Virtual Reality (VR) is becoming a valuable tool in addiction recovery, offering benefits like controlled exposure to triggers, enhanced engagement, and stress management. However, it also presents challenges, including physical discomfort, potential psychological impacts, and high costs. Ethical concerns related to privacy and informed consent, as well as equitable access, must be carefully managed. Community strategies are crucial for integrating VR effectively, focusing on accessibility, training, and collaboration to optimize its benefits while addressing potential drawbacks.
The Growing Role of Virtual Reality in Addiction Recovery
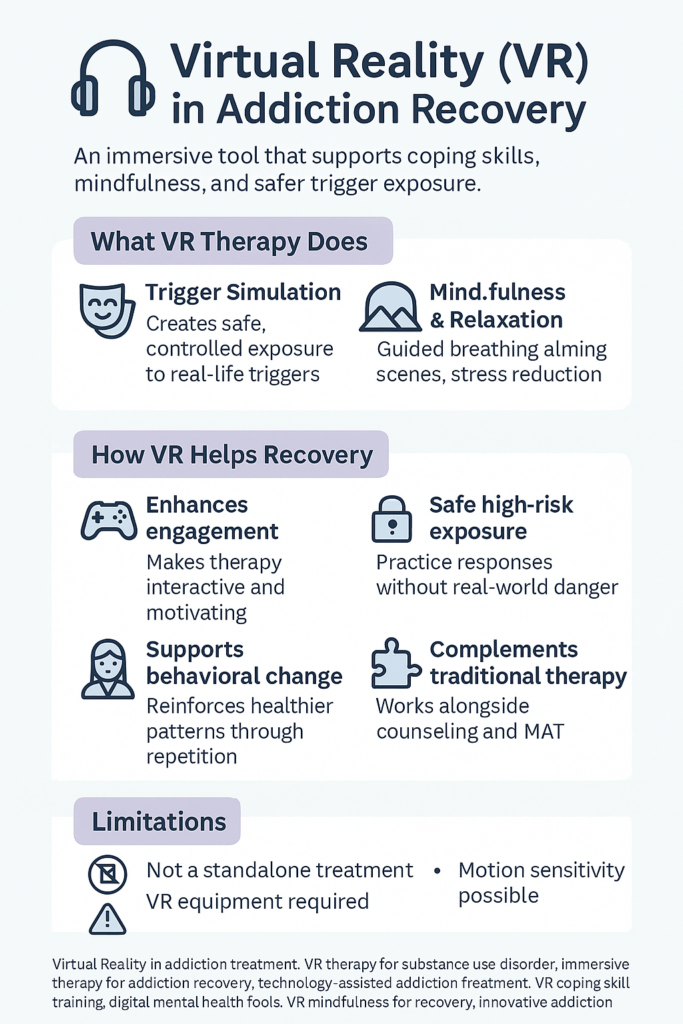
Virtual Reality (VR) is becoming an innovative tool in addiction recovery, offering new ways to support therapeutic interventions and enhance the recovery process. Here’s how VR is revolutionizing addiction treatment:
1. Exposure Therapy
- Controlled Environments: VR creates safe, immersive environments where individuals can confront triggers and cravings without the risk of real-world consequences. This controlled exposure allows for the development of resilience and coping strategies.
- Gradual Exposure: By simulating addiction-related scenarios, VR helps individuals manage cravings and anxiety gradually, reducing their impact over time.
2. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
- Immersive CBT: VR enhances traditional CBT by providing interactive, immersive experiences. These experiences help individuals recognize and change negative thought patterns and behaviors linked to addiction.
- Skill Development: Real-time VR environments allow users to practice new coping skills, making therapeutic techniques more engaging and practical.
3. Stress Management and Relaxation
- Relaxation Techniques: VR offers guided relaxation exercises and stress-reducing immersive environments that promote mindfulness, which is crucial for addiction recovery.
- Mindfulness Training: Through immersive VR experiences, individuals can learn mindfulness and meditation practices to manage cravings and enhance mental well-being.
4. Enhancing Motivation and Engagement
- Gamification: VR incorporates gamified elements like rewards and challenges, increasing motivation and sustaining engagement in the recovery process.
- Virtual Support Groups: VR facilitates virtual support groups where individuals can interact with peers and therapists, enhancing the sense of community and support.
5. Simulation of Real-World Situations
- Realistic Scenarios: VR simulates real-life situations, such as social gatherings or stressful environments, allowing individuals to practice coping strategies safely.
