resource Strategies to Prevent the Consequences of Alcohol Addiction and Fame
Fame can create extraordinary opportunities, but it can also introduce intense stress, public scrutiny, and social environments where alcohol use is normalized or encouraged. Individuals in high-visibility roles—such as entertainers, influencers, athletes, executives, or public figures—may face unique pressures that increase vulnerability to alcohol misuse. Community resources play a critical preventive role by providing structure, education, accountability, and confidential support. When communities invest in coordinated services, they help protect individuals from the potential consequences of alcohol addiction while promoting resilience, stability, and long-term well-being.
1. Accessible Mental Health and Addiction Services
Community clinics, counseling centers, and telehealth programs offer confidential support that allows individuals to address stress, anxiety, or substance concerns early. Easy access to licensed professionals helps people develop coping strategies before alcohol becomes a primary stress-management tool. Confidentiality is especially important for those in the public eye, as privacy concerns often delay help-seeking.
2. Preventive Education and Awareness Programs
Public health organizations and community initiatives can provide education about how fame, stress, and substance use interact. Workshops, seminars, and digital campaigns help individuals recognize warning signs, understand risk factors, and learn healthier coping strategies. Awareness reduces stigma and empowers individuals to seek help proactively.
3. Peer Support Networks
Peer-led support groups and mentorship programs offer connection and shared understanding. For individuals experiencing pressure from public visibility, speaking with others who have faced similar challenges can normalize struggles and reduce isolation. Peer communities reinforce accountability and remind participants they are not alone in managing stress or expectations.
4. Wellness and Stress-Management Programs
Community centers, wellness organizations, and nonprofit groups often provide structured activities such as mindfulness training, exercise programs, creative workshops, and stress-management classes. These resources offer healthy alternatives to alcohol for relaxation and emotional regulation. Structured wellness opportunities also create routine, which supports psychological stability.
5. Crisis Intervention and Referral Systems
Hotlines, crisis teams, and referral networks ensure rapid access to professional help when someone is struggling. These systems are particularly valuable when early signs of alcohol misuse appear, allowing for quick intervention before problems escalate. Immediate support reduces risk and promotes safety.
6. Collaborative Community Systems
The most effective prevention environments involve coordination among healthcare providers, educational institutions, employers, event organizers, and public health agencies. When these systems communicate and share resources, they create a safety net that identifies risks early and provides consistent guidance. Collaborative communities are better equipped to support individuals navigating high-pressure lifestyles.
7. Responsible Event and Industry Practices
Communities can influence social norms by encouraging responsible event planning. This may include offering alcohol-free options, promoting moderation messaging, and training staff to recognize signs of intoxication. Such practices reduce environmental pressure to drink and make healthier choices more socially acceptable.
Why Community Strategies Matter
While personal choices and family support are important, community environments strongly influence behavior. Communities that provide accessible resources, supportive networks, and preventive education create conditions where individuals can thrive without relying on alcohol to cope with stress or public pressure. In this way, prevention becomes a shared responsibility rather than an individual burden.
Conclusion
The intersection of fame and alcohol risk highlights the importance of strong community infrastructure. Accessible treatment services, peer networks, wellness programs, crisis support, and responsible social environments all help reduce the likelihood that alcohol use will lead to harmful consequences. When communities actively support mental health and healthy coping, they create protective environments that empower individuals to maintain stability, resilience, and well-being—both in the spotlight and beyond it.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some common questions:
1. Why is alcohol misuse sometimes more common among famous individuals?
Fame often brings intense pressure, public scrutiny, irregular schedules, and social environments where alcohol is readily available. These factors can increase stress and make alcohol seem like a quick way to relax or cope, raising the risk of unhealthy drinking patterns.
2. Does fame itself cause alcohol addiction?
No. Fame alone does not cause addiction. However, the lifestyle factors often associated with public visibility—such as stress, isolation, performance demands, and constant attention—can increase vulnerability for individuals who already have risk factors.
3. What psychological pressures of fame can contribute to alcohol misuse?
Common stressors include fear of public criticism, loss of privacy, performance expectations, online scrutiny, and maintaining a public image. These pressures can create chronic stress, which may lead some individuals to use alcohol as a coping mechanism.
4. Are celebrities more likely to develop addiction than others?
Not necessarily. Addiction can affect anyone regardless of status or wealth. However, certain aspects of celebrity culture—like easy access to substances, social normalization of drinking, and lack of privacy—may increase risk for some individuals.
5. How does public scrutiny affect recovery?
Public visibility can make seeking treatment more difficult because individuals may fear judgment, media attention, or career consequences. This can delay help-seeking and allow alcohol problems to worsen before intervention.
6. What warning signs might appear in high-profile individuals?
Signs may include increased reliance on alcohol at events, mood swings, withdrawal from trusted relationships, declining performance, legal or financial issues, or visible behavioral changes. These are similar to warning signs seen in anyone experiencing alcohol misuse.
7. Why is isolation a risk factor despite constant attention?
Being surrounded by fans or colleagues does not always translate into an emotional connection. Public figures may struggle to trust others or maintain authentic relationships, leading to loneliness—a known risk factor for substance misuse.
8. Can alcohol affect professional performance for famous individuals?
Yes. Alcohol misuse can impair concentration, memory, judgment, and emotional regulation. Over time, it may affect reliability, public image, and professional opportunities.
9. What protective factors reduce risk in high-visibility lifestyles?
Protective factors include strong support systems, mental health care, structured routines, healthy coping skills, clear boundaries, and trusted advisors who provide honest feedback rather than flattery or pressure.
10. How can society respond constructively when public figures struggle?
Compassionate responses—rather than ridicule or stigma—encourage individuals to seek help. Public understanding that addiction is a health condition can reduce shame and support recovery for anyone, regardless of status.
Conclusion
Examining the link between alcohol addiction and fame highlights an important truth: external success does not guarantee internal stability. The pressures of public life can magnify stress and emotional strain, making healthy coping strategies essential. Recognizing this dynamic encourages compassion, early intervention, and stronger support systems for individuals navigating high-visibility lifestyles. Ultimately, understanding the relationship between fame and alcohol use is not about criticism—it is about promoting insight, reducing stigma, and supporting long-term well-being for anyone living under pressure, whether in the spotlight or behind the scenes.
Video: