Maintaining sobriety requires a comprehensive approach that includes essential survival skills and a structured relapse prevention plan. These strategies help individuals manage triggers, develop healthy habits, and build a strong support network. A relapse prevention plan provides a personalized roadmap with coping mechanisms and emergency procedures. Family support offers emotional and practical assistance, while community resources provide access to support groups, counseling, educational programs, and other services. Integrating these elements enhances the ability to stay sober and lead a fulfilling, addiction-free life.
Essential Strategies to Maintain a Life Free from Addiction
Achieving sobriety is a significant milestone in the journey of recovery, but maintaining that sobriety can be a continuous challenge. Developing practical survival skills is crucial for individuals in recovery, as these strategies help prevent relapse and foster a healthy, fulfilling life. Here are some essential survival skills for sobriety:
1. Developing a Strong Support Network
- Attend Support Groups: Engaging with support groups like Alcoholics Anonymous (AA) or Narcotics Anonymous (NA) can provide a sense of community and understanding among individuals who share similar experiences.
- Build a Sober Community: Surround yourself with friends and family who encourage your sobriety and distance yourself from those who might trigger a relapse.
2. Managing Triggers and Cravings
- Identify Triggers: Recognizing people, places, and situations that provoke cravings for substances is essential in recovery.
- Develop Coping Strategies: Having a plan to handle cravings can be lifesaving. This might include hobbies, reaching out to a sponsor, or practicing mindfulness exercises.
3. Maintaining a Healthy Lifestyle
- Exercise Regularly: Physical activity is an excellent way to reduce stress and enhance mood, making it easier to stay sober.
- Eat a Balanced Diet: Proper nutrition supports overall health and can mitigate the risk of relapse.
- Get Adequate Sleep: Ensuring you get enough rest is vital, as fatigue can compromise your commitment to sobriety.
4. Practicing Mindfulness and Stress Management
- Mindfulness Meditation: Mindfulness helps individuals stay present and manage stress effectively.
- Stress-Relief Techniques: Use yoga, deep breathing, or progressive muscle relaxation to cope with daily stressors.
5. Setting and Achieving Goals
- Short-term Goals: Small, attainable goals can provide motivation and a sense of accomplishment.
- Long-term Goals: Having broader objectives gives direction and purpose, encouraging sustained recovery.
6. Therapy and Counseling
- Individual Therapy: Working with a therapist can help address underlying issues related to addiction.
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): Utilizing CBT techniques can transform negative thought patterns and behaviors into positive ones.
7. Avoiding High-Risk Situations
- Plan Ahead: Developing a strategy for social situations where substances may be present is crucial for staying sober.
- Know Your Limits: Be mindful of environments and activities that may increase the risk of relapse, and avoid them whenever possible.
8. Building New, Healthy Habits
- Engage in Hobbies: Discover new interests and hobbies that do not involve substances to create a fulfilling routine.
- Volunteer: Helping others through volunteering can instill a sense of purpose and enhance overall well-being.
9. Learning from Relapses
- Understand Triggers: If a relapse occurs, it’s vital to analyze what led to it and develop strategies to avoid similar situations.
- Seek Immediate Help: Contact your support network or a counselor right after a relapse to reinforce your commitment to recovery.
10. Staying Committed
- Daily Affirmations: Using positive affirmations can strengthen your resolve to remain sober.
- Gratitude Practice: Regularly reflecting on your gratitude can help shift focus from struggles to positive aspects of life and recovery.
Incorporating these survival skills into daily life can significantly enhance the chances of maintaining long-term sobriety. By actively engaging in these strategies, individuals can foster a healthy, fulfilling life free from the grasp of addiction. Remember, recovery is a journey, and every step forward is a victory.
Crafting a Relapse Prevention Plan: A Roadmap to Sustained Sobriety
Maintaining sobriety can be a challenging journey, filled with potential pitfalls and triggers that may lead to relapse. A relapse prevention plan is a strategic, personalized approach designed to help individuals navigate their recovery journey effectively. This plan includes identifying potential triggers, developing coping mechanisms, and creating a structured approach for managing situations that could lead to a return to substance use. Here’s a comprehensive outline of what a relapse prevention plan typically encompasses:
1. Understanding Triggers and Cravings
- Identify Triggers: Begin by listing specific people, places, situations, and emotions that prompt cravings for alcohol or drugs.
- Types of Triggers: Distinguish between external triggers (e.g., environmental cues) and internal triggers (e.g., emotional states) to develop targeted strategies for each.
