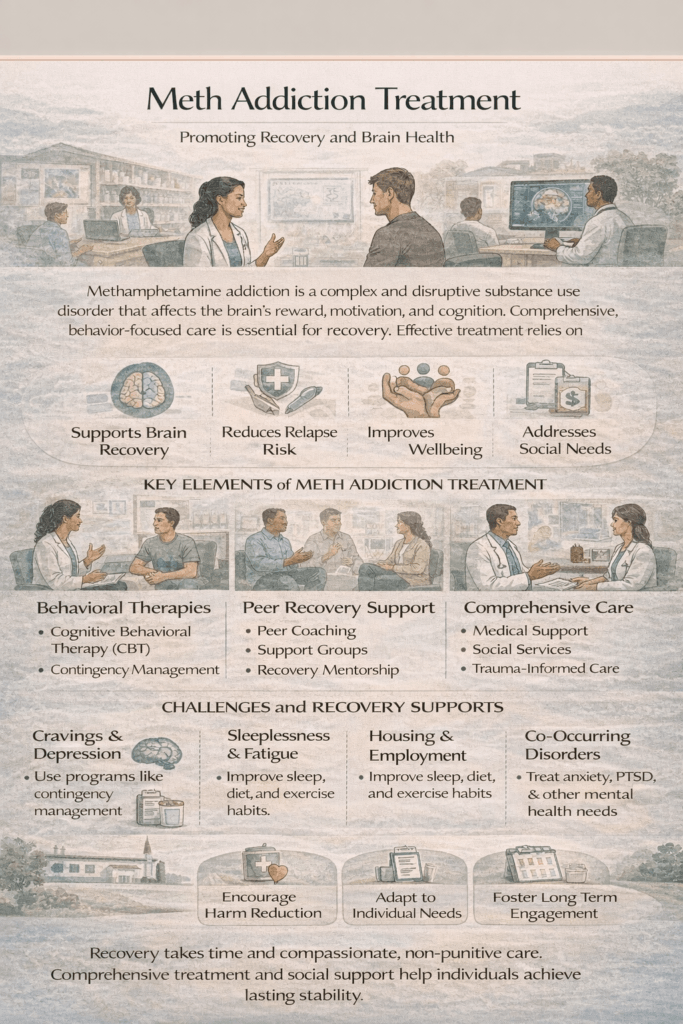
Addressing methamphetamine addiction often involves using medications like naltrexone and bupropion alongside other treatment approaches. While these medications can help reduce cravings and support recovery efforts, they may also pose challenges, such as side effects and variable effectiveness. Ethical concerns include ensuring patient autonomy and addressing the stigma associated with medication-assisted treatment. Community resources, such as support groups and education programs, complement pharmacological treatments and support individuals throughout their recovery.
Exploring Two-Drug Treatment for Methamphetamine Addiction: Naltrexone and Bupropion
Two-drug treatment for methamphetamine (meth) addiction leverages a combination of medications to help manage cravings and withdrawal symptoms, enhancing the chances of recovery. A promising combination is naltrexone, an opioid antagonist, and bupropion, an antidepressant and smoking cessation aid. This approach targets different brain pathways involved in addiction and withdrawal.
How It Works:
- Naltrexone: This medication blocks opioid receptors in the brain, which can help reduce the rewarding effects of meth and decrease cravings. By interfering with the brain’s reward system, naltrexone diminishes the pleasure derived from meth use, which can support long-term recovery.
- Bupropion: This antidepressant increases levels of dopamine and norepinephrine, neurotransmitters that are often depleted in individuals with meth addiction. By restoring these neurotransmitter levels, bupropion can help alleviate withdrawal symptoms and reduce cravings, making the recovery process more manageable.
Research Findings:
- Clinical studies have indicated that the combination of naltrexone and bupropion can significantly reduce meth use compared to a placebo.
- Participants in these trials reported fewer cravings and demonstrated a higher likelihood of abstaining from meth use, suggesting that this combination can be effective in supporting recovery.
Benefits:
- Increased Efficacy: Using both naltrexone and bupropion together may offer greater effectiveness than single-drug treatments by addressing addiction from multiple angles.
- Improved Patient Outcomes: Reduced cravings and withdrawal symptoms can lead to better recovery rates and increased chances of sustained abstinence.
- Non-Addictive: Both medications have established safety profiles for long-term use, minimizing the risk of developing new dependencies.
Challenges:
- Access and Availability: Ensuring that naltrexone and bupropion are readily available and accessible to those in need remains challenging, particularly in underserved areas.
- Side Effects: As with any medication, side effects can occur; not all patients may tolerate the treatment well. Common side effects include nausea, headaches, and insomnia.