- Skill Transfer: Practicing in VR helps individuals transfer these skills to real-world situations, improving their ability to handle challenging scenarios outside therapy.
6. Education and Awareness
- Educational Modules: VR provides interactive educational modules that teach individuals about addiction and recovery, enhancing their understanding and awareness.
- Visualizing Consequences: Immersive VR experiences allow individuals to visualize the long-term consequences of substance use, reinforcing their motivation to recover.
7. Overcoming Geographic and Accessibility Barriers
- Remote Therapy: VR enables remote therapy sessions and support groups, making recovery resources more accessible to individuals in underserved or remote areas.
- Accessibility: VR enables people with mobility issues to participate in therapeutic activities without physical constraints.
Virtual Reality offers innovative and engaging ways to support addiction recovery through controlled exposure, enhanced cognitive behavioral therapy, stress management, and increased motivation. While the benefits are promising, VR should complement traditional treatments, providing a comprehensive approach to addiction recovery.
The Benefits of Virtual Reality in Addiction Recovery
Virtual Reality (VR) is revolutionizing addiction recovery by providing innovative tools and experiences that can make treatment more effective. Here are some key benefits of incorporating VR into addiction therapy:
1. Controlled exposure
- Safe Simulation of Triggers: VR allows individuals to face simulated triggers and high-risk scenarios in a controlled environment, where they can practice coping strategies without facing real-world consequences.
- Gradual Exposure: It supports gradual exposure therapy, enabling users to confront cravings and triggers at their own pace, helping them build resilience over time.
2. Enhanced Engagement and Motivation
- Interactive and Immersive Experiences: VR creates engaging and immersive experiences that can increase motivation and participation in recovery, making therapy more appealing and enjoyable.
- Gamification: Incorporating gamified elements, such as rewards and challenges, boosts motivation by making the recovery process more interactive and rewarding.
3. Improved Skill Development
- Realistic Practice: Individuals can practice and refine their coping skills in realistic yet safe environments, improving their ability to handle real-world situations.
- Skill Transfer: Practicing these skills in VR helps individuals transfer them to real-life scenarios, enhancing their ability to manage cravings and avoid relapse.
4. Stress Reduction and Relaxation
- Relaxation Techniques: VR offers immersive relaxation and mindfulness exercises, helping users manage stress and reduce anxiety—common triggers for substance use.
- Stress Management: Calming and soothing virtual environments aid in stress management, supporting overall mental well-being.
5. Enhanced Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
- Immersive CBT: VR enhances CBT by providing interactive scenarios that help users identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviors related to addiction.
- Interactive Exercises: VR’s engaging nature makes therapeutic exercises more interactive, increasing the impact of CBT techniques.
6. Virtual Support and Community
- Virtual Support Groups: VR can facilitate support groups in an immersive setting. It allows individuals to connect with peers and therapists, fostering a strong sense of community and support.
- Social Interaction Practice: VR simulates social interactions and environments, allowing users to practice social skills and build a support network in a safe space.
7. Education and Awareness
- Educational Experiences: Interactive VR modules can teach individuals about addiction, recovery, and coping strategies, enhancing understanding and awareness of the recovery process.
- Visualizing Consequences: Immersive experiences can help individuals visualize the long-term effects of substance use, reinforcing their commitment to recovery.
8. Accessibility and Flexibility
- Remote Access: VR can facilitate remote therapy sessions and support groups, making treatment and resources more accessible for individuals in underserved or remote areas.
- Overcoming Physical Barriers: It provides therapeutic activities for individuals with mobility issues or other barriers that may limit access to traditional in-person therapy.
Virtual Reality offers significant advantages in addiction recovery by providing controlled exposure, enhancing engagement, supporting skill development, and increasing accessibility. As a complement to traditional treatments, VR can help make the recovery journey more effective and engaging.
The Challenges and Disadvantages of Using Virtual Reality in Addiction Recovery
While Virtual Reality (VR) offers promising benefits for addiction recovery, it also presents several challenges and limitations that must be addressed for practical integration into therapeutic practice. Here are some critical disadvantages associated with using VR in addiction treatment:
1. Accessibility and Cost
- High Costs: The expense of VR equipment and software can be a barrier, limiting access for individuals who cannot afford the technology or for facilities that lack the resources to invest in it.
- Technological Barriers: VR requires specific hardware and a stable internet connection, which may not be available to everyone, especially those in underserved or remote areas.