2. Developing Coping Strategies
- Healthy Distractions: Engage in activities that can divert attention from cravings, such as exercising, pursuing hobbies, or spending time with supportive friends.
- Relaxation Techniques: To manage stress and anxiety effectively, practice mindfulness, deep breathing, meditation, or yoga.
- Problem-Solving Skills: Cultivate skills to address and resolve problems that might lead to cravings constructively.
3. Building a Support Network
- Support Groups: Regularly attend meetings of support groups like Alcoholics Anonymous (AA) or Narcotics Anonymous (NA) to connect with others in recovery.
- Trusted Contacts: Maintain a list of individuals you can contact when cravings arise, including sponsors, friends, and family members.
- Professional Help: Contact counselors or therapists specializing in addiction recovery for guidance and support.
4. Establishing Healthy Routines
- Daily Schedule: Create a structured routine that includes time for work, exercise, meals, and relaxation to promote stability.
- Self-Care: To enhance overall well-being, prioritize activities like proper nutrition, adequate sleep, and regular physical activity.
5. Setting Realistic Goals
- Short-Term Goals: Establish achievable short-term goals to maintain motivation and focus throughout recovery.
- Long-Term Goals: Identify long-term aspirations that offer a sense of purpose and direction, reinforcing commitment to sobriety.
6. Avoiding High-Risk Situations
- Plan Ahead: Develop strategies for handling situations where temptation may arise, preparing yourself mentally and emotionally.
- Know Your Limits: Steer clear of places, events, and individuals associated with past substance use to reduce the risk of relapse.
7. Emergency Plan for Relapse
- Immediate Actions: Outline steps to take if a relapse occurs, such as contacting a sponsor or counselor immediately.
- Learn from Mistakes: Analyze the circumstances that led to the relapse and update your prevention plan to address these triggers going forward.
8. Regular Review and Adjustment
- Evaluate Progress: Regularly assess your recovery progress and make necessary adjustments to your relapse-prevention plan.
- Stay Flexible: Be open to changing strategies that aren’t working and experimenting with new approaches that may be more effective.
9. Education and Self-Awareness
- Understand Addiction: Invest time in learning about addiction and recovery to foster self-awareness.
- Recognize Warning Signs: Learn to identify early warning signs of relapse, such as changes in behavior, thoughts, or emotions, enabling proactive responses.
10. Celebrating Milestones
- Acknowledge Success: Celebrate your achievements and milestones in recovery to reinforce your commitment and motivation.
- Reward Yourself: Find healthy ways to reward yourself for maintaining sobriety, creating positive reinforcement for your efforts.
Example of a Relapse Prevention Plan
- Triggers: Identify personal triggers, such as work stress, social gatherings, or feelings of loneliness.
- Coping Strategies:
- When feeling stressed, practice deep breathing and meditation.
- Attend a support group meeting if you feel lonely.
- Engage in hobbies like painting or running to distract from cravings.
- Support Network:
- Call your sponsor when cravings become overwhelming.
- Spend time with supportive friends who understand your recovery journey.
- Schedule regular appointments with your therapist for ongoing support.
- Daily Routine:
- Morning: Meditation and exercise.
- Afternoon: Productive work activities.
- Evening: Attend a support group meeting or spend quality time with family.
- Emergency Plan:
- If a relapse occurs, contact your sponsor and schedule an emergency session with your therapist.
- Reflect on the circumstances surrounding the relapse and update your plan accordingly.
By having a well-thought-out relapse prevention plan, individuals can better manage their sobriety, anticipate challenges, and take proactive steps to maintain their recovery. Remember, recovery is a dynamic process, and each step taken is a victory on the journey to a healthier, substance-free life.
A Step-by-Step Guide to Creating Your Personalized Relapse Prevention Plan
Creating a relapse prevention plan is a crucial step in maintaining sobriety and avoiding the potential pitfalls of substance use. A thoughtful, personalized approach equips individuals with strategies to manage triggers and fosters a supportive environment conducive to long-term recovery. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you craft an effective relapse prevention plan:
Step 1: Self-Assessment
- Understand Your Addiction: Begin by reflecting on your history of substance use. Identify patterns and recognize the factors contributing to your addiction.
- Acknowledge Your Motivation: Clearly define your reasons for wanting to stay sober, whether for personal health, family, career, or other significant aspects of your life.
