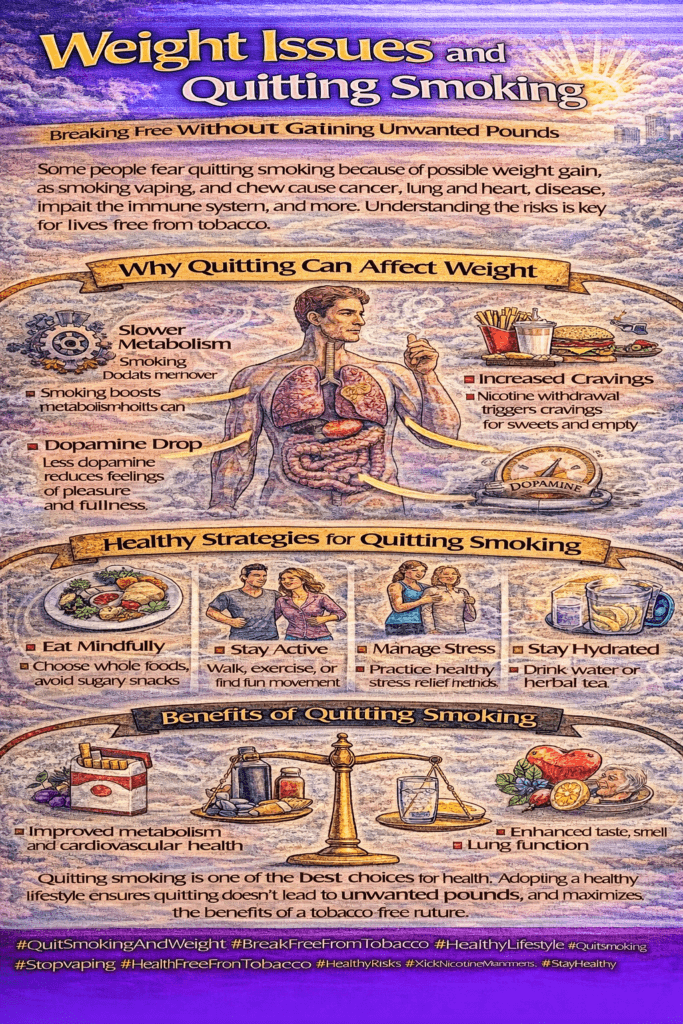
Nicotine, the central component in tobacco, influences the body’s metabolism, leading to various physiological changes. As individuals contemplate quitting tobacco, concerns about potential weight gain surface, accompanied by both myths and realities. This exploration delves into the effects of nicotine on metabolism, dispels common post-cessation misconceptions, and examines the interplay with dieting. Additionally, it explores self-management, family support, and community resource strategies to prevent weight gain after quitting tobacco, providing a comprehensive approach to overall well-being during this transformative journey.
How Nicotine Affects Metabolism: The Complex Relationship Between Smoking and Metabolic Health
Nicotine, the primary addictive substance in tobacco, not only affects the brain but also influences the body’s metabolism in various ways. While the metabolic effects of nicotine may seem to provide short-term benefits like appetite suppression or increased energy expenditure, the long-term health risks of smoking far outweigh any potential metabolic advantages. Understanding how nicotine affects metabolism can offer insight into why quitting smoking may lead to temporary changes in weight and metabolism. Here are some key ways in which nicotine influences metabolic processes in the body:
1. Increased Metabolic Rate
Nicotine can stimulate the sympathetic nervous system, which is responsible for the “fight or flight” response. This stimulation leads to the release of neurotransmitters such as norepinephrine and dopamine, both of which are involved in the body’s stress response. As a result, nicotine can temporarily boost the metabolic rate, causing the body to burn calories slightly faster. While this effect is short-lived, it contributes to the increased energy expenditure seen in smokers.
2. Appetite Suppression
One of the more noticeable effects of nicotine is its appetite-suppressing properties. Smokers often report having a reduced appetite, which can lead to lower food intake. This reduced consumption of calories can contribute to weight loss in individuals who smoke. In fact, many smokers are concerned about weight gain when they try to quit smoking, as they no longer experience the same appetite suppression that nicotine provides.
3. Release of Glucose and Fatty Acids
Nicotine stimulates the release of glucose from the liver and free fatty acids from fat stores into the bloodstream. This provides the body with an immediate energy source, helping fuel its heightened metabolic activity. This rapid release of energy can give smokers a temporary feeling of alertness or increased energy, but it also places stress on the body’s metabolic processes, potentially contributing to long-term health issues like insulin resistance.
4. Impact on Insulin Sensitivity
Nicotine has been shown to affect how the body responds to insulin, the hormone that regulates blood sugar levels. Smokers may experience reduced insulin sensitivity, meaning their bodies become less effective at processing glucose. This can lead to changes in glucose metabolism and may increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes over time. The impact of nicotine on insulin sensitivity is one of the many reasons smoking is linked to metabolic disorders and cardiovascular disease.
5. Stress Response
Nicotine activates the body’s stress response by triggering the release of cortisol, the hormone responsible for the “fight or flight” reaction. Cortisol can temporarily increase energy expenditure and influence metabolic processes. However, chronic elevation of cortisol due to nicotine use can contribute to other health problems, such as weight gain, particularly around the abdomen, and an increased risk of developing metabolic syndrome.
Nicotine’s Short-Term Metabolic Effects vs. Long-Term Health Risks
While nicotine may have some short-term effects on metabolism, such as an increased metabolic rate and appetite suppression, the overall impact of smoking on health is profoundly negative. The metabolic changes caused by nicotine are part of a larger picture of how smoking affects the body, from increased risk of heart disease and lung cancer to respiratory issues and reduced life expectancy.
Moreover, nicotine’s effects on metabolism can also play a role in addiction. As the body becomes accustomed to these metabolic changes, individuals may find themselves craving nicotine not just for its addictive properties but also for the perceived metabolic benefits it provides. This creates a vicious cycle, making it more challenging to quit smoking.
What Happens After Quitting Smoking?
When individuals quit smoking, they may experience changes in their metabolism, including weight gain. This can happen because the body no longer has nicotine stimulating appetite suppression or increasing metabolic rate. The result is often a period where individuals may feel hungrier and may experience a slower metabolism. However, it is important to note that these changes are typically temporary and are outweighed by the long-term health benefits of quitting.
Managing Post-Smoking Metabolic Changes
After quitting smoking, individuals can adopt healthy lifestyle changes to manage weight and metabolism. Regular physical activity, a balanced diet, and maintaining healthy eating habits are key strategies for supporting overall well-being and preventing excessive weight gain. Staying active can help speed up metabolism and reduce the temptation to revert to smoking as a means of appetite control.
In summary, nicotine’s influence on metabolism is complex, with short-term effects like increased energy expenditure and appetite suppression. However, these effects are far outweighed by the many serious health risks associated with smoking. While quitting smoking may lead to temporary changes in metabolism, the long-term benefits of quitting—such as a reduced risk of heart disease, cancer, and improved overall health—are substantial. By adopting a healthy lifestyle after quitting, individuals can support their body’s metabolism and manage any potential weight gain, ultimately achieving a healthier, smoke-free life.
Debunking the Myths of Quitting Tobacco: What You Need to Know
Quitting tobacco use is a significant health decision, but it’s often clouded by myths and misconceptions that can make the process seem more daunting than it actually is. Understanding the realities behind these myths can empower you to make informed choices about your quit journey. Here’s a breakdown of common myths and the truths that dispel them:
Myth 1: Quitting is Easy and Immediate.
Reality: Quitting tobacco is rarely easy or immediate. For many people, the process is challenging and involves withdrawal symptoms, cravings, and changes in daily habits. These difficulties can persist for some time, and the journey often requires patience, commitment, and support. It’s important to acknowledge that quitting is a process, not an event, and persistence is key.
Myth 2: Weight Gain is Inevitable.
Reality: Weight gain can be a concern for some when quitting smoking, but it’s not inevitable. Many individuals manage to quit without gaining weight, and for those who do gain a few pounds, adopting a balanced diet and regular physical activity can help mitigate the effects. It’s important to focus on long-term health improvements rather than short-term weight changes.
Myth 3: Nicotine Replacement Therapies (NRT) are as Harmful as Smoking.
Reality: Nicotine replacement therapies like patches, gums, or lozenges provide controlled doses of nicotine to help manage withdrawal symptoms. They are significantly safer than smoking because they don’t involve the harmful tar and toxins found in tobacco smoke. NRTs help reduce cravings and withdrawal while supporting the body through the transition, making them a valuable tool for many quitters.
Myth 4: “Cold Turkey” is the Only Effective Method.
Reality: While some individuals find success quitting “cold turkey,” this approach is not the only effective method. Others may benefit more from gradually reducing their tobacco use, using nicotine replacement therapy (NRT), or seeking professional support and counseling. The best method for quitting depends on personal preference and the severity of the addiction.
Myth 5: It’s Too Late to Quit – Damage is Permanent.
Reality: It is never too late to quit smoking. Regardless of how long you’ve been smoking, quitting provides significant health benefits. The body begins to repair itself almost immediately after quitting, and within weeks, improvements in lung function, circulation, and energy levels can be noticed. Long-term smokers can also reduce their risk of heart disease, cancer, and other tobacco-related illnesses by quitting.
Myth 6: Smoking Helps Manage Stress.
Reality: Many people believe that smoking helps them cope with stress, but this is a misconception. While smoking may provide temporary relief, it does not reduce stress in the long run. In fact, nicotine withdrawal can increase stress levels. Quitting smoking allows individuals to explore healthier and more effective stress management techniques, such as exercise, meditation, and therapy, which have lasting benefits for mental health.
Myth 7: You Can’t Quit Successfully If You’ve Tried Before.
Reality: Quitting is a process that often involves multiple attempts. If you’ve tried to quit before and relapsed, it’s important to recognize that each attempt brings valuable lessons. Most people need more than one attempt to quit for good, and each relapse provides insight into what works and what doesn’t. Keep trying, and your chances of success increase over time.
Myth 8: Only Heavy Smokers Need to Quit.
Reality: Even light or occasional smoking poses serious health risks, including an increased risk of heart disease, lung cancer, and respiratory issues. Quitting tobacco, no matter how much you smoke, significantly improves your health outcomes. It’s never too early or too late to quit, and the benefits are immediate and long-lasting.
Myth 9: Using Smokeless Tobacco is a Safer Alternative.
Reality: Smokeless tobacco, including chewing tobacco and snuff, still contains harmful chemicals that can increase the risk of oral, esophageal, and pancreatic cancers. These products may not involve the risks associated with smoking, such as lung cancer or respiratory diseases, but they still present serious health risks. The safest option is to quit all forms of tobacco use.
Myth 10: Quitting Means Gaining Nothing.
Reality: Quitting tobacco brings a wide range of benefits that extend beyond health improvements. Aside from reducing your risk of chronic diseases, quitting can lead to enhanced quality of life, increased life expectancy, and improved mental health. Many quitters also experience financial benefits, as they no longer spend money on cigarettes or tobacco products.
The Takeaway
Dispelling these myths about quitting tobacco helps individuals understand the true nature of the process and empowers them to make better decisions about their health. It’s important to approach quitting with realistic expectations and a commitment to long-term success. Support from healthcare professionals, quitlines, and counseling services can also provide additional tools to increase your chances of quitting successfully.
Remember, quitting tobacco is not just about stopping a habit—it’s about improving your overall health and reclaiming your life. With the right mindset, support, and strategies, you can overcome these challenges and live a tobacco-free life.
How Dieting Affects Your Journey to Quit Smoking: Key Considerations for Success
Quitting smoking is a significant achievement, but for many people, the journey to becoming smoke-free is accompanied by concerns about weight gain and changes in eating habits. While dieting itself may not necessarily hinder your quit attempt, the approach to dieting and eating habits can impact the success of your journey. Here are some important considerations to keep in mind when balancing smoking cessation and diet:
Weight Gain Concerns:
A common concern when quitting smoking is the potential for weight gain. Many smokers fear gaining extra pounds once they give up cigarettes, which may lead them to adopt restrictive or extreme dieting practices. However, overly strict dieting can add unnecessary stress and negatively affect your mood, making it more difficult to manage nicotine withdrawal symptoms. Instead of focusing solely on weight loss, it’s more beneficial to maintain a balanced diet that supports your overall well-being.
Emotional Eating:
Quitting smoking often triggers emotional changes. Nicotine withdrawal can leave some individuals feeling anxious, irritable, or stressed. As a result, it’s common for people to turn to food for comfort, especially if they associate smoking with coping mechanisms for emotional distress. If you’re following a restrictive diet at the same time, it can increase the likelihood of unhealthy eating habits or emotional overeating. Finding new ways to cope with emotions, such as practicing relaxation techniques or engaging in physical activity, can help reduce the temptation to use food as an emotional crutch.
Nutrient Deficiency:
Adopting an overly restrictive diet while quitting smoking can lead to nutrient deficiencies. This can negatively impact your health and your body’s recovery process after quitting smoking. A healthy, balanced diet rich in nutrient-dense foods is crucial during this time. It supports your immune system, boosts your energy, and helps your body repair itself from the damage caused by smoking. Ensuring you’re eating a variety of whole foods—including fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains—can provide your body with the nourishment it needs to thrive as you quit smoking.
Stress and Coping Mechanisms:
Dieting-induced stress may also undermine your quit attempt. Stress is one of the most common triggers for smoking, and dieting can sometimes increase stress levels if you feel deprived or frustrated by the process. Stress can also interfere with your ability to maintain a smoke-free lifestyle. Instead of stressing about dieting, try healthier, more effective ways to manage stress, such as exercising, journaling, meditating, or spending time with loved ones. Having a variety of stress-relief tools will help you stay focused on your quit goals without turning to smoking or overeating as coping mechanisms.
Balanced Approach:
Rather than following a strict diet, adopting a balanced approach to eating can support both smoking cessation and maintaining a healthy weight. Focus on nutrient-dense foods like fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains. Staying hydrated and incorporating regular physical activity, such as walking, yoga, or cycling, into your daily routine can also support your overall health. A balanced approach allows you to nourish your body properly while also supporting your goal of quitting smoking.
Behavioral Changes:
Quitting smoking often requires changing old habits and routines, and this is where diet can play a role in your transformation. Replacing the smoking habit with healthier behaviors is crucial, and food choices can be a part of that change. Instead of reaching for a cigarette, try snacking on healthy alternatives such as nuts, fruits, or vegetables, or drink water to keep your hands and mouth busy. Making mindful, healthy food choices aligns with the goal of leading a tobacco-free life and can be empowering as you navigate through the quitting process.
The Bottom Line:
Striking a balance between managing weight and successfully quitting smoking is key. Extreme dieting during your quit attempt can create unnecessary stress and potentially lead to unhealthy eating behaviors. A balanced approach—focused on nourishing your body and managing stress—will better support both your weight-loss and smoking-cessation goals.
For those struggling with diet-related concerns during smoking cessation, seeking professional guidance from healthcare providers, nutritionists, or smoking cessation programs can help. Building a comprehensive plan that addresses both your dietary needs and your journey to quit smoking will improve your chances of success. By focusing on overall well-being and finding healthier coping strategies, you can make lasting changes that support a smoke-free, healthier lifestyle.
Managing Weight Gain While Quitting Tobacco: Effective Strategies for Success
Quitting tobacco is a significant accomplishment that improves overall health and well-being, but for many individuals, the fear of gaining weight can be a concern during the process. While weight gain is a common challenge, it can be managed through strategic self-care and healthy habits. Here are some practical strategies to prevent weight gain while quitting tobacco, and to support long-term health and success:
1. Regular Physical Activity:
Exercise plays a crucial role in managing weight during the quit process. Physical activity helps boost metabolism, reduces stress, and combats cravings. Activities like walking, jogging, cycling, or joining fitness classes can provide both physical and mental benefits. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days of the week. Regular movement not only helps with weight management but also improves mood and energy levels, which can be particularly helpful as you navigate the challenges of quitting.
2. Healthy Eating Habits:
Eating a balanced, nutritious diet is essential for managing weight while quitting smoking. Focus on incorporating a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats into your meals. These nutrient-dense foods will keep you full and satisfied without excessive calorie intake. Try to limit your consumption of high-calorie, low-nutrient foods, such as processed snacks and sugary drinks, which can contribute to unwanted weight gain.
3. Hydration:
Drinking plenty of water throughout the day can help with weight management and overall health. Staying hydrated not only helps control hunger but may also reduce the temptation to snack mindlessly. Aim to drink at least eight cups of water a day, and consider drinking a glass of water before meals to help prevent overeating.
4. Mindful Eating:
Mindful eating involves paying attention to your body’s hunger and fullness cues, eating slowly, and savoring each bite. This practice can help prevent overeating and support weight management during your quit journey. By being more aware of portion sizes and eating mindfully, you can avoid consuming excess calories, which may contribute to weight gain.
5. Healthy Snacking:
Cravings for snacks can often arise when quitting smoking, but choosing healthy snacks can help you stay on track. Opt for nutritious snacks such as fresh fruit, vegetables, nuts, or yogurt. These options are satisfying and full of essential nutrients. Be mindful of portion sizes, as even healthy snacks can contribute to weight gain if consumed in excess.
6. Meal Planning:
Planning your meals and snacks in advance is an effective way to avoid impulsive food choices. By preparing healthy meals ahead of time, you ensure nutritious options are readily available, reducing the temptation to choose unhealthy foods. Make a weekly meal plan and stick to it as closely as possible to stay on track with both your quitting and weight management goals.
7. Stress Management:
Stress can be a significant trigger for both smoking and overeating, so it’s essential to adopt healthy coping mechanisms. Practice stress-reduction techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, yoga, or even journaling. Managing stress effectively can help you avoid turning to food for comfort and support your quit journey without additional challenges.
8. Behavioral Strategies:
Replacing smoking-related habits with positive behaviors is an important part of quitting. For example, if you used to smoke after meals, try going for a short walk, practicing deep breathing, or engaging in another healthy activity instead. These small behavior changes can help prevent the urge to snack mindlessly or turn to tobacco.
9. Support System:
Having a strong support system is critical for both quitting smoking and managing weight. Reach out to friends, family, or support groups who can offer encouragement and motivation. A network of individuals who understand your goals and challenges can make a significant difference in maintaining focus and avoiding potential setbacks.
10. Celebrate Non-Scale Victories:
Instead of focusing solely on weight, celebrate other victories during your quit journey. These may include increased energy levels, improved sleep quality, reduced stress, or enhanced physical fitness. Recognizing these non-scale wins can help keep you motivated and provide a sense of accomplishment as you continue your journey to becoming smoke-free.
11. Professional Guidance:
Consulting with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian can provide personalized advice on managing weight during smoking cessation. These professionals can help you create a plan that incorporates healthy eating, exercise, and stress management tailored to your specific needs. Their support can guide you through the process and increase your chances of long-term success.
The Bottom Line:
Weight gain during the quitting process is a common concern, but with the right strategies in place, it can be effectively managed. Focus on adopting a balanced approach that combines regular physical activity, healthy eating, stress management, and mindful behaviors. Creating a healthy lifestyle that supports both quitting tobacco use and overall well-being is essential for long-term success. By building a foundation of good habits and seeking support when needed, you can achieve a smoke-free life without the worry of significant weight gain.
Family Support: A Key to Preventing Weight Gain While Quitting Tobacco
Quitting tobacco is a major life change that can positively impact an individual’s health. However, one common concern for many people trying to quit is the potential for weight gain. Family support can play a crucial role in helping individuals navigate this transition while maintaining a healthy lifestyle. By adopting family-centered strategies, the quitting process can be made smoother, healthier, and more sustainable. Here are some effective family support strategies to prevent weight gain while quitting tobacco:
1. Encourage Healthy Lifestyle Changes:
A successful quit attempt involves more than just quitting smoking—it’s about adopting a healthier lifestyle. Families can help by emphasizing the importance of regular physical activity, balanced nutrition, and overall well-being. Encourage healthy habits such as exercising together, cooking at home, and making time for relaxation. The family’s collective effort to focus on health will provide motivation and support during the quitting process.
2. Prepare Nutritious Meals Together:
Meal preparation can be a fun and engaging family activity. When everyone in the household is involved in planning and cooking nutritious meals, it fosters a sense of togetherness and positive reinforcement. Include a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats in your meals. This shared commitment to healthier eating will not only help with quitting smoking but also reduce the risk of unhealthy weight gain.
3. Provide Healthy Snack Options:
Stocking the house with healthy snack options is an easy way to support the individual who is quitting tobacco. When cravings hit, having readily available nutritious snacks—such as fruits, nuts, yogurt, or vegetables—can help prevent overeating and steer individuals toward healthier options. Make these snacks easy to grab, and encourage everyone to enjoy these healthy choices.
4. Participate in Physical Activities:
Exercise is one of the best ways to manage both stress and weight during the quitting process. Families can incorporate physical activity into their routines, making it an enjoyable part of everyday life. Whether it’s taking walks after dinner, cycling on weekends, or playing sports together, engaging in regular physical activity can boost metabolism, reduce stress, and promote a sense of well-being.
5. Offer Emotional Support:
Quitting tobacco is not just a physical challenge; it’s an emotional one as well. Family members can offer essential emotional support by providing understanding and encouragement during moments of stress, frustration, or cravings. Be a source of positivity and reassurance, reminding the individual that they are not alone in this journey.
6. Create a Smoke-Free Home:
One of the most important things families can do to support a tobacco quit attempt is to create a smoke-free environment at home. This eliminates the temptation to smoke and reduces exposure to triggers that can derail the quitting process. A clean, smoke-free home fosters a sense of well-being and allows the individual to focus on their goal of quitting.
7. Be Mindful of Triggers:
Everyone has unique triggers that might encourage smoking or overeating. Family members can work together to identify these triggers and find healthier alternatives to deal with them. Discuss strategies to avoid or cope with stress, boredom, or situations that may cause cravings, and find solutions that everyone can support.
8. Celebrate Milestones Together:
Celebrating achievements, no matter how small, is a great way to keep motivation high. Celebrate milestones such as a week, a month, or longer without smoking, as well as improvements in physical health, energy levels, and mood. Recognizing these accomplishments not only reinforces the individual’s commitment to quitting but also fosters a positive environment that celebrates progress.
9. Promote Stress Reduction:
Stress is a common trigger for both smoking and overeating. Families can support the individual by promoting relaxation and stress reduction techniques that everyone can participate in. Encourage activities such as meditation, yoga, deep-breathing exercises, or hobbies that help everyone unwind and reduce stress in healthy ways.
10. Participate in Supportive Activities:
Sharing supportive experiences can strengthen bonds and reinforce the quitting process. Attend support group meetings together, or participate in family counseling if needed. This shared participation can provide valuable insights, boost morale, and offer encouragement from others who are on a similar journey.
11. Educate on Healthy Coping Mechanisms:
Help family members understand the importance of finding healthy coping mechanisms for stress. Encourage alternatives to food or smoking, such as walking, practicing mindfulness, or engaging in a hobby. By developing healthier ways to cope, individuals can avoid falling back into old habits that may lead to weight gain or smoking relapse.
12. Be Patient and Understanding:
The quitting process is rarely linear, and setbacks are common. Families can provide the most support by being patient and understanding throughout the journey. Offer encouragement during challenging times and create a supportive, non-judgmental environment. This approach fosters confidence and reinforces the commitment to a tobacco-free life.
