Alcohol: Oldest Abused Drug
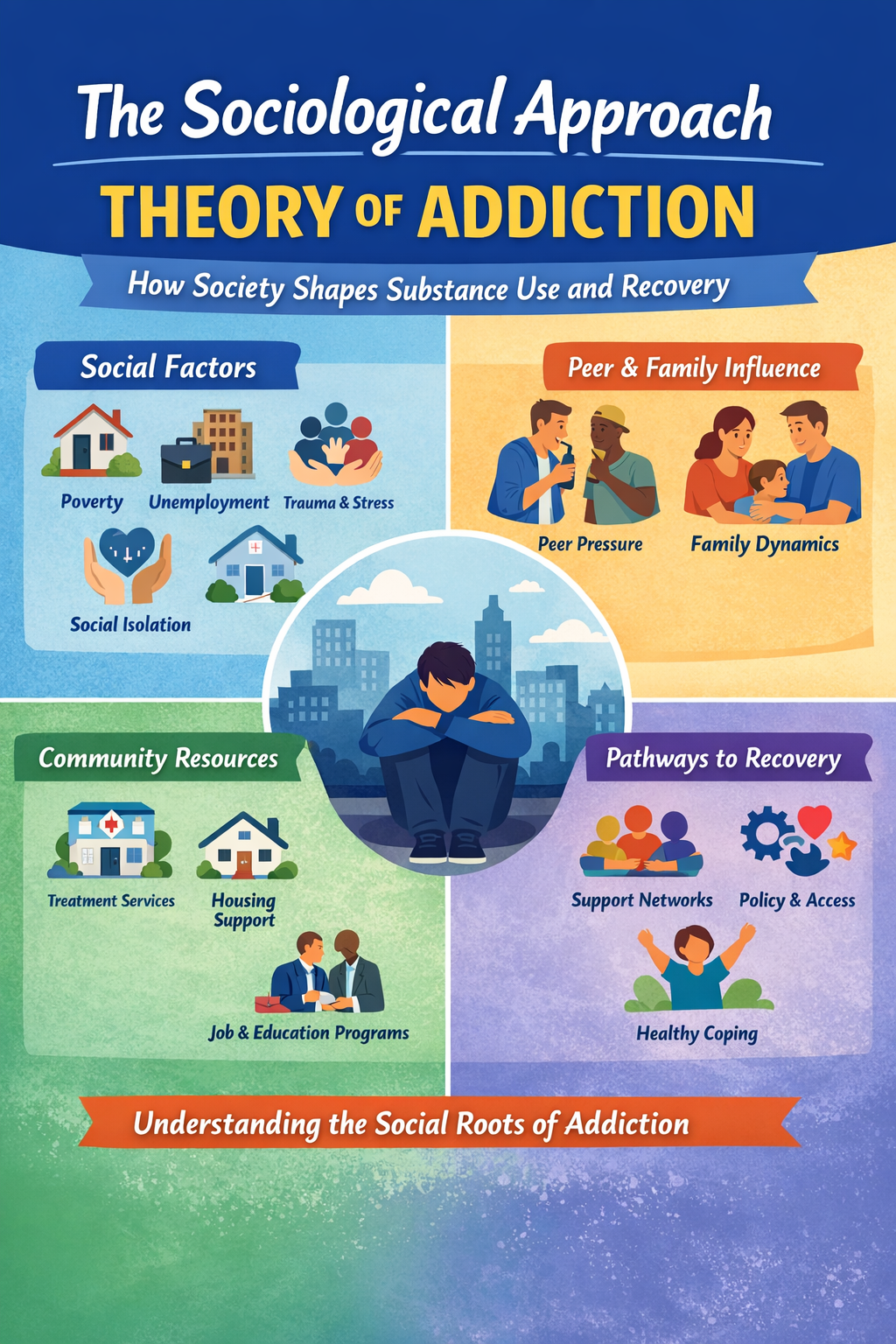
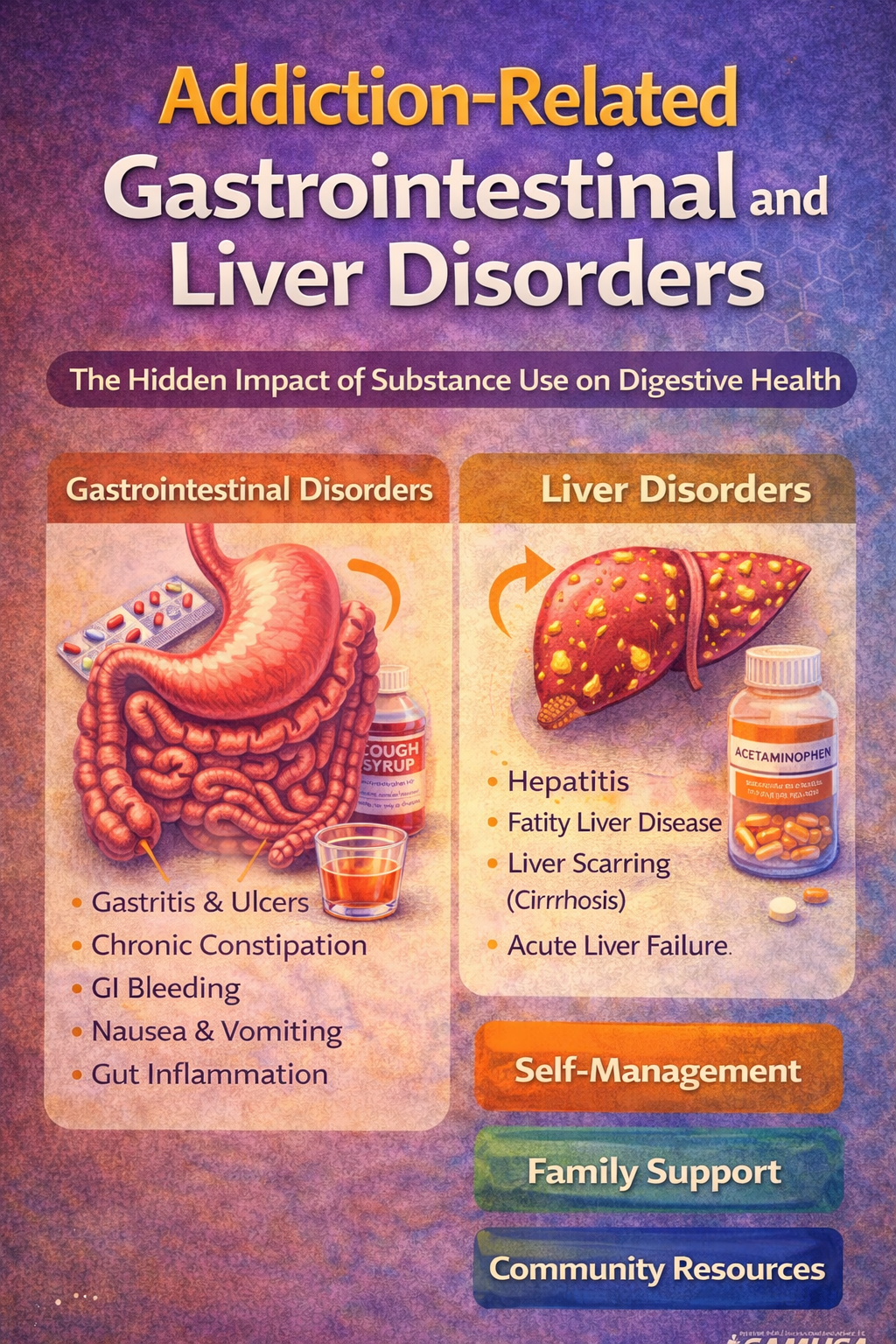
Alcohol is widely recognized as the oldest abused drug in human history, deeply woven into human culture, rituals, and social life for thousands of years. While alcohol has long been accepted and even celebrated, its widespread availability and social normalization have also contributed to significant health, social, and economic harm. Understanding alcohol abuse through a … Read more