2. Technical Limitations and Issues
- Technical Problems: Users may face software glitches, hardware malfunctions, or connectivity problems, which can disrupt therapy sessions and hinder progress.
- Learning Curve: Using VR technology can involve a significant learning curve, which may be challenging for individuals who are not tech-savvy or have limited experience with digital tools.
3. Potential for Over-Reliance
- Over-Reliance on Technology: There is a risk of becoming overly dependent on VR for therapy, potentially neglecting the value of human interaction, traditional therapeutic methods, and real-world experiences.
- Limited Human Connection: While VR can simulate therapeutic scenarios, it cannot fully replicate the empathetic, personal connection of human therapists, which is crucial for effective addiction treatment and emotional support.
4. Safety and Comfort Concerns
- Physical Discomfort: Some users may experience discomfort or motion sickness while using VR, which can detract from the therapeutic experience and limit their ability to engage with the technology.
- Psychological Effects: Immersive experiences might trigger intense emotions or psychological responses that could overwhelm some individuals, especially if they are not adequately prepared or supported.
5. Effectiveness and Evidence
- Limited Research: While promising, research on VR’s effectiveness in addiction recovery is still in its early stages. There may be insufficient evidence to fully validate its long-term benefits and outcomes.
- Variable Results: The effectiveness of VR-based interventions can vary among individuals, with some users experiencing more benefits than others.
6. Ethical and Privacy Concerns
- Data Privacy: Many VR applications collect personal data to tailor experiences and track progress. Ensuring data protection and addressing privacy concerns is essential.
- Ethical Issues: Immersive technology involves ethical considerations, including informed consent and the potential for data misuse.
7. Integration with Traditional Therapy
- Complementary Role: VR should complement rather than replace traditional therapeutic methods. Integrating VR into existing treatment frameworks requires careful planning and coordination.
- Limited Therapeutic Scope: VR alone may not address all aspects of addiction recovery and should be combined with other therapeutic approaches to provide a comprehensive treatment plan.
While VR offers innovative advantages in addiction recovery, such as controlled exposure and enhanced engagement, it also presents several challenges, including high costs, technical issues, and the potential for over-reliance on technology. Addressing these challenges requires ensuring accessibility, managing safety and comfort, integrating VR with traditional therapies, and evaluating its effectiveness through ongoing research.
Potential Side Effects of Using Virtual Reality in Addiction Recovery
Virtual Reality (VR) offers promising benefits for addiction recovery by providing immersive and engaging therapeutic experiences. However, there are potential side effects that may impact the therapeutic experience. Here are some possible side effects associated with using VR in addiction treatment:
1. Physical Discomfort
- Motion Sickness: Due to the disconnect between visual and physical sensations, users may experience motion sickness or dizziness, often referred to as VR motion sickness.
- Eye Strain: Prolonged use of VR headsets can cause significant eye strain or discomfort if the hardware is not adjusted correctly or if sessions are too long.
2. Psychological Effects
- Overstimulation: Immersive VR experiences can be overwhelming, potentially leading to anxiety or stress, especially if the content is intense or triggering.
- Disorientation: VR’s immersive nature can cause temporary disorientation, making it difficult to distinguish between virtual and real-world environments.
3. Emotional Impact
- Intense Emotional Responses: VR simulations can evoke strong emotional reactions that may be challenging to process, especially if the user is not adequately prepared or supported.
- Increased Vulnerability: Users might experience heightened vulnerability or emotional distress if VR experiences bring up unresolved issues or intense cravings.
4. Technical Issues
- Hardware Problems: Technical issues with VR equipment, such as malfunctions or connectivity problems, can disrupt therapy sessions and negatively affect the user experience.
- Learning Curve: Adapting to VR technology can be challenging for some users, leading to frustration and impacting their engagement in therapy.
5. Safety Concerns
- Physical Safety: There is a risk of bodily injury if users are not in a safe, clear space while using VR, as they may move around or react to virtual stimuli without awareness of their physical surroundings.
- Accidents: VR’s immersive nature could increase the risk of accidents or injuries if users are not cautious about their environment.
6. Social and Behavioral Effects
- Isolation: Excessive use of VR therapy may contribute to social isolation if users prioritize virtual interactions over real-world relationships and activities.
- Escapism: There is a risk of using VR as a form of escapism, in which individuals avoid real-world challenges rather than addressing them through traditional therapeutic methods.
7. Integration Challenges
- Incompatibility: VR therapy may not seamlessly integrate with other treatment modalities or existing therapeutic frameworks, potentially complicating the overall treatment plan.
- Limited Scope: VR may not address all aspects of addiction recovery, necessitating complementary approaches for comprehensive treatment.
While VR has the potential to enhance addiction recovery through immersive experiences, it also presents side effects such as physical discomfort, psychological effects, and safety concerns. Managing these side effects requires careful planning, proper user preparation, and integrating VR with traditional therapies to ensure a balanced and practical approach to addiction treatment.
Ethical Dilemmas of Using Virtual Reality in Addiction Recovery
Virtual Reality (VR) in addiction recovery introduces various ethical dilemmas that must be addressed to ensure the technology is used responsibly and effectively. Here are some critical ethical concerns surrounding the use of VR in addiction treatment:
1. Privacy and Data Security
- Sensitive Data: VR applications often collect personal data, including behavioral patterns, emotional responses, and potentially sensitive information. Protecting this data from breaches and misuse is critical to safeguarding user privacy.
- Informed Consent: Users must be fully informed about what data is being collected, how it will be used, and who will have access to it. Ensuring consent is genuinely informed and voluntary is essential for ethical data handling.
2. Informed Consent and Autonomy
- Understanding VR: Users must understand how VR works and what to expect from the experience. Otherwise, they might not fully grasp the implications or potential effects of using VR for therapy.
- Coercion and Pressure: Participation in VR therapy should always be voluntary. It is essential to ensure that users do not feel coerced or pressured into participating by therapists, institutions, or other entities.
3. Psychological Impact and Well-being
- Emotional Safety: VR experiences can evoke strong emotional reactions and potentially trigger distressing memories or feelings. Providing users with adequate support and coping mechanisms to handle these responses is crucial.
- Long-Term Effects: The long-term psychological impact of immersive VR experiences is not fully understood. Continuous monitoring and evaluation are needed to identify potential adverse effects over time.
4. Equity and Accessibility
- Access Disparities: VR technology can be expensive, making it less accessible for individuals in underserved or low-resource areas. Ensuring equitable access to VR therapy is an important ethical consideration.
- Technology Barriers: Not all users have the technological literacy or resources to use VR effectively, potentially creating disparities in who can benefit from this therapy.
5. Over-Reliance on Technology
- Complementary Use: There is a risk that VR could be used as a substitute for, rather than a complement to, traditional therapeutic methods. It is crucial to ensure that VR is thoughtfully integrated with other forms of treatment.
- Human Interaction: VR’s immersive nature may reduce the emphasis on face-to-face interactions with therapists and support networks, which are essential for holistic recovery.
6. Ethical Use of Immersive Technology
- Manipulation and Influence: VR can be highly persuasive and immersive, raising concerns about the potential for manipulation or undue influence on users’ thoughts and behaviors.
- Content Appropriateness: The scenarios presented in VR must be carefully designed to avoid harmful or inappropriate situations that could negatively impact users’ well-being.
7. Research and Validation
- Evidence-Based Practice: It is essential to ensure that VR applications are supported by rigorous research to validate their efficacy and safety. Ongoing research is needed to understand the benefits and risks of using VR in addiction recovery.
- Long-Term Evaluation: Research should include long-term studies to identify potential risks and continually validate the benefits of VR-based therapy.
8. Ethical Development and Implementation
- Developer Responsibility: Developers must create ethical VR applications by considering user welfare, data protection, and the social impact of their technology.
- Regulatory Compliance: To protect users and maintain trust, VR applications must comply with relevant regulations and ethical standards.
The ethical dilemmas associated with using Virtual Reality in addiction recovery encompass issues such as privacy, informed consent, psychological impact, and equity. Addressing these concerns requires responsible data handling, equitable access, and the careful integration of VR with traditional therapies. By navigating these ethical challenges thoughtfully, VR can enhance addiction recovery while ensuring user well-being and rights are protected.
Community Resource Strategies for Integrating Virtual Reality in Addiction Recovery
Integrating Virtual Reality (VR) into addiction recovery can be supported and enhanced through various community resource strategies. These approaches focus on ensuring accessibility, optimizing implementation, and maximizing the impact of VR therapy. Here are some key strategies to consider:
1. Collaborative Partnerships
- Healthcare Providers: Work with local healthcare providers, addiction treatment centers, and mental health professionals to incorporate VR into existing treatment programs. These partnerships can help ensure that VR is used appropriately and effectively in therapeutic settings.
- Technology Companies: Partner with VR technology companies to develop customized solutions tailored to the specific needs of addiction recovery, making the technology more relevant and accessible.
