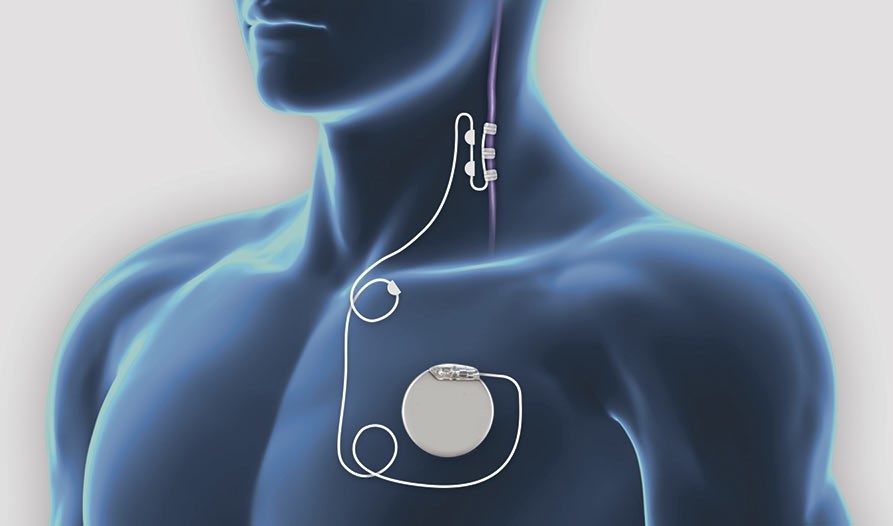
Vagus nerve stimulation (VNS) is an innovative therapy for addiction, using electrical impulses to modulate brain activity and potentially reduce cravings. This emerging treatment involves implanting a small device that sends electrical signals to the vagus nerve, which is thought to influence brain regions involved in addiction and mood regulation. While VNS presents promising benefits, such as the potential to alleviate cravings and support recovery, it also comes with significant disadvantages and ethical concerns that must be addressed as research progresses.
The promise and challenges of Vagus Nerve Stimulation in addiction treatment
Vagus Nerve Stimulation (VNS) presents a promising approach to addiction treatment by modulating brain activity to potentially reduce cravings and improve outcomes for individuals struggling with addiction. By targeting specific neural circuits, VNS offers a novel therapeutic option for those who have not responded well to traditional treatments. However, this innovative therapy also faces several challenges that must be addressed to realize its full potential.
Modulating Brain Activity for Improved Outcomes
One of VNS’s key advantages is its ability to influence brain activity in ways that may be beneficial for addiction management. The device works by sending electrical impulses to the vagus nerve, which can affect various neural circuits involved in addiction and cravings. This modulation of brain activity could help individuals better manage their addiction by reducing the intensity of cravings and supporting improved treatment outcomes.
VNS offers a new tool that could complement or enhance existing treatment options for those who have not succeeded with conventional therapies. The ability to target specific brain circuits represents a significant advancement in addiction treatment, potentially offering hope for those who have struggled to find relief.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite its potential benefits, VNS is not without challenges. One significant concern is the variability in individuals’ responses to the therapy. While some patients may experience significant improvements, others might see minimal or no benefit. This variability can complicate the decision-making process and make it difficult to predict who will benefit most from VNS.
Additionally, the procedure’s invasive nature, high cost, and potential side effects must be carefully considered. These factors can impact the overall feasibility and accessibility of VNS for addiction treatment.
Navigating the Future
As research on VNS continues, it is crucial to address these challenges to maximize the therapy’s potential. Efforts should focus on improving the efficacy of VNS, reducing its invasiveness and cost, and ensuring equitable access to treatment. By addressing these issues, the medical community can work towards making VNS a more effective and accessible option for those struggling with addiction.
Vagus Nerve Stimulation holds promise as a transformative tool in addiction treatment, offering potential benefits through its ability to modulate brain activity and reduce cravings. However, overcoming the associated challenges will be vital to unlocking its full potential and ensuring it remains a valuable option for individuals who need it most.
Understanding the Drawbacks of Vagus Nerve Stimulation
Vagus Nerve Stimulation (VNS) is a treatment option for conditions such as epilepsy and depression. It involves the surgical implantation of a small device that stimulates the vagus nerve. While VNS has shown promise for some patients, it is not without its challenges.