- Comprehensive Care: Medication alone is often insufficient for treating meth addiction. Effective recovery typically requires a comprehensive approach that includes counseling, support services, and lifestyle changes.
In summary, the two-drug treatment approach using naltrexone and bupropion represents a promising strategy for addressing methamphetamine addiction. By combining these medications, individuals may experience reduced cravings and withdrawal symptoms, potentially improving recovery outcomes. However, successful treatment also depends on ensuring access to these medications, managing side effects, and integrating comprehensive care strategies.
Advantages of Combining Naltrexone and Bupropion for Methamphetamine Addiction
Combining naltrexone and bupropion to treat methamphetamine (meth) addiction presents several notable advantages:
1. Dual Mechanism of Action: Naltrexone works by blocking opioid receptors, which helps diminish the rewarding effects of meth and reduces cravings. Bupropion, on the other hand, boosts levels of dopamine and norepinephrine—neurotransmitters often depleted by meth use. This dual approach targets different brain pathways involved in addiction, potentially enhancing the overall efficacy of treatment.
2. Reduced Cravings: Both naltrexone and bupropion contribute to reducing methamphetamine cravings. By mitigating these cravings, individuals find it easier to abstain from use, which is crucial for successful recovery.
3. Withdrawal Symptom Management: Bupropion can help manage withdrawal symptoms associated with methamphetamine, such as depression, fatigue, and irritability. This can improve patient comfort during detoxification and the early stages of recovery, making the process more manageable.
4. Non-Addictive: Naltrexone and bupropion are not addictive substances, reducing the risk of developing a new dependency while undergoing treatment. This characteristic makes them safer options compared to some other medications used in addiction treatment.
5. Established Safety Profiles: Both medications have been extensively studied, and their safety profiles are well established when used as prescribed. This supports their suitability for long-term use in managing meth addiction.
6. Improved Treatment Outcomes: Clinical trials have demonstrated that the combination of naltrexone and bupropion can lead to higher rates of abstinence from methamphetamine compared to placebo or single-drug treatments. This suggests that the combined approach may enhance overall treatment outcomes.
7. Complementary Effects: The medications complement each other by addressing different aspects of addiction—craving reduction and neurotransmitter balance. This complementary effect can lead to synergistic outcomes, potentially making the treatment more effective in managing methamphetamine use disorder.
Overall, the combination of naltrexone and bupropion offers a promising pharmacological strategy for treating methamphetamine addiction. With their dual mechanisms, ability to manage withdrawal symptoms, non-addictive nature, and established safety profiles, these medications can significantly improve treatment effectiveness and patient outcomes.
Disadvantages of Using Naltrexone and Bupropion for Methamphetamine Addiction
While combining naltrexone and bupropion for managing methamphetamine (meth) addiction offers several benefits, there are notable disadvantages and considerations to keep in mind:
1. Limited Effectiveness for Some Individuals: Not everyone with meth addiction will respond equally well to this medication combination. Effectiveness can vary based on individual factors such as the severity of addiction, the presence of co-occurring mental health conditions, and genetic differences.
2. Side Effects: Both naltrexone and bupropion can cause side effects that may be unpleasant or intolerable for some individuals. Naltrexone may cause nausea, headaches, and insomnia, while bupropion may cause dry mouth, dizziness, and an increased heart rate. These side effects can impact adherence to treatment and overall quality of life.
3. Cost and Access: The cost of naltrexone and bupropion, along with insurance coverage limitations, can be significant barriers to access. Some individuals may struggle to obtain these medications, which can hinder their ability to receive adequate treatment.
4. Complex Treatment Regimens: Managing a combination of medications requires careful monitoring and coordination. Patients may need support to adhere to their treatment regimen, including managing multiple doses per day and potential drug interactions.
5. Potential for Drug Interactions: Bupropion, in particular, can interact with other medications and substances. Healthcare providers must carefully evaluate potential interactions with any other medications the patient is taking.
6. Need for Comprehensive Care: Medications alone may not be sufficient for managing methamphetamine addiction. Effective treatment often requires a comprehensive approach, including behavioral therapies, counseling, and support services to address the psychological and social aspects of addiction.
7. Individual Variability: Responses to naltrexone and bupropion can vary widely among individuals. Some may experience significant benefits, while others may not achieve the desired outcomes or may experience adverse effects that outweigh the benefits.
8. Long-Term Treatment Considerations: The long-term effectiveness and safety of using naltrexone and bupropion for methamphetamine addiction need further research. Ongoing monitoring and potential adjustments to the treatment may be required to maintain its efficacy over time.