In summary, family support is one of the most powerful tools in preventing weight gain while quitting tobacco. By working together as a family, individuals can adopt healthier habits, reduce stress, and celebrate successes. Supporting each other through this transformative process not only strengthens the individual’s resolve to quit but also fosters a healthier, more connected family unit. With the right mindset, patience, and collaboration, families can create an environment that supports long-term success in quitting tobacco and maintaining overall well-being.
Community Support Strategies for Preventing Weight Gain While Quitting Tobacco
Quitting tobacco is a significant challenge, and many individuals worry about weight gain during the process. Fortunately, community support can play a pivotal role in helping people navigate this transition while maintaining a healthy lifestyle. By engaging in community-driven strategies, individuals can receive the encouragement, resources, and opportunities they need to quit smoking without compromising their health. Here are several community support strategies that can contribute to a healthier transition when quitting tobacco:
1. Quitting Support Groups:
Community-based smoking cessation support groups offer individuals a safe space to share their struggles, experiences, and strategies. These groups can provide a sense of belonging and reassurance, address concerns about weight gain, and offer advice on maintaining a healthy lifestyle. Having a network of like-minded individuals helps reinforce the commitment to quitting and supports the individual in managing cravings and developing new habits.
2. Physical Activity Programs:
Staying physically active is crucial for managing weight during the quit process. Many communities offer fitness programs or exercise classes that can help individuals stay active and reduce stress. Whether through group workouts, walking clubs, or yoga sessions, these programs foster a supportive environment and help individuals prioritize physical health during their quit journey.
3. Nutrition Workshops:
Education is key to managing food cravings and maintaining a balanced diet. Community health organizations or local centers often organize workshops on nutrition, offering tips for healthy eating habits and meal planning. These workshops can teach individuals how to manage their diet to support their tobacco-free lifestyle and prevent unwanted weight gain.
4. Smoke-Free Events:
Hosting smoke-free events and activities can create an atmosphere where tobacco use is not only discouraged but actively avoided. These events offer individuals a chance to stay engaged with their communities while remaining committed to their quit goals. Participating in social gatherings without the pressure of smoking can help reinforce the decision to quit and prevent relapse, while also avoiding the risk of weight gain associated with smoking.
5. Community Gardens:
Community gardens offer individuals an opportunity to engage in physical activity while cultivating fresh, nutritious produce. Growing your own fruits and vegetables not only promotes healthy eating but also encourages outdoor exercise and social interaction. Access to locally grown produce supports healthier eating habits, making it easier to maintain a balanced diet during the quitting process.
6. Educational Campaigns:
Community-wide educational campaigns can raise awareness about the relationship between tobacco use, weight management, and overall health. These campaigns can provide valuable information, debunk myths about quitting and weight gain, and encourage healthier lifestyle choices. By sharing accurate, science-based information, communities can help individuals feel more informed and empowered to quit tobacco without fear of weight gain.
7. Access to Healthy Food Options:
Advocating for better access to healthy food options in the community is essential for supporting individuals who are quitting smoking. This can include supporting local farmers’ markets, promoting healthy food vendors, and ensuring access to fresh produce. Communities that make healthy food more accessible can help individuals make better dietary choices and avoid unhealthy food temptations during the quit process.
8. Partnerships with Healthcare Providers:
Collaborating with healthcare providers can enhance community support for individuals quitting tobacco. Offering integrated programs that address both smoking cessation and weight management ensures that individuals receive the guidance they need to navigate both challenges. Healthcare providers can offer resources such as counseling, medical advice, and support for managing withdrawal symptoms, helping individuals prioritize their health throughout the quitting journey.
9. Online Communities:
Virtual platforms and social media groups can connect individuals who are quitting tobacco. Online communities offer continuous support, allowing members to share advice, successes, and struggles in a safe, non-judgmental environment. These digital spaces provide encouragement and foster a sense of solidarity, which can be especially helpful for individuals who may not have access to in-person support groups.
10. Employee Wellness Programs:
Local businesses and employers can support their employees in quitting smoking by implementing wellness programs. These programs may include fitness classes, smoking cessation workshops, and nutritional counseling. A workplace that offers comprehensive wellness resources can help employees stay healthy and motivated as they work towards quitting tobacco and managing their weight.
