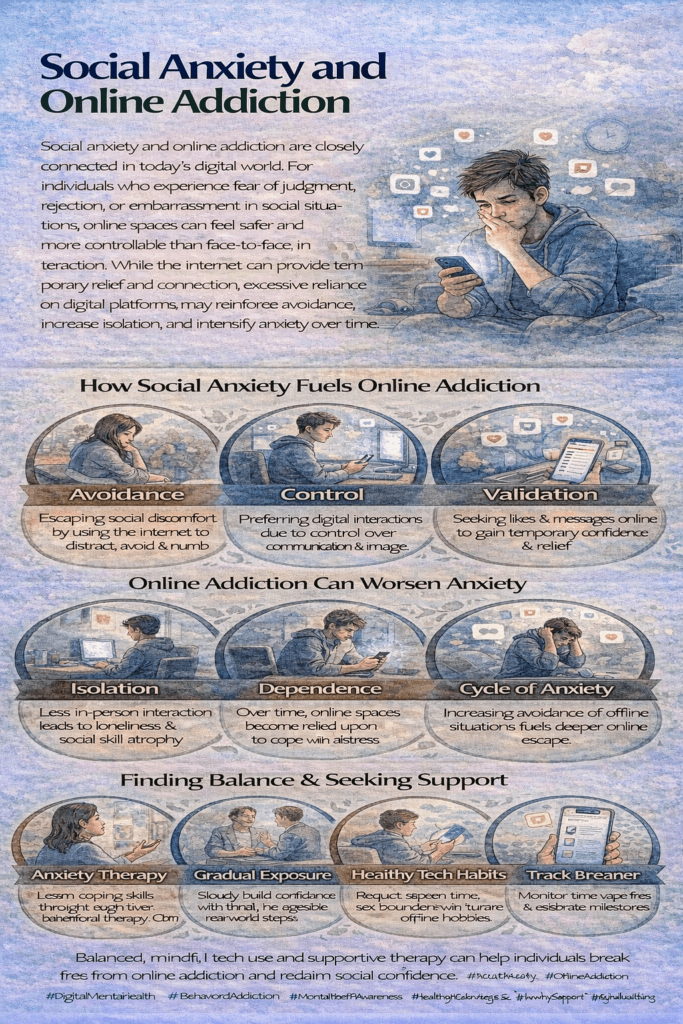
Social anxiety often fuels internet addiction as individuals seek refuge from real-world interactions online. This reliance can worsen anxiety and perpetuate a cycle of dependency. Prevention strategies include self-management, family support, and community resources. Self-management involves healthy coping mechanisms and setting limits on internet use. Family support provides understanding and guidance, while community resources offer education and counseling. Together, these approaches empower individuals to effectively manage social anxiety and internet use, promoting well-being and resilience.
How Social Anxiety Can Lead to Addiction: Understanding the Connection
Social anxiety, also known as social phobia, is a mental health condition characterized by intense fear or anxiety in social situations. Individuals with social anxiety often experience overwhelming worry or self-consciousness, fearing judgment, embarrassment, or humiliation in social settings. This can happen in situations like meeting new people, public speaking, or even casual social gatherings. The persistent fear of social interactions can lead people to avoid or endure them with significant distress. When untreated, social anxiety can severely impact daily life, relationships, and overall well-being.
One of the more concerning consequences of social anxiety is its potential to contribute to addiction. Here is how social anxiety can lead to substance abuse and addiction:
1. Self-Medication
Individuals with social anxiety often turn to alcohol, drugs, or prescription medications to self-medicate and cope with their overwhelming feelings of nervousness. Substances such as alcohol or benzodiazepines temporarily reduce anxiety, making social situations feel more manageable. However, this relief is short-lived and can lead to a cycle of dependency, where the person increasingly relies on substances to face social situations, ultimately resulting in addiction.
2. Avoidance Coping
People with social anxiety often use substances to avoid facing social interactions that trigger their fears. Drinking alcohol or using drugs can become a way to “numb” the anxiety, avoiding the discomfort associated with social gatherings or events. Over time, this avoidance behavior becomes a habit, increasing their reliance on substances to get through daily challenges, which may eventually lead to substance abuse and addiction.