Step 2: Identify Triggers
- List External Triggers:
- People: Identify individuals who may encourage substance use or have been part of your previous habits.
- Places: Recognize locations where you previously used substances, such as bars or specific social settings.
- Situations: Pinpoint scenarios that may evoke cravings, like parties or stressful events.
- List Internal Triggers:
- Emotions: Understand feelings that might prompt cravings, such as loneliness, anger, or sadness.
- Thoughts: Identify specific thought patterns that lead to substance cravings, allowing you to address them proactively.
Step 3: Develop Coping Strategies
- Healthy Distractions: To keep your mind occupied, engage in hobbies and activities you enjoy, such as sports, the arts, or reading.
- Relaxation Techniques: To effectively manage stress and anxiety, practice mindfulness, deep breathing, meditation, or yoga.
- Problem-Solving Skills: Develop constructive strategies to address challenges and resolve issues without substance use.
Step 4: Build a Support Network
- Support Groups: Regularly attend meetings such as Alcoholics Anonymous (AA) or Narcotics Anonymous (NA) to connect with others who understand your journey.
- Trusted Contacts: Create a list of people, including sponsors, friends, or family members, whom you can call when cravings strike.
- Professional Help: Contact counselors or therapists specializing in addiction recovery for guidance and support.
Step 5: Establish Healthy Routines
- Daily Schedule: To create stability, plan a structured daily routine that includes time for work, exercise, meals, and relaxation.
- Self-Care: To support overall well-being, prioritize self-care activities such as proper nutrition, adequate sleep, and regular physical activity.
Step 6: Set Realistic Goals
- Short-Term Goals: Set achievable goals to maintain motivation and focus your efforts on recovery.
- Long-Term Goals: Identify long-term aspirations that provide a sense of purpose and direction in your life.
Step 7: Avoid High-Risk Situations
- Plan Ahead: Prepare for situations you might be tempted to use, and develop strategies to handle them effectively.
- Know Your Limits: Avoid places, events, and people associated with your past substance use to reduce the risk of relapse.
Step 8: Create an Emergency Plan for Relapse
- Immediate Actions: Have a clear plan for what to do if you relapse, such as contacting your sponsor or counselor immediately.
- Learn from Mistakes: Analyze what led to the relapse and adjust your prevention plan to prevent similar occurrences in the future.
Step 9: Regular Review and Adjustment
- Evaluate Progress: Regularly assess your recovery progress and adjust your relapse prevention plan.
- Stay Flexible: Be open to modifying ineffective strategies and try new approaches as needed.
Step 10: Education and Self-Awareness
- Understand Addiction: Educate yourself about addiction and the recovery process to foster greater self-awareness.
- Recognize Warning Signs: Learn to identify early warning signs of relapse, such as changes in behavior, thoughts, or emotions, so that you can intervene early.
Step 11: Celebrate Milestones
- Acknowledge Success: Celebrate your achievements and milestones in recovery, no matter how small, to stay motivated.
- Reward Yourself: Find healthy ways to reward yourself for staying sober, reinforcing positive behavior, and commitment.
Example Relapse Prevention Plan
- Triggers:
- External Triggers: Social gatherings with alcohol, seeing old friends who use.
- Internal Triggers: Stress from work, feelings of loneliness.
- Coping Strategies:
- Healthy Distractions: Running, painting, reading.
- Relaxation Techniques: Meditation, deep breathing exercises.
- Problem-Solving Skills: Breaking tasks into manageable steps and seeking advice when needed.
- Support Network:
- Support Groups: Attend AA meetings twice a week.
- Trusted Contacts: Call a sponsor or close friend when urged to use.
- Professional Help: Weekly therapy sessions.
- Daily Routine:
- Morning: Exercise and meditation.
- Afternoon: Work and productive activities.
- Evening: Support group meetings or family time.
- Emergency Plan:
- Immediate Actions: Contact the sponsor and therapist.
- Learn from Mistakes: Reflect on the circumstances and update the plan to address new triggers.
By following these steps, you can create a personalized and effective relapse prevention plan that supports your long-term sobriety. Remember, the journey to recovery is ongoing, and a solid plan can help you navigate challenges with confidence and resilience.
Essential Family Support Strategies for Effective Relapse Prevention
Family support plays a critical role in the recovery process for individuals battling addiction. It can provide the love, accountability, and encouragement necessary for maintaining sobriety and preventing relapse. Here are several strategies that families can implement to support their loved one’s relapse prevention plan:
1. Education and Understanding
- Learn About Addiction: Take the time to educate yourself about addiction and the recovery process. Understanding what your loved one is experiencing can foster empathy and patience.