11. Counseling Services:
Professional counseling services can address the emotional and psychological aspects of quitting tobacco and managing weight gain. Community-based counseling options, whether individual or group-based, can provide personalized guidance, helping individuals develop coping strategies and healthier habits. A holistic approach that combines emotional support with practical advice can be invaluable during the quit process.
12. Accessible Recreational Facilities:
Accessible recreational facilities, such as parks, walking trails, and community fitness centers, encourage physical activity in convenient, supportive environments. These public spaces allow individuals to incorporate exercise into their daily routines, which can help mitigate the risk of weight gain after quitting smoking. Community advocacy for accessible recreational spaces fosters healthier, tobacco-free living.
In summary, community support is a powerful tool in preventing weight gain while quitting tobacco. By engaging in programs, accessing resources, and participating in supportive activities, individuals are more likely to successfully quit smoking without compromising their health. A community that prioritizes health and well-being creates an environment where people feel supported on their journey to live tobacco-free. With the right community resources and a supportive network, individuals can enjoy a smoother transition to a healthier, tobacco-free life while maintaining a balanced, active lifestyle.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some common questions:
1. Why do people gain weight after quitting smoking?
Nicotine suppresses appetite and increases metabolism. When nicotine is removed, appetite may increase, and metabolism may slow slightly, leading to temporary weight gain.
2. How much weight do people typically gain after quitting?
Most people gain between 5 and 10 pounds. Some gain less, and many return to a stable weight within several months.
3. Is weight gain after quitting smoking permanent?
No. With healthy eating and activity, weight usually stabilizes. The body adjusts as nicotine withdrawal fades.
4. Does fear of weight gain prevent people from quitting?
Yes. Many people delay quitting due to concerns about weight. However, the health benefits of quitting far outweigh the risks of modest weight gain.
5. Why does food taste better after quitting?
Smoking dulls taste and smell. When quitting, these senses improve, making food more enjoyable and sometimes leading to increased eating.
6. Can quitting smoking trigger sugar cravings?
Yes. Nicotine affects blood sugar regulation. After quitting, cravings for sweets or snacks may temporarily increase.
7. How can I prevent excessive weight gain after quitting?
Eat regular, balanced meals
Choose healthy snacks
Drink water
Stay physically active
Avoid replacing cigarettes with sugary foods
8. Does exercise help during smoking cessation?
Yes. Exercise reduces cravings, improves mood, and helps regulate weight.
9. Is it safe to diet while quitting smoking?
It’s better to focus on quitting first. Once smoke-free stability is achieved, weight management becomes easier.
10. Can nicotine replacement therapy help with weight control?
Yes. Nicotine patches or gum can reduce withdrawal-related appetite increases during early quitting.
11. Do stress and emotions affect weight after quitting?
Yes. Many people use smoking to cope with stress. Learning new coping skills prevents emotional eating.
12. How long do weight-related changes last after quitting?
Most changes in appetite and metabolism normalize within 3–6 months.
13. Should I quit smoking even if I’m worried about weight?
Yes. Smoking-related health risks are far greater than risks from modest weight gain.
14. Can quitting smoking improve long-term metabolism?
Yes. Over time, oxygen delivery and physical endurance improve, supporting healthier weight control.
15. What is the key message about weight and quitting smoking?
A few pounds can be managed, but lung, heart, and life lost to smoking cannot be regained.
Conclusion
Navigating the complexities of nicotine’s impact on the body’s metabolism and the multifaceted process of quitting tobacco demands a nuanced understanding. As we debunk myths about weight gain after cessation, it becomes clear that adopting a balanced diet is essential. Self-management strategies, including regular physical activity and mindful eating, stand as pillars for a healthier transition. Family support plays a pivotal role in reinforcing positive habits, while community resources offer a collective environment for shared experiences and encouragement. By collectively embracing these strategies, individuals can embark on a tobacco-free journey that prioritizes overall well-being and effectively mitigates the challenges of weight gain.
Video: