Patient safety in addiction treatment relies on strong standards and support systems. Government policies enforce safe practices, while individuals contribute through self-management and informed care. Families offer supervision and advocacy, and communities provide certified programs, education, and peer support. Together, these efforts create a safer, more effective path to recovery.
Patient Safety Standards in Addiction Treatment: Protecting Health, Building Trust
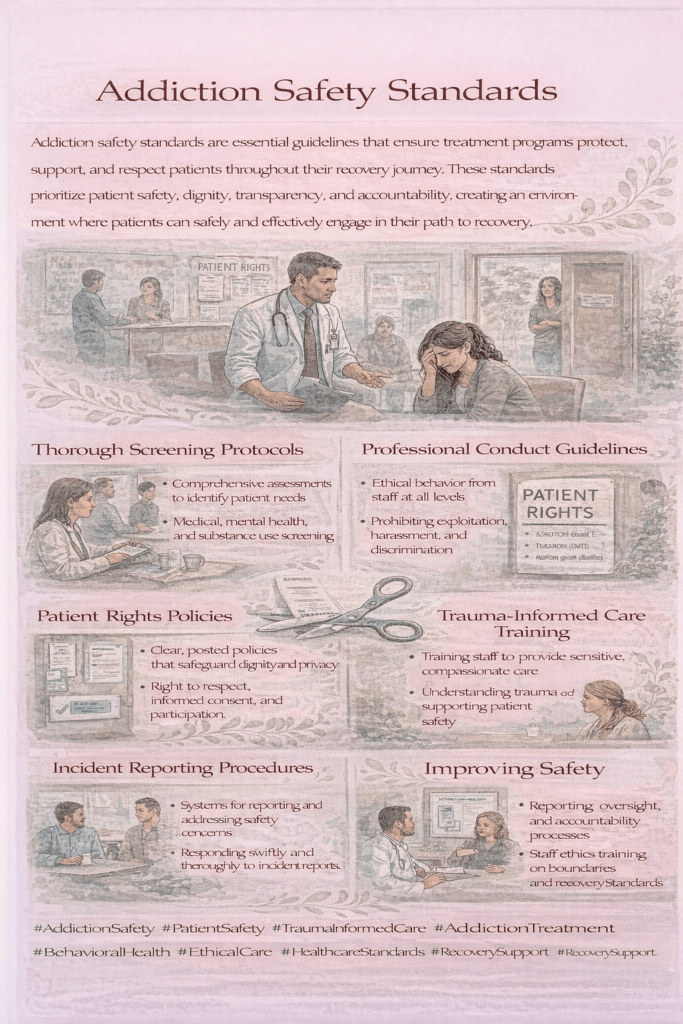
Patient safety standards in addiction treatment are essential guidelines and protocols designed to protect individuals from harm, ensure high-quality care, and support lasting recovery. These standards focus on minimizing risks while promoting positive health outcomes.
1. Comprehensive Assessment
Conduct thorough evaluations of medical, psychological, and social factors before starting treatment. This ensures that care plans are tailored to each patient’s unique needs for maximum safety and effectiveness.
2. Evidence-Based Treatment
Rely on scientifically proven therapies and medications to minimize risks and improve treatment success rates.
3. Medication Safety
Closely monitor dosing, potential drug interactions, and side effects—especially when using medications such as methadone or buprenorphine.
4. Infection Control
Maintain strict hygiene and sterilization protocols to prevent infections, particularly in inpatient or residential settings.
5. Monitoring and Managing Withdrawal
Provide safe, medically supervised detoxification to prevent complications such as seizures, dehydration, or severe discomfort.
6. Patient Education and Informed Consent
Clearly explain all treatment options, potential risks, and expected outcomes so patients can make informed decisions about their care.
7. Privacy and Confidentiality
Safeguard patient information in compliance with legal and ethical standards.
8. Staff Training and Competency
Ensure that all healthcare providers are trained and competent in addiction care and safety procedures.
9. Emergency Preparedness
Have clear protocols in place to handle overdoses, medical emergencies, and psychiatric crises swiftly and effectively.
10. Continuous Quality Improvement
Regularly evaluate and update safety measures in light of new research, clinical guidelines, and patient feedback.