- Recognize Triggers: Familiarize yourself with specific triggers and stressors that could lead to relapse. This knowledge will empower you to help manage these situations effectively.
2. Effective Communication
- Open Dialogue: Encourage honest and non-judgmental conversations about recovery struggles and achievements. This openness can help your loved one feel more comfortable sharing their feelings and concerns.
- Express Support: Regularly affirm your support and commitment to their recovery journey. Simple words of encouragement can make a significant difference.
3. Encouraging Healthy Habits
- Promote Routine: Help your loved one establish and maintain a daily routine incorporating healthy habits, such as regular exercise, balanced nutrition, and sufficient sleep.
- Participate in Activities: Engage in healthy-lifestyle activities together, such as family walks, cooking nutritious meals, or exploring new hobbies. Shared experiences can strengthen your bond and promote well-being.
4. Creating a Supportive Environment
- Substance-Free Home: Ensure that your home is free of alcohol and drugs, reducing temptation and creating a safe space for recovery.
- Safe Space: Foster a home environment that feels secure and supportive, where your loved one can relax and be themselves without fear of judgment.
5. Attending Support Groups
- Family Support Groups: Consider joining support groups for families of individuals in recovery, such as Al-Anon or Nar-Anon. These groups can provide valuable insights and emotional support.
- Joint Meetings: Occasionally, attend support group meetings with your loved one to demonstrate solidarity and commitment to their recovery journey.
6. Being Involved in Treatment
- Therapy Participation: If recommended, participate in family therapy sessions to address underlying issues and improve family dynamics, fostering a healthier home environment.
- Stay Informed: Keep in touch with your loved one’s treatment team to stay updated on their progress and any recommended family involvement.
7. Developing a Crisis Plan
- Emergency Contacts: Know who to contact in case of a relapse, including therapists, sponsors, and emergency services, to ensure a prompt response.
- Crisis Plan: Create a clear plan outlining steps to take and the individuals to involve in the event of a relapse, providing a roadmap for managing potential setbacks.
8. Setting Boundaries
- Healthy Boundaries: Establish and maintain healthy boundaries to protect your well-being while supporting your loved one. This balance is essential for sustainable support.
- Consistency: Maintain clear boundaries and expectations to avoid enabling behaviors. Clear boundaries can help your loved one understand the importance of accountability.
9. Positive Reinforcement
- Celebrate Milestones: Acknowledge and celebrate recovery milestones and achievements, no matter how small, to keep motivation high and recognize progress.
- Encouragement: Provide positive reinforcement for healthy behaviors and coping strategies. Celebrating successes fosters a sense of accomplishment and resilience.
10. Addressing Co-Occurring Issues
- Mental Health Support: Encourage and support treatment for any co-occurring mental health issues, such as depression or anxiety, that may affect recovery.
- Holistic Approach: Support a holistic recovery approach that addresses physical, mental, and emotional health, recognizing that each aspect contributes to overall well-being.
Example of Family Support Strategies in a Relapse Prevention Plan
- Education and Understanding: Attend workshops on addiction and recovery to better understand your loved one’s experience.
- Effective Communication: Schedule weekly family meetings to discuss recovery progress and concerns in a supportive environment.
- Encouraging Healthy Habits: Plan and engage in daily exercise routines together, such as evening walks or weekend hikes.
- Creating a Supportive Environment: Remove all alcohol from the home and establish a sober living agreement with the entire family.
- Attending Support Groups: Join a family support group and attend sessions regularly to share experiences and gain mutual support.
- Being Involved in Treatment: Participate in scheduled family therapy sessions to address and resolve family-related issues.
- Developing a Crisis Plan: Create a list of emergency contacts and agree on a step-by-step action plan for handling potential relapses.
- Setting Boundaries: Communicate and consistently enforce boundaries on unacceptable behaviors.
- Positive Reinforcement: Celebrate each month of sobriety with a special family dinner or outing to acknowledge progress.
- Addressing Co-Occurring Issues: Encourage and support regular appointments with a mental health professional if needed.
By implementing these family support strategies, you can create a robust, nurturing environment that significantly increases your loved one’s likelihood of adhering to their relapse-prevention plan. Together, you can promote long-term recovery and foster a healthier family dynamic.