3. Peer Influence
Social anxiety can lead people to seek comfort in social groups where substance use is normalized. The need to “fit in” can pressure individuals with social anxiety to engage in substance use, whether it’s drinking at parties or using recreational drugs in social settings. This social pressure, combined with anxiety, makes it more likely that the person will develop a dependency on substances.
4. Escapism
For many, substances offer an escape from the distressing thoughts and feelings associated with social anxiety. Alcohol, drugs, or even prescription medications may provide temporary relief from their constant fear of social judgment. Unfortunately, the fleeting relief that substances offer can reinforce the behavior, making addiction more likely as individuals become dependent on this form of escape.
5. Dual Diagnosis
Social anxiety often co-occurs with other mental health disorders, such as depression or generalized anxiety disorder (GAD). This combination of disorders—known as dual diagnosis—increases the risk of addiction. In such cases, individuals may use substances not only to manage their social anxiety but also to cope with other mental health symptoms, leading to a complex cycle of addiction that can be difficult to break without comprehensive treatment.
6. Impaired Decision-Making
Chronic social anxiety can impair an individual’s judgment and decision-making, increasing their vulnerability to risky behaviors like substance use. When social situations feel overwhelming, the ability to think clearly about the long-term consequences of substance use can be diminished. This impaired decision-making heightens the risk of engaging in substance use, further reinforcing the cycle of addiction.
7. Low Self-Esteem
Social anxiety can significantly damage an individual’s self-esteem, leading them to feel inadequate or inferior in social situations. Some individuals turn to substances to temporarily boost confidence or ease their discomfort. However, the temporary relief that substances provide can lead to a deeper erosion of self-esteem as the addiction takes over, making them feel increasingly dependent on drugs or alcohol to function socially.
Social anxiety is a significant risk factor for addiction, as individuals often turn to substances to cope with the distress and fear they experience in social situations. This self-medicating behavior creates a dangerous cycle that can lead to both addiction and worsening mental health. Early intervention and treatment that address both social anxiety and any resulting substance use are essential for breaking this cycle. Comprehensive approaches that include therapy, social skills training, and support for mental health and substance use issues are critical to helping individuals with social anxiety regain control of their lives and well-being.
Understanding the connection between social anxiety and addiction is vital for developing effective prevention and treatment strategies, especially for vulnerable populations such as young people and those experiencing dual diagnoses.
How Social Anxiety Contributes to Internet Addiction
Social anxiety, characterized by intense fear or discomfort in social situations, often leads individuals to seek ways to manage or avoid their anxiety. One of the most common coping mechanisms in the modern digital age is turning to the Internet. While online activities can provide temporary relief from social fears, they can also lead to internet addiction, a growing concern in mental health. Here’s how social anxiety contributes to excessive internet use and addiction:
1. Avoidance of Social Situations
Individuals with social anxiety frequently turn to the Internet to avoid face-to-face interactions that trigger their fears. The safety and anonymity of online spaces allow them to escape from uncomfortable social situations and the fear of judgment or rejection. Spending too much time online becomes an easy way to avoid real-world interactions, reinforcing their isolation and reliance on the Internet.
2. Social Comparison and Validation
Social media platforms offer users a way to seek social connection and validation without the perceived risks of in-person interactions. For those with social anxiety, this can feel like a safer way to connect with others. However, social media can also fuel harmful behaviors, such as comparing oneself to others and constantly seeking validation through likes, comments, and followers. This need for social validation can exacerbate feelings of inadequacy, leading to even more time spent online in search of affirmation, thereby increasing the risk of addiction.
3. Reduced Social Skills Development
Spending excessive time online can stunt the development of essential social skills. As individuals with social anxiety become more dependent on online communication, they may find it increasingly difficult to engage in real-world social interactions. This lack of practice further isolates them and makes it even harder to confront their social fears, leading to a cycle of withdrawal from offline social activities and deeper reliance on the Internet.
4. Distraction and Coping Mechanism
The Internet provides a constant source of distraction and offers a wide array of activities—such as browsing, gaming, or streaming videos—that can temporarily soothe anxiety symptoms. Individuals with social anxiety often use these online activities as a coping mechanism to distract themselves from distressing thoughts or social fears. While this may provide short-term comfort, it can lead to compulsive internet use, making it difficult to manage anxiety in healthier ways.