Invasiveness and Surgical Risks
One of the primary drawbacks of VNS is its invasive nature. The procedure requires surgery to implant a pulse generator under the skin in the chest and a lead that connects to the vagus nerve in the neck. As with any surgical procedure, there are inherent risks, including infection, anesthesia-related complications, and potential damage to surrounding tissues. These risks can be significant considerations for patients weighing their treatment options.
Variable Efficacy
Another notable challenge is the variable efficacy of VNS. While some patients may experience substantial improvements in their symptoms, others may see little to no benefit. This variability in response can complicate the decision-making process for patients and healthcare providers. Predicting who will benefit most from VNS is complex, making it challenging to determine if the potential benefits outweigh the risks for each individual.
Decision-Making Complexities
The variability in response to VNS adds a layer of complexity to treatment decision-making. Patients and healthcare providers must carefully consider the potential risks and benefits, and often, uncertainty is involved. This unpredictability can be frustrating for those seeking effective treatment and may influence the overall approach to managing their condition.
In summary, while Vagus Nerve Stimulation offers a treatment avenue for certain conditions, its invasiveness and variable efficacy present significant challenges. Understanding these drawbacks is crucial for patients and healthcare providers as they navigate the complex landscape of treatment options.
Economic Barriers to Vagus Nerve Stimulation
Vagus Nerve Stimulation (VNS) represents a significant advancement in the treatment of conditions such as epilepsy and depression. Despite its potential benefits, the high cost of VNS poses a considerable barrier to access for many individuals.
The High Cost of VNS
The financial burden of VNS is multifaceted. It encompasses the expense of the device, the surgical procedure required for implantation, and the ongoing maintenance and follow-up care. These costs can be prohibitive for many patients, particularly those without comprehensive insurance coverage. The price tag associated with VNS often includes the initial outlay and the costs of regular device adjustments and medical consultations.
Impact on Access and Equity
The economic barriers associated with VNS raise significant concerns about equity and access to treatment. High costs can limit availability for those who might benefit from VNS but cannot afford it. This financial hurdle may disproportionately affect lower-income individuals and those without adequate insurance coverage, potentially excluding a significant portion of the population from accessing this life-changing treatment.
Addressing the Access Gap
Addressing these economic challenges is crucial to ensuring that VNS therapy is accessible to a broader range of patients. Efforts to reduce costs, improve insurance coverage, and provide financial assistance can help mitigate the barriers posed by the high price of VNS. Additionally, policymakers and healthcare providers must work together to explore strategies to enhance equitable access to treatment and ensure that financial constraints do not prevent individuals from receiving the care they need.
In conclusion, while Vagus Nerve Stimulation offers promising therapeutic potential, its high cost presents a significant challenge. Understanding and addressing these economic barriers is essential to improving access to this treatment and ensuring it benefits a broader, more diverse population.
Side Effects of Vagus Nerve Stimulation: Impact on the Quality of Life
Vagus Nerve Stimulation (VNS) offers a therapeutic option for conditions like epilepsy and depression. Still, patients must be mindful of the potential side effects that can affect their quality of life.
Common Side Effects
Patients undergoing VNS may experience several side effects, varying in intensity. Common issues include:
- Hoarseness: The stimulation can affect the vocal cords, leading to a raspy or hoarse voice.
- Throat Discomfort: The device’s placement near the vagus nerve can cause discomfort or irritation in the throat.
- Dizziness: Some patients report feeling dizzy or lightheaded, especially when the device is stimulating.
While generally manageable, these side effects can be distressing and may impact daily functioning. Discomfort and changes in voice quality can affect personal interactions and professional life, while dizziness may hinder daily activities and overall well-being.
Weighing the Risks and Benefits
When considering VNS, patients and healthcare providers must carefully weigh these potential side effects against the therapy’s benefits. The decision to proceed with VNS involves evaluating how the side effects might impact a patient’s quality of life compared to the potential improvements in their condition.
Managing Side Effects
Effective management strategies can help mitigate the impact of side effects. For example, adjusting the stimulation settings may alleviate some discomfort, and supportive care can address specific symptoms like hoarseness or throat irritation. Open communication between patients and healthcare providers is crucial for effectively addressing and managing side effects.
Vagus Nerve Stimulation can provide significant therapeutic benefits, but patients must consider and manage the side effects that accompany the treatment. Understanding the potential impact on quality of life is essential for making an informed decision and optimizing the treatment experience.