2. Accessibility and Equity
- Community-Based Access: Set up community centers or recovery hubs equipped with VR technology to provide access to individuals who may not have VR at home. This approach helps make VR therapy available to everyone, regardless of personal resources.
- Subsidized Programs: Seek funding or grants to subsidize the cost of VR equipment and software for low-income individuals or underserved communities. This ensures equitable access to VR technology and reduces financial barriers to participation.
3. Training and Education
- Training Programs: Develop comprehensive training programs for therapists, counselors, and addiction recovery professionals. Proper training ensures these professionals can effectively use VR technology and integrate it into their therapeutic practices.
- Public Education: Educate the community about the benefits and limitations of VR in addiction recovery through workshops, seminars, and informational materials. Public awareness helps dispel misconceptions and encourages more people to consider VR therapy.
4. Support Networks and Peer Support
- Virtual Support Groups: Leverage VR to create immersive environments where individuals can connect with peers. This fosters a sense of community, shared experience, and mutual support, essential for recovery.
- Peer Training: Train peer support specialists to use VR tools effectively, enabling them to assist others in their recovery journey. Peer-led support can make VR therapy more relatable and encouraging for individuals.
5. Research and Evaluation
- Community-Based Research: Engage in community-based research to evaluate the effectiveness of VR interventions in addiction recovery. Data on outcomes and user experiences can help inform future practices and improve the technology’s application.
- Feedback Mechanisms: Implement mechanisms to collect feedback from users and providers about their experiences with VR therapy. This feedback can refine the technology and better address community needs.
6. Integration with Traditional Services
- Complementary Use: Integrate VR therapy with traditional addiction treatment services, such as counseling, therapy, and support groups. A comprehensive approach combining multiple treatment modalities can enhance overall recovery outcomes.
- Referral Systems: Develop referral pathways to guide individuals from traditional treatment settings to VR-based interventions when appropriate. This ensures a smooth transition and continuity of care.
7. Outreach and Engagement
- Community Outreach: Conduct outreach campaigns to raise awareness of the availability and benefits of VR therapy for addiction recovery—target outreach efforts to individuals and families who could benefit from this innovative approach.
- Engagement Strategies: Use interactive methods, such as demonstrations, trials, and success stories, to encourage participation in VR therapy. Engaging strategies can help overcome hesitation and generate interest.
8. Policy and Advocacy
- Advocacy for Support: Advocate for policies that support the inclusion of VR in addiction recovery programs. This includes pushing for funding, grants, and insurance coverage to make VR therapy more accessible.
- Standards and Guidelines: Develop and promote standards for the ethical and practical use of VR in addiction recovery to ensure consistency and quality across programs and communities.
Community resource strategies for VR in addiction recovery emphasize collaboration, accessibility, training, support, and continuous evaluation. By fostering partnerships, ensuring equitable access, and integrating VR with traditional therapeutic methods, communities can effectively leverage this technology to enhance addiction treatment and support recovery. These efforts expand access to innovative therapies and create a more inclusive and supportive recovery ecosystem.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some common questions:
Who may benefit most from VR in addiction therapy?
Individuals who struggle with cravings, emotional regulation, or real-world exposure may benefit most. It can be invaluable for early recovery or treatment-resistant cases.
How many VR sessions are typically used?
The number of sessions varies depending on treatment goals and program design. VR is usually delivered over multiple sessions alongside standard therapy.
Is VR therapy widely available?
Availability is growing but still limited to specialized clinics, research programs, and some digital health platforms.
What are the limitations of VR in addiction therapy?
VR requires specialized equipment and trained staff and may not be suitable for everyone. It also cannot address all social or environmental factors affecting addiction.
Does insurance cover VR therapy?
Coverage varies widely. Some programs include VR as part of bundled services, while others offer it as an out-of-pocket option.
Conclusion
Virtual Reality (VR) holds significant promise for addiction recovery by providing immersive, engaging therapeutic experiences that can enhance traditional treatment methods. Its advantages include controlled exposure to triggers and improved engagement, though it also poses challenges such as physical discomfort, psychological impacts, and high costs. Addressing ethical dilemmas related to privacy and access is essential to ensure responsible use. Effective community resource strategies are vital for integrating VR into addiction recovery, emphasizing accessibility, training, and collaboration. Balancing these factors can maximize VR’s potential to support and improve recovery outcomes while navigating its complexities.
Video: VR lets you face addiction safely before real life #mentalhealth #vr #therapy