In summary, by following these safety standards, addiction treatment providers can not only reduce harm but also build trust, enhance recovery outcomes, and create a safe environment where patients feel respected, informed, and supported throughout their journey.

How Government Policies Strengthen Patient Safety in Addiction Treatment
Government policies are vital in ensuring patient safety within addiction treatment. By establishing regulations, funding programs, and enforcing quality standards, policymakers help create treatment environments that are both effective and secure. Key policy approaches include:
1. Licensing and Accreditation Requirements
Facilities must meet recognized safety and quality benchmarks, often verified through certification bodies such as The Joint Commission or CARF International.
2. Medication-Assisted Treatment (MAT) Regulations
Guidelines govern the safe prescribing, dispensing, and monitoring of medications like methadone and buprenorphine to prevent misuse and reduce risks.
3. Confidentiality and Privacy Laws
Laws such as HIPAA and 42 CFR Part 2 protect patient information, encouraging individuals to seek care without fear of stigma or exposure.
4. Workforce Training and Certification
Ongoing education and credentialing requirements ensure providers remain competent in addiction care and up to date with safety protocols.
5. Monitoring and Reporting Systems
Surveillance programs track treatment outcomes, adverse events, and overdose incidents, enabling continuous quality improvement.
6. Funding for Quality Improvement Initiatives
Government funding supports evidence-based safety programs, including safe detoxification protocols and overdose prevention training.
7. Integration of Behavioral and Physical Health Services
Policies promoting coordinated care help providers address co-occurring mental and physical health conditions safely and effectively.
8. Emergency Response and Overdose Prevention
Expanding access to naloxone and training first responders and communities enhances rapid, life-saving responses to overdoses.
In summary, by implementing and enforcing these policies, governments not only uphold patient safety but also foster public trust, support effective recovery, and reduce the overall harms of substance use disorders.
Self-Management Strategies to Support Safety in Addiction Treatment
Self-management plays a critical role in maintaining safety during addiction treatment. By staying engaged, informed, and proactive, individuals can help ensure their care remains effective and risk-free. Key strategies include:
1. Active Communication
Share your complete medical history, current medications, allergies, and any concerns with your healthcare providers.
2. Education and Informed Decision-Making
Understand your treatment options, potential side effects, and safety precautions so you can make confident, informed choices.
3. Medication Adherence
Follow your prescribed medication plan carefully and report any side effects or problems right away.
4. Monitoring Symptoms and Side Effects
Track any physical or mental changes and update your care team promptly.
5. Engaging in Treatment Planning
Please take part in developing and adjusting your treatment plan to ensure it meets your needs while maintaining safety.
6. Using Support Networks
Involve trusted family or friends to help with reminders, provide encouragement, and support your recovery goals.
7. Practicing Healthy Lifestyle Habits
Maintain good nutrition, regular sleep, and stress-reduction practices to support overall well-being and reduce treatment risks.
8. Recognizing Warning Signs
Be alert to signs of relapse, overdose, or adverse reactions and seek immediate help if they occur.
9. Advocating for Yourself
Speak up if you feel unsafe, uncertain, or need clarification about your care.
In summary, by actively managing their treatment and communicating openly, individuals can help uphold patient safety standards and create a more effective recovery experience.
Family Support Strategies to Maintain Safety in Addiction Treatment
Family support is a decisive factor in ensuring safety and success during addiction treatment. By staying involved and informed, families can help protect their loved ones while reinforcing treatment goals. Key strategies include:
1. Open Communication
Encourage honest, nonjudgmental conversations about treatment progress, medication use, and any concerns or side effects.
2. Education and Awareness
Learn about addiction, treatment protocols, and patient safety standards to better understand your loved one’s journey and how to support them effectively.
3. Monitoring and Supervision
Assist in tracking medications, appointments, and behavioral changes to identify potential safety risks early.
4. Supporting Medication Adherence
Remind and assist your loved one in taking medications as prescribed, and promptly report any adverse effects to healthcare providers.
5. Creating a Safe Environment
Remove access to drugs, alcohol, or unsafe items, and reduce environmental triggers that could lead to relapse or harm.
6. Advocacy
Attend treatment meetings when appropriate, ask questions, and advocate for high-quality, safe, and patient-centered care.