Ethical Dilemmas in Vagus Nerve Stimulation
Vagus Nerve Stimulation (VNS) is a promising therapy for conditions like epilepsy and depression, but its use raises several ethical concerns that complicate its implementation and acceptance.
Informed Consent
A critical ethical issue surrounding VNS is ensuring informed consent. Before agreeing to the treatment, patients must comprehensively understand the procedure’s risks, benefits, and potential outcomes. This involves clear communication about what the procedure entails and an honest discussion about the possible side effects and the variability in treatment response. Ensuring patients are fully informed empowers them to make decisions that align with their values and expectations, which is fundamental to ethical medical practice.
Access Equity
Access to VNS is another significant ethical concern. The high cost of the device, surgical procedure, and ongoing maintenance can limit availability to those with substantial financial resources or comprehensive insurance coverage. This disparity in access may exacerbate existing inequalities in addiction treatment and other therapeutic areas. Ensuring that VNS is accessible to a broader population is crucial for promoting equity in healthcare and addressing the needs of underserved or economically disadvantaged groups.
Stigmatization of Addiction
There is also the potential for stigmatization if VNS is perceived as a “last resort” or “experimental” therapy. If VNS is seen as a treatment of last resort, it could reinforce negative stereotypes about addiction and mental health, influencing public perception and affecting patient self-esteem. The perception of VNS as a less conventional or experimental option might contribute to feelings of stigma or inadequacy among patients, further complicating their treatment journey.
Addressing Ethical Concerns
Healthcare providers, policymakers, and the medical community must collaborate to navigate these ethical dilemmas. Strategies to ensure comprehensive informed consent, improve access to treatment, and address potential stigmatization are vital. Developing policies and support systems that promote fairness and respect in the treatment of conditions requiring VNS can help mitigate these ethical concerns and enhance the overall effectiveness and acceptance of the therapy.
Vagus Nerve Stimulation presents valuable opportunities for treatment, but its ethical implications—ranging from informed consent to access equity and stigmatization—must be carefully considered and addressed. By confronting these issues head-on, the medical community can work toward a more equitable and respectful approach to patient care.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some common questions:
What is vagus nerve stimulation (VNS) therapy?
Vagus nerve stimulation therapy is a neuromodulation treatment that uses mild electrical impulses to stimulate the vagus nerve and influence brain regions involved in mood, stress regulation, and autonomic function.
What is the vagus nerve, and why is it important?
The vagus nerve is a major nerve connecting the brain to the heart, lungs, gut, and other organs. It plays a key role in regulating stress response, emotional regulation, inflammation, heart rate, and digestion.
What conditions is VNS therapy used for?
VNS is FDA-approved for epilepsy and treatment-resistant depression. It is also being studied for anxiety, PTSD, chronic pain, inflammatory conditions, and substance use disorders.
How does VNS therapy work?
VNS sends electrical signals to the vagus nerve, which then influences brain circuits involved in mood, reward, stress, and impulse control, helping rebalance nervous system activity.
Is VNS therapy invasive?
There are two types. Implanted VNS requires a surgical procedure, while non-invasive VNS uses external devices applied to the neck or ear and does not require surgery.
How might VNS help with addiction recovery?
VNS may reduce stress-driven cravings, improve emotional regulation, support impulse control, and enhance engagement in therapy by calming the nervous system.
Can VNS help with anxiety and depression?
Yes. VNS has been shown to improve symptoms in people with treatment-resistant depression and may reduce anxiety by shifting the nervous system out of chronic fight-or-flight mode.
How long does it take to see results from VNS therapy?
Results vary. Some people notice gradual improvements over weeks to months, especially when VNS is combined with therapy and other treatments.
Are there side effects of VNS therapy?
Side effects may include throat discomfort, voice changes, coughing, tingling, or mild neck sensations during stimulation. Non-invasive VNS generally has fewer side effects.
Is VNS therapy safe?
VNS is generally considered safe when used under medical supervision. Implanted devices require a surgical risk assessment, while non-invasive devices have a lower risk profile.
Conclusion
As research on VNS continues, it is crucial to address these challenges and ethical issues to prioritize patient well-being and uphold high standards of care. This involves improving the efficacy and reducing the invasiveness and cost of VNS, ensuring equitable access, and addressing the broader social implications of its use. By carefully considering these factors, the medical community can better navigate the complexities of VNS and its role in addiction treatment, ultimately striving to offer more effective and compassionate care for those in need.
Video: Vagus Nerve Stimulation Actually Works #stressrelief #trauma