9. Ethical Considerations: Ethical issues may arise regarding pharmacological treatments for addiction, including ensuring informed consent, respecting patient autonomy, and addressing any stigma associated with medication-assisted treatment.
In conclusion, while naltrexone and bupropion offer a promising approach to managing methamphetamine addiction, healthcare providers and patients need to consider these potential disadvantages. Developing individualized treatment plans that integrate a holistic approach to addiction recovery can often provide the best support for achieving long-term sobriety and well-being.
Ethical Dilemmas in Using Naltrexone and Bupropion for Methamphetamine Addiction
Using naltrexone and bupropion to manage methamphetamine (meth) addiction presents several ethical dilemmas. Addressing these issues is crucial for providing practical, fair, and respectful care. Here are some key ethical considerations:
1. Informed Consent: Ensuring that patients fully understand the purpose, potential benefits, and risks of using naltrexone and bupropion for addiction treatment is fundamental. Healthcare providers must offer comprehensive information so patients can make informed decisions about their treatment options.
2. Stigma and Bias: Medication-assisted treatment (MAT) for addiction can be subject to stigma and bias. Both patients and healthcare providers may hold negative beliefs about using medications to treat addiction, potentially impacting access to care and patient willingness to accept treatment. Addressing these biases is essential for ensuring equitable care.
3. Equitable Access: Ensuring that naltrexone and bupropion are accessible to all individuals who could benefit, regardless of socioeconomic status, race, ethnicity, or other factors, is a significant ethical concern. Disparities in healthcare access can exacerbate existing health inequalities and impact treatment outcomes.
4. Privacy and Confidentiality: Protecting patient privacy and confidentiality is critical, particularly in addiction treatment, where stigma and discrimination may be prevalent. Patients need to feel confident that their treatment details will be kept confidential to encourage openness and trust in the treatment process.
5. Coercion vs. Autonomy: Balancing the desire to help individuals overcome addiction by respecting their autonomy and right to make their own treatment decisions is a complex ethical issue. Coercive practices or undue pressure to accept medication-assisted treatment can undermine patient autonomy and trust in healthcare providers.
6. Long-Term Use Considerations: The ethical implications of long-term use of naltrexone and bupropion must include questions about dependency, safety, and potential unintended consequences. The benefits and risks must be evaluated continuously to ensure ethical, long-term treatment practices.
7. Patient-Centered Care: Treatment decisions should be based on the best interests of the patient, taking into account their unique circumstances, preferences, and treatment goals. Engaging patients in shared decision-making and respecting their treatment choices are key components of patient-centered care.
8. Dual Diagnosis and Comprehensive Care: When managing patients with co-occurring mental health disorders and addiction, ethical considerations include providing integrated, holistic care that effectively addresses both conditions. Ensuring that treatment approaches are comprehensive and ethical is crucial for overall patient well-being.
Navigating these ethical dilemmas involves upholding principles of beneficence (acting in the patient’s best interest), autonomy (respecting patient choice), justice (ensuring fair treatment and access), and non-maleficence (avoiding harm). Open communication, patient education, and a patient-centered approach are essential in addressing these challenges and providing adequate care for methamphetamine addiction.
Community Resource Strategies for Supporting Naltrexone and Bupropion in Methamphetamine Addiction Treatment
Effective community resource strategies are essential in supporting the use of naltrexone and bupropion for managing methamphetamine addiction. Here are several strategies that can enhance support and improve outcomes for individuals undergoing treatment:
1. Education and Awareness Programs:
- Objective: Increase public understanding of naltrexone and bupropion and their roles in treating methamphetamine addiction.
- Strategies:
- Community Workshops: Host workshops and seminars to educate the public, healthcare providers, and individuals about the benefits and availability of these medications.
- Public Campaigns: Launch awareness campaigns to reduce the stigma associated with medication-assisted treatment (MAT) and encourage acceptance of these options.
2. Support Groups and Peer Counseling:
- Objective: Provide emotional support and accountability for individuals in treatment.
- Strategies:
- Peer Support Groups: Establish support groups where individuals can share experiences and provide mutual encouragement.
- Peer Counselors: Employ peer counselors with personal experience in addiction and MAT to offer insights and support.
3. Access to Healthcare Providers:
- Objective: Ensure individuals can access knowledgeable, supportive healthcare providers.
- Strategies:
- Healthcare Partnerships: Collaborate with community health centers and clinics to integrate MAT into routine care.
- Provider Training: Train healthcare providers on the use of naltrexone and bupropion, as well as the complexities of addiction treatment.
4. Transportation and Logistics Support:
- Objective: Remove barriers to accessing treatment and medical appointments.
- Strategies:
- Transportation Services: Provide transportation assistance to help individuals attend regular medical appointments.
- Logistics Support: Help navigate treatment logistics, including medication pickup and appointment scheduling.
5. Crisis Intervention and Hotline Services:
- Objective: Provide immediate support during crises or challenges with medication adherence.
- Strategies:
- Crisis Hotlines: Establish hotlines staffed by trained professionals to offer immediate guidance and support.
- Crisis Intervention Teams: Develop teams that can respond to urgent addiction-related situations.
6. Harm Reduction Initiatives:
- Objective: Reduce risks associated with methamphetamine use.
- Strategies:
- Needle Exchange Programs: Support programs that reduce the spread of infectious diseases through safe needle disposal.
- Overdose Prevention Training: Offer training and resources to prevent overdose and provide naloxone.
7. Collaboration with Law Enforcement and Justice Systems:
- Objective: Provide treatment options within the justice system.
- Strategies:
- Diversion Programs: Work with law enforcement to implement programs that divert individuals from incarceration to treatment.
- Treatment Integration: Integrate MAT into justice system rehabilitation programs.
8. Employment and Vocational Training:
- Objective: Promote stability and self-sufficiency in recovery.
- Strategies:
- Job Placement Services: Offer employment and vocational training to support economic stability.
- Career Counseling: Provide counseling to help individuals prepare for and find meaningful work.
9. Family Support and Counseling:
- Objective: Involve and educate family members in the recovery process.
- Strategies:
- Family Therapy: Offer counseling to address family dynamics and support the individual’s recovery.
- Family Education Programs: Educate family members about addiction and MAT to foster supportive environments.
10. Integration with Mental Health Services:
- Objective: Address co-occurring mental health disorders alongside addiction.
- Strategies:
- Comprehensive Care Plans: Develop treatment plans integrating mental health and addiction services.
- Coordination of Care: Ensure collaboration between mental health professionals and addiction treatment providers.
By implementing these community resource strategies, communities can better support individuals using naltrexone and bupropion for methamphetamine addiction. These efforts create a more comprehensive approach to addiction treatment, addressing the diverse needs of individuals and promoting long-term recovery and well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some common questions:
What is meth addiction?
Meth addiction, also known as methamphetamine use disorder, is a chronic condition characterized by compulsive stimulant use despite harmful physical, psychological, and social consequences.
Why is meth addiction difficult to treat?
Methamphetamine strongly affects dopamine pathways involved in reward, motivation, and impulse control. These brain changes can persist after stopping use, leading to intense cravings, mood symptoms, and relapse risk.
Are there medications to treat meth addiction?
Currently, there is no single FDA-approved medication that treats meth addiction. Treatment primarily relies on behavioral therapies and supportive care, though medications may help manage co-occurring symptoms like depression or anxiety.
What treatments are most effective for meth addiction?
Behavioral therapies are the foundation of care. Cognitive behavioral therapy helps individuals identify triggers and develop coping skills, while contingency management has strong evidence for reducing stimulant use through positive reinforcement.
What is contingency management?
Contingency management is a treatment approach that provides tangible rewards for behaviors such as negative drug tests or consistent treatment attendance, reinforcing recovery-oriented behaviors.
How long does recovery from meth addiction take?
Recovery is a long-term process. Withdrawal symptoms may last weeks, and cognitive or emotional recovery can take months, but brain function often improves with sustained abstinence and treatment engagement.
Why do cravings persist after stopping meth use?
Meth alters dopamine signaling and stress-response systems, causing cravings and mood disturbances that can continue well into early recovery.
Is relapse common in meth addiction recovery?
Yes. Relapse is common and should be viewed as a signal to adjust or intensify treatment rather than as failure. Re-engagement in care improves outcomes.
How do mental health conditions affect meth addiction treatment?
Co-occurring conditions such as depression, anxiety, PTSD, and psychosis are typical and must be addressed to support sustained recovery.
What role do social factors play in meth addiction recovery?
Stable housing, employment, medical care, and social support significantly influence the success of recovery. Addressing these needs is essential for long-term outcomes.
Conclusion
Using naltrexone and bupropion to manage meth addiction offers a promising approach by reducing cravings and supporting recovery efforts. However, this method has disadvantages, including potential side effects and variable effectiveness among individuals. Ethical dilemmas, such as ensuring patient autonomy and addressing stigma associated with medication-assisted treatment, must also be considered. Community resource strategies, such as support groups, education programs, and access to healthcare providers, are crucial in complementing pharmacological treatments and enhancing overall outcomes for individuals in recovery. Through a comprehensive and supportive approach, the potential for successful addiction management and long-term recovery can be significantly improved.
Video: How Long Does Meth Recovery Actually Take #addictionrecovery #sobriety #healing