7. Emotional Support
Offer encouragement and reassurance to reduce stress and anxiety, thereby strengthening recovery and improving safety outcomes.
8. Crisis Preparedness
Recognize the signs of overdose or medical emergencies and keep emergency contacts and naloxone on hand if needed.
In summary, through these actions, families become active partners in the recovery process—helping to maintain safety, build trust, and improve long-term treatment outcomes.
How Community Resources Strengthen Safety Standards in Addiction Treatment
Community resources are essential in promoting and upholding safety standards in addiction treatment. By offering support, education, and coordinated care, communities can enhance recovery outcomes and reduce risks. Key strategies include:
1. Providing Access to Certified Treatment Programs
Ensure that local treatment centers meet licensing and accreditation requirements to deliver safe, evidence-based care.
2. Offering Education and Training
Host workshops for healthcare providers, patients, and families on topics such as patient safety, medication management, and overdose prevention.
3. Supporting Medication-Assisted Treatment (MAT) Access
Facilitate the availability of MAT services with proper monitoring to prevent misuse and reduce adverse effects.
4. Establishing Peer Support Networks
Develop peer-led groups that promote adherence to treatment plans and provide a safety net for early detection of relapse or side effects.
5. Coordinating Integrated Care Services
Encourage collaboration between addiction treatment providers, mental health professionals, and primary care clinicians to manage co-occurring conditions safely.
6. Implementing Harm Reduction Programs
Offer services such as needle exchanges, naloxone distribution, and safe-use education to reduce health risks during recovery.
7. Monitoring and Reporting Systems
Collect and analyze data on treatment outcomes and safety incidents to guide continuous quality improvement efforts.
8. Emergency Response Support
Provide training and resources to recognize and respond to overdoses in the community.
By leveraging these strategies, community resources ensure addiction treatment is not only practical but also safe, responsive, and aligned with both individual and public health needs.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some common questions:
Question: What patient safety standards can be implemented by clinic facilities?
Answer: A structured list of patient safety standards that addiction treatment clinics can implement to protect patients, improve care quality, and meet regulatory expectations:
Patient Safety Standards for Addiction Treatment Clinics
1. Comprehensive Intake and Assessment
- Perform thorough medical, psychiatric, and social evaluations before beginning treatment.
- Include screening for co-occurring mental health disorders and infectious diseases.
2. Evidence-Based Treatment Protocols
- Use therapies and medications supported by scientific research.
- Avoid unproven or high-risk interventions.
3. Medication Safety Procedures
- Implement double-check systems for dosing.
- Maintain secure storage and inventory control of controlled substances.
- Monitor for drug interactions and adverse reactions.
4. Infection Control Measures
- Follow CDC guidelines for hygiene, sterilization, and PPE use.
- Provide safe injection equipment for medically supervised programs.
5. Withdrawal and Detoxification Safety
- Offer medically supervised detox when appropriate.
- Have protocols for preventing complications like seizures or dehydration.
6. Patient Education and Informed Consent
- Clearly explain treatment options, risks, and benefits in understandable language.
- Document patient consent and understanding.
7. Privacy and Confidentiality Compliance
- Adhere to HIPAA and 42 CFR Part 2 requirements.
- Train staff on secure handling of patient records.
8. Staff Competency and Ongoing Training
- Require addiction-specific training for all clinical staff.
- Provide continuing education on safety protocols and emerging best practices.
9. Emergency Preparedness
- Maintain naloxone and other emergency equipment onsite.
- Train staff in overdose response, CPR, and crisis de-escalation.
10. Continuous Quality Improvement (CQI)
Update protocols based on new research and safety data.
Regularly review patient outcomes, incident reports, and feedback.
Question: What patient safety standards can be implemented in the pharmacy setting?
Answer: A detailed list of patient safety standards that can be implemented in a pharmacy setting, particularly when dispensing addiction treatment medications such as methadone, buprenorphine, or naltrexone:
Patient Safety Standards for Pharmacies in Addiction Treatment
1. Accurate Prescription Verification
- Confirm the prescriber’s credentials and patient identity before dispensing.
- Double-check dosage, frequency, and formulation against treatment guidelines.
2. Secure Medication Storage
- Store controlled substances in locked, access-restricted areas.
- Maintain temperature and humidity controls to ensure medication stability.
3. Dispensing Accuracy Protocols
- Use barcode scanning or independent double-check systems before handing medications to patients.
- Clearly label medications with instructions, warnings, and expiration dates.
4. Patient Education at Dispensing
- Counsel patients on correct usage, dosing schedules, side effects, and missed-dose procedures.
- Provide written instructions in plain language.
5. Monitoring for Drug Interactions
- Use pharmacy management systems to flag potential interactions or contraindications.
- Communicate with prescribers about any safety concerns.
6. Documentation and Record-Keeping
- Maintain accurate logs of controlled substance dispensing in accordance with DEA and state regulations.
- Record counseling provided and any adverse reactions reported.
7. Confidentiality and Privacy
- Protect patient information in compliance with HIPAA and 42 CFR Part 2.
- Provide private areas for patient counseling when discussing sensitive information.
8. Adverse Event and Side Effect Reporting
- Have a straightforward process for reporting suspected medication errors, adverse reactions, or overdoses.
- Collaborate with prescribers to adjust treatment if needed.
9. Safe Return and Disposal Programs
- Offer take-back programs for unused or expired medications to prevent diversion or misuse.
10. Staff Training and Competency
Train staff to recognize and respond to intoxication, withdrawal, or medical emergencies.
Provide ongoing education on addiction pharmacotherapy, overdose prevention, and controlled substance regulations.
Question: What patient safety standards can be implemented in the hospital setting?
Answer: A structured list of patient safety standards that hospitals can implement—especially relevant for addiction treatment units, detox services, and patients with substance use disorders in general medical care:
Patient Safety Standards for Hospitals in Addiction Care
1. Comprehensive Screening and Assessment
- Screen all patients for substance use history during intake.
- Evaluate medical, psychiatric, and social factors to guide safe, individualized care.
2. Safe Medication Management
- Use standardized protocols for prescribing and administering methadone, buprenorphine, naltrexone, and other high-risk medications.
- Implement double-check systems and barcode scanning before administration.
- Monitor for side effects, drug interactions, and signs of misuse or diversion.
3. Withdrawal Management Protocols
- Provide medically supervised detox with continuous monitoring for complications like seizures, delirium tremens, or severe dehydration.
- Follow evidence-based symptom management scales (e.g., CIWA-Ar, COWS).
4. Infection Control
- Maintain strict hygiene and sterilization in inpatient units.
- Implement precautions for patients at risk of infectious diseases like HIV, hepatitis B/C, and endocarditis.
5. Pain Management with Safety Oversight
- Use multimodal pain management strategies to minimize the risk of misuse.
- Monitor closely when opioids are prescribed for legitimate pain needs.
6. Mental Health Integration
- Screen for co-occurring mental health disorders.
- Ensure psychiatric care is integrated into addiction treatment.
7. Patient Education and Informed Consent
- Clearly explain treatment plans, medication use, and potential risks.
- Provide overdose prevention education before discharge, including naloxone training if appropriate.
8. Privacy and Confidentiality
- Adhere to HIPAA and 42 CFR Part 2 when handling patient information.
- Provide private spaces for sensitive discussions.
9. Emergency Preparedness
- Ensure naloxone is readily available in all clinical areas.
- Train staff to respond quickly to overdose, psychiatric crises, and medical emergencies.
10. Discharge Planning and Continuity of Care
- Arrange follow-up appointments before discharge.
- Connect patients with community-based treatment, housing, peer support, and harm reduction resources.
11. Staff Competency and Training
- Require ongoing education on substance use disorder treatment, stigma reduction, and patient safety practices.
- Train security and non-clinical staff in de-escalation and trauma-informed care.
12. Continuous Quality Improvement (CQI)
Monitor treatment outcomes, adverse events, and patient feedback to update safety protocols regularly.
Conclusion
Ensuring patient safety in addiction treatment requires a coordinated approach involving clear standards, supportive policies, and active participation. Government regulations set the foundation for safe, evidence-based care, while individuals contribute through self-management and informed decisions. Family support and community resources further strengthen safety by providing guidance, supervision, and access to essential services. Together, these elements help create a safer, more supportive environment for long-term recovery.
Video: Self-Care in Addiction Recovery