5. Escapism and Fantasy
For many, online environments offer a chance to escape the everyday stress and challenges of life. Virtual worlds, social media, and gaming platforms allow individuals to create new identities or immerse themselves in fantasy scenarios. For someone with social anxiety, the internet can serve as a refuge where they feel in control, away from the pressures of real-life social interactions. However, this escapism can quickly become addictive as they retreat further into these virtual spaces, neglecting real-life responsibilities and relationships.
6. Reinforcement of Avoidant Behaviors
Excessive internet use can reinforce the avoidant behaviors associated with social anxiety. Instead of confronting social fears or seeking treatment, individuals may retreat into the safety of online spaces. This avoidance perpetuates their anxiety, as they miss opportunities to develop coping mechanisms or improve their social skills in real-world settings. Over time, internet use becomes an escape rather than a solution, trapping individuals in a cycle of addiction and avoidance.
Social anxiety can significantly contribute to the development of internet addiction by fostering a reliance on online interactions as a way to manage social fears. The perceived safety and ease of the internet offer temporary relief, but they can lead to excessive and problematic internet use that ultimately worsens anxiety and isolation.
Addressing the underlying causes of social anxiety is critical for breaking this cycle. Therapeutic interventions such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and social skills training can help individuals develop healthier coping strategies, confront their fears, and reduce their reliance on the internet for emotional comfort. By understanding the link between social anxiety and internet addiction, individuals can take steps toward reclaiming control over their online habits and improving their overall mental health.
Effective Self-Management Strategies to Prevent Social Anxiety and Internet Addiction
Social anxiety and internet addiction are increasingly prevalent issues that can significantly impact individuals’ quality of life. Fortunately, self-management strategies can empower individuals to take control of their mental health, reduce anxiety, and create healthier relationships with technology. Here are some effective self-management techniques to help prevent social anxiety and internet addiction:
1. Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques
Mindfulness meditation, deep breathing exercises, or progressive muscle relaxation can significantly reduce stress and anxiety. These techniques help increase present-moment awareness and promote a sense of calm, enabling individuals to better manage their anxiety in social situations or while using the internet.
2. Set Limits on Internet Use
Establishing boundaries around internet usage is crucial for preventing addiction. Set specific time limits for internet and social media use. Utilizing apps or browser extensions to track screen time can help enforce these limits and create a more balanced relationship with technology.
3. Engage in Offline Activities
Dedicate time to offline activities that promote social interaction, physical exercise, and hobbies. Whether joining a sports team, attending community events, or exploring creative outlets, engaging in these activities can reduce reliance on the Internet for social connections and entertainment.
4. Challenge Negative Thoughts
Negative thoughts and beliefs related to social anxiety and internet use can perpetuate feelings of inadequacy. Identify and challenge these thoughts using cognitive-behavioral techniques. Reframing negative thinking patterns can help develop more realistic and positive perspectives, fostering a healthier mindset.
5. Develop Healthy Coping Mechanisms
Identify healthy coping mechanisms for managing stress and anxiety. Activities such as regular exercise, creative expression (like art or writing), spending time in nature, or seeking support from friends and family can provide effective outlets for stress relief and emotional support.
6. Practice Social Skills
Gradually exposing yourself to social situations that trigger anxiety can build confidence and improve social skills. Start small—practice assertiveness, active listening, and effective communication in less intimidating settings, and gradually increase exposure over time.
7. Limit Exposure to Triggers
Identify specific triggers for social anxiety and internet use and take proactive steps to limit exposure to them. This might involve avoiding certain social situations that feel overwhelming or steering clear of online environments that exacerbate anxiety or addictive behaviors.
8. Establish a Routine
Creating a daily routine that includes structured activities, regular sleep patterns, and time for relaxation can significantly reduce stress. A consistent routine provides a sense of stability and control, helping to manage anxiety and maintain balance in life.
9. Seek Professional Help
Consider seeking support from a mental health professional, such as a therapist or counselor, who can offer guidance, support, and evidence-based treatment for social anxiety and internet addiction. Professional help can provide valuable tools and strategies for effective management.
10. Monitor Progress
Track your progress in managing social anxiety and internet use. Celebrate small victories and adjust strategies as needed to continue making positive changes. Keeping a journal can be an effective way to reflect on challenges and successes over time.
By implementing these self-management strategies, individuals can take proactive steps to prevent social anxiety and internet addiction. These techniques not only improve overall well-being but also foster healthier relationships with technology and social interactions. Remember, change takes time and patience, so be kind to yourself as you embark on this journey toward better mental health.
The Vital Role of Family Support in Preventing Social Anxiety and Internet Addiction
Family support is a cornerstone in addressing mental health challenges such as social anxiety and internet addiction. A nurturing family environment can make a significant difference in helping loved ones navigate these issues. Here are some effective strategies families can use to provide support:
1. Open Communication
Creating a supportive and non-judgmental atmosphere encourages family members to openly discuss their feelings and challenges. Regular family discussions about social anxiety and internet use can help everyone express their concerns and share experiences, fostering understanding and connection.
2. Educate About Healthy Habits
Providing information about the potential risks and benefits of internet use and social media is essential. Families should educate themselves and their loved ones on strategies for managing social anxiety while promoting balanced lifestyles that include offline activities and meaningful social interactions.
3. Set Boundaries and Limits
Establishing clear guidelines around the internet and screen time helps promote moderation. Families can create agreements about when and how long to use screens, encouraging a healthy balance between online and offline activities for everyone.
4. Lead by Example
Demonstrating balanced screen-time habits is crucial. Family members should model healthy internet use by engaging in offline activities together—such as sports, hobbies, or family outings—showing that real-life connections are equally valuable.
5. Provide Emotional Support
Empathy and understanding are essential for family members struggling with social anxiety or internet addiction. Validating their feelings and experiences helps create a safe space where they know they are not alone in their struggles.
6. Encourage Healthy Coping Mechanisms
Supporting the development of healthy coping strategies is vital. Encourage family members to participate in activities that promote relaxation, mindfulness, and self-care, such as yoga, meditation, or creative expression.
7. Promote Social Engagement
Facilitating opportunities for both online and offline social interaction can help strengthen connections. Plan family activities, outings, and gatherings that foster engagement and build meaningful relationships, helping to counteract feelings of isolation.
8. Monitor and Supervise
Staying informed about family members’ internet use and social media activity is crucial, especially if there are concerns about excessive use. Monitoring screen time and online interactions allows families to intervene constructively when necessary.
9. Seek Professional Help
If social anxiety or internet addiction becomes a significant concern, encourage your loved one to seek professional support. Offer to assist them in finding appropriate resources, therapists, or counselors who specialize in these areas.
10. Provide Structure and Routine
Establishing a structured daily routine can help create stability. Designate specific times for meals, activities, and relaxation. Consistent routines reduce stress and provide a sense of security, which is especially beneficial for individuals struggling with anxiety or addiction.
Implementing these family support strategies can play a vital role in preventing social anxiety and internet addiction. Promoting healthy habits and offering unwavering support significantly enhances the overall well-being of loved ones. Families can create a positive environment that fosters resilience and healthy coping strategies through understanding, open communication, and active engagement. Together, they can navigate these challenges and build a brighter, healthier future.
Building Stronger Communities: Strategies to Prevent Social Anxiety and Internet Addiction
Community resource strategies are essential for addressing mental health challenges such as social anxiety and internet addiction. By fostering supportive environments and promoting awareness, communities can effectively prevent these issues. Here are some impactful strategies that can be implemented:
1. Education and Awareness Programs
Community-wide education programs can significantly raise awareness about social anxiety, internet addiction, and healthy internet use. Providing information on the signs, symptoms, and consequences of these conditions equips individuals to recognize and address them early. Workshops and seminars can promote prevention and intervention strategies to the public.
2. Support Groups and Counseling Services
Establishing support groups and counseling services tailored for individuals struggling with social anxiety or internet addiction is vital. These groups can offer peer support, guidance, and resources, helping participants feel less isolated and more empowered to manage their symptoms. Trained counselors can facilitate discussions, provide coping strategies, and promote healing through shared experiences.
3. Screening and Assessment Programs
Implementing screening and assessment programs in community settings—such as schools, libraries, and community centers—can help identify individuals at risk for social anxiety or internet addiction. These programs can offer referrals to appropriate resources and treatment options, ensuring individuals receive the help they need promptly.
4. Skill-Building Workshops
Organizing workshops focused on skill-building can provide individuals with the tools to manage stress and develop social skills. Training sessions on healthy coping strategies, communication skills, and problem-solving can empower individuals to confront challenges and reduce reliance on maladaptive behaviors, including excessive internet use.
5. Parenting Workshops and Support Groups
Parenting workshops can play a crucial role in promoting healthy internet use among children and adolescents. These workshops can equip parents with strategies for setting limits and boundaries around screen time, ensuring their children develop a balanced relationship with technology. Support groups for parents can also facilitate discussion and provide resources to help them navigate these challenges.
6. Community Activities and Events
Organizing community activities that promote social interaction and connection is essential for reducing social isolation. Encouraging participation in group activities, clubs, sports teams, and community service projects fosters relationships and strengthens community bonds, providing alternatives to excessive internet use.
7. Digital Literacy Programs
Developing digital literacy programs can empower individuals—especially children and adolescents—to navigate the online world safely and responsibly. Teaching responsible internet use, online safety, and media literacy skills can help individuals make informed choices and minimize the risks of excessive screen time.
8. Public Policy and Advocacy
Advocating for public policies that support mental health awareness, prevention, and treatment services is crucial. Collaborating with policymakers, community leaders, and healthcare providers can address social anxiety and internet addiction at local and national levels, promoting systemic changes that support mental well-being.
9. Community Partnerships
Forging partnerships with local organizations, businesses, schools, and healthcare providers creates a comprehensive network of support and resources for individuals affected by social anxiety and internet addiction. Pooling resources and expertise can maximize impact and ensure that community members have access to the services they need.
10. Crisis Intervention and Hotline Services
Establishing crisis intervention and hotline services is vital for individuals experiencing distress due to social anxiety or internet addiction. Providing immediate support, guidance, and referrals to appropriate resources ensures that individuals receive help when needed.
By implementing these community resource strategies, we can work together to prevent social anxiety and internet addiction, promoting mental health and well-being. Building supportive environments for individuals and families fosters resilience and connection, ensuring everyone can thrive. Together, we can create a healthier future for our communities, where mental health is prioritized and valued.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some common questions:
What is the connection between social anxiety and online addiction?
Social anxiety can make in-person interactions feel stressful or overwhelming. Online spaces often feel safer and more controllable, which can lead individuals to rely heavily on digital platforms for connection and relief, increasing the risk of online addiction.
Why do people with social anxiety prefer online interactions?
Online communication reduces fear of immediate judgment. People can control what they say, how they appear, and when they respond, which lowers anxiety compared to face-to-face interactions.
Can online use actually make social anxiety worse?
Yes. While online use may reduce anxiety in the short term, excessive reliance can reinforce avoidance of real-world situations, limit social skill practice, and increase fear of in-person interaction over time.
Is online addiction the same as internet addiction?
Online addiction is a type of behavioral addiction involving compulsive use of digital platforms such as social media, gaming, streaming, or forums. It often overlaps with anxiety, depression, or loneliness.
What are the warning signs of unhealthy online use related to anxiety?
Signs include avoiding social events, spending excessive time online, feeling anxious when offline, disrupted sleep, declining relationships, and using the internet to escape uncomfortable emotions.
Does reducing screen time fix social anxiety?
No. Reducing screen time alone doesn’t treat social anxiety. Anxiety-focused treatment, such as therapy and gradual exposure to real-world situations, is essential for long-term improvement.
What treatments help with both social anxiety and online addiction?
Cognitive behavioral therapy, exposure therapy, coping skills training, and mindfulness are effective. Treatment often includes setting healthy digital boundaries while building confidence offline.
Should technology be eliminated completely?
No. Technology is not the problem—avoidance is. The goal is balanced, intentional use alongside real-world connection and coping skills.
How can someone start breaking the cycle?
Small steps help, such as limiting certain apps, practicing brief social interactions, setting screen-free times, and seeking professional support for anxiety.
Can people recover from both social anxiety and online addiction?
Yes. With the right support, individuals can reduce anxiety, rebuild confidence, and develop healthier relationships with both technology and social interaction.
Conclusion
Addressing the intersection of social anxiety and internet addiction requires a multifaceted approach that incorporates self-management, family support, and community resources. By implementing strategies to promote healthy coping mechanisms, set boundaries on internet use, and foster understanding within families, individuals can navigate social anxiety and internet use more effectively. Additionally, community resources such as education programs, support groups, and counseling services offer valuable support and guidance. Together, these prevention strategies aim to empower individuals to manage their social anxiety and internet use in a balanced and healthy manner, promoting overall well-being and resilience in the digital age.
Video: Social anxiety and online addiction be like… #shorts #relatable