Lowest Drug Addiction Country
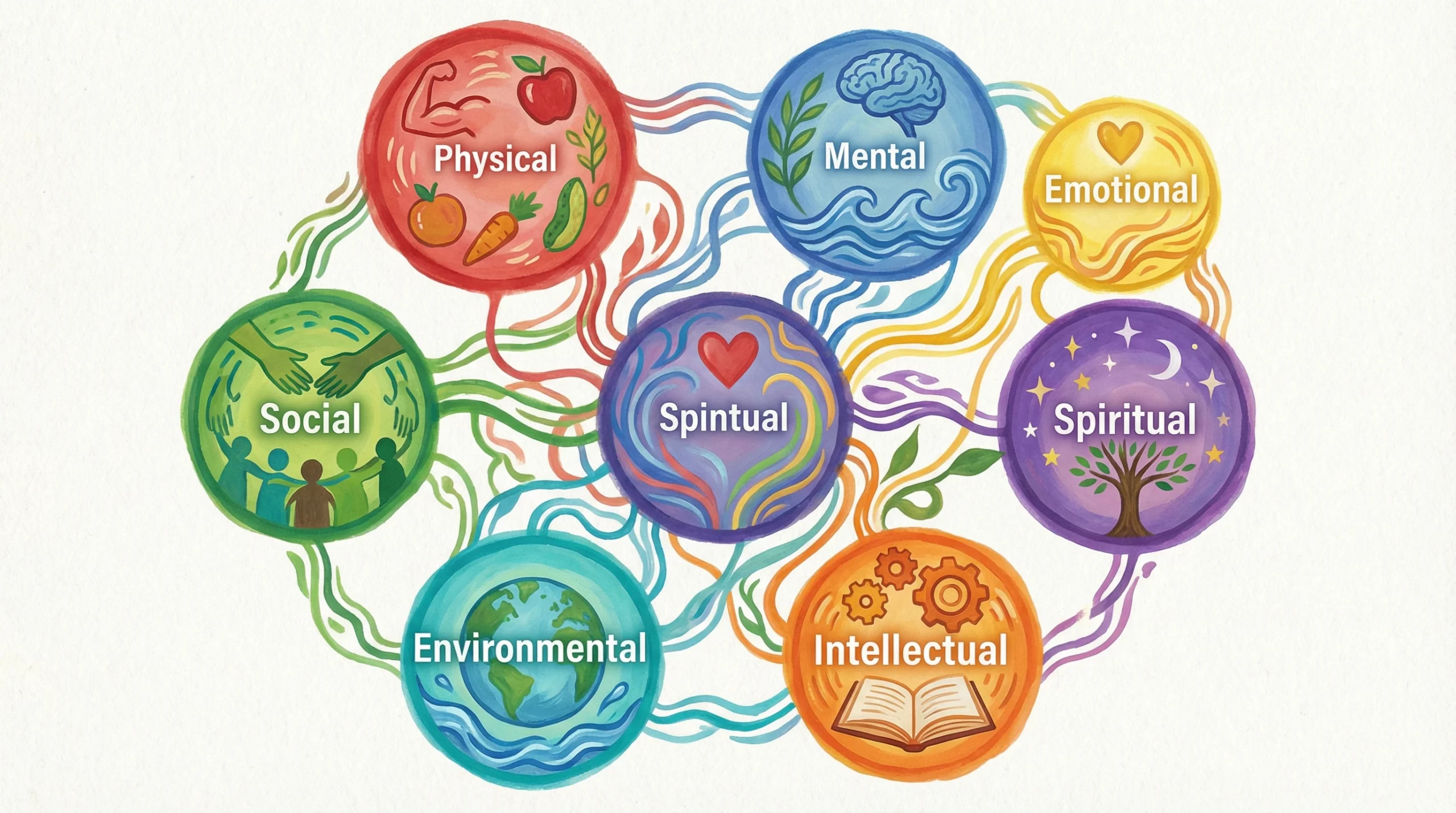
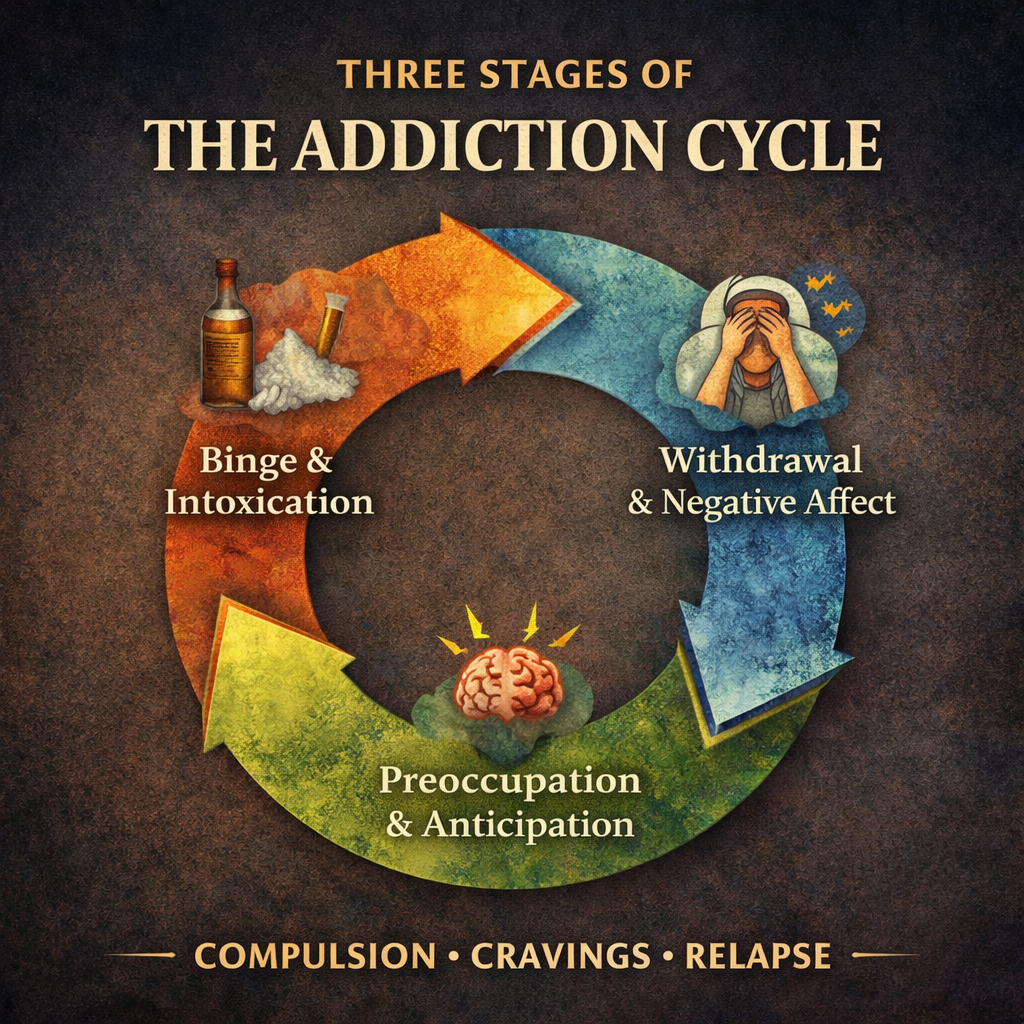
Exploring which country has the lowest levels of drug addiction offers valuable insight into how culture, policy, and social structure shape public health outcomes. Low addiction rates often spark curiosity about what those societies are doing differently—from prevention strategies and healthcare access to education, community connection, and social norms around substance use. Rather than reflecting … Read more