Leveraging Community Resources for Effective Relapse Prevention
Community resource strategies are crucial to relapse-prevention plans, offering a robust network of support, education, and services to help individuals maintain sobriety. By tapping into these resources, individuals can strengthen their recovery journey and build a fulfilling life free from substance use. Here are several community resource strategies to consider:
1. Support Groups and Meetings
- 12-Step Programs: Encourage participation in well-established 12-step programs such as Alcoholics Anonymous (AA) or Narcotics Anonymous (NA), which offer regular meetings and a supportive network.
- Non-12-Step Groups: Explore alternative support groups such as SMART Recovery or Refuge Recovery, which offer different approaches to recovery and can cater to varying needs.
2. Professional Counseling and Therapy
- Substance Abuse Counselors: Utilize local substance abuse counselors for individualized therapy sessions that target specific recovery challenges.
- Group Therapy: Participate in group therapy sessions through community health centers to share experiences and learn from others.
3. Healthcare Services
- Primary Care Providers: Schedule regular check-ups to monitor overall health and ensure physical well-being is prioritized in recovery.
- Mental Health Services: Access mental health services through community mental health centers to address co-occurring disorders, which are common in individuals in recovery.
4. Educational Programs
- Workshops and Seminars: Attend workshops on addiction, recovery, and essential life skills offered by local community organizations to enhance knowledge and coping strategies.
- Online Resources: Utilize online educational resources and webinars from reputable organizations to enable flexible learning opportunities.
5. Employment and Vocational Support
- Job Training Programs: Engage with community job-training programs to develop new skills and improve employment opportunities, thereby aiding long-term stability.
- Employment Services: Access community employment services to find job opportunities and support with navigating the workplace.
6. Housing and Shelter Services
- Sober Living Homes: During the early stages of recovery, consider moving into a sober living home that offers a structured, supportive environment.
- Transitional Housing: Utilize transitional housing programs to stabilize living conditions post-rehabilitation and ensure a smooth transition back to independent living.
7. Recreational and Social Activities
- Community Centers: Participate in activities and events at local community centers to build a sober social network and foster connections with others in recovery.
- Fitness Programs: Join fitness programs and sports leagues to promote physical health while meeting new people in a positive environment.
8. Legal and Financial Assistance
- Legal Aid Services: Access legal aid services for any legal issues during recovery, ensuring that obstacles do not derail progress.
- Financial Counseling: Seek financial counseling to manage money effectively and alleviate stress related to economic issues.
9. Volunteer Opportunities
- Community Service: Volunteer work can help build a sense of purpose and connection to the community, reinforcing the value of contributing positively to society.
- Peer Support Programs: Participate in peer support programs to help others in recovery. These programs can also reinforce your own commitment to sobriety.
10. Faith-Based Support
- Religious Groups: Connect with faith-based organizations that offer support groups and counseling for individuals in recovery, providing spiritual guidance and fellowship.
- Spiritual Counseling: Utilize spiritual counseling services to explore personal beliefs and find inner strength during challenging times.
Example of Community Resource Strategies in a Relapse Prevention Plan
- Support Groups and Meetings: For additional support, attend AA meetings 3 times a week and SMART Recovery meetings once a week.
- Professional Counseling and Therapy: Schedule weekly sessions with a substance abuse counselor and attend group therapy at the local community health center.
- Healthcare Services: To monitor overall well-being, have regular check-ups with a primary care provider and monthly visits with a mental health professional.
- Educational Programs: Enroll in a life skills workshop offered by a community organization and participate in online relapse prevention webinars.
- Employment and Vocational Support: Engage in a job training program to develop new skills and utilize employment services to find job opportunities.
- Housing and Shelter Services: Move into a sober living home for a structured, supportive environment during early recovery.
- Recreational and Social Activities: To build a sober social network, join a local fitness program and participate in community center events.
- Legal and Financial Assistance: Access legal aid services for legal issues and seek financial counseling to manage money effectively.
- Volunteer Opportunities: Volunteer at a local charity once a week to build a sense of purpose and connection to the community.
- Faith-Based Support: Connect with a faith-based organization that offers support groups and attends weekly spiritual counseling sessions.
By incorporating these community resource strategies into a relapse prevention plan, individuals can leverage the support and services available in their communities. This proactive approach helps maintain sobriety and fosters a healthier, more fulfilling life. Together, these resources can create a safety net that enhances recovery and supports long-term well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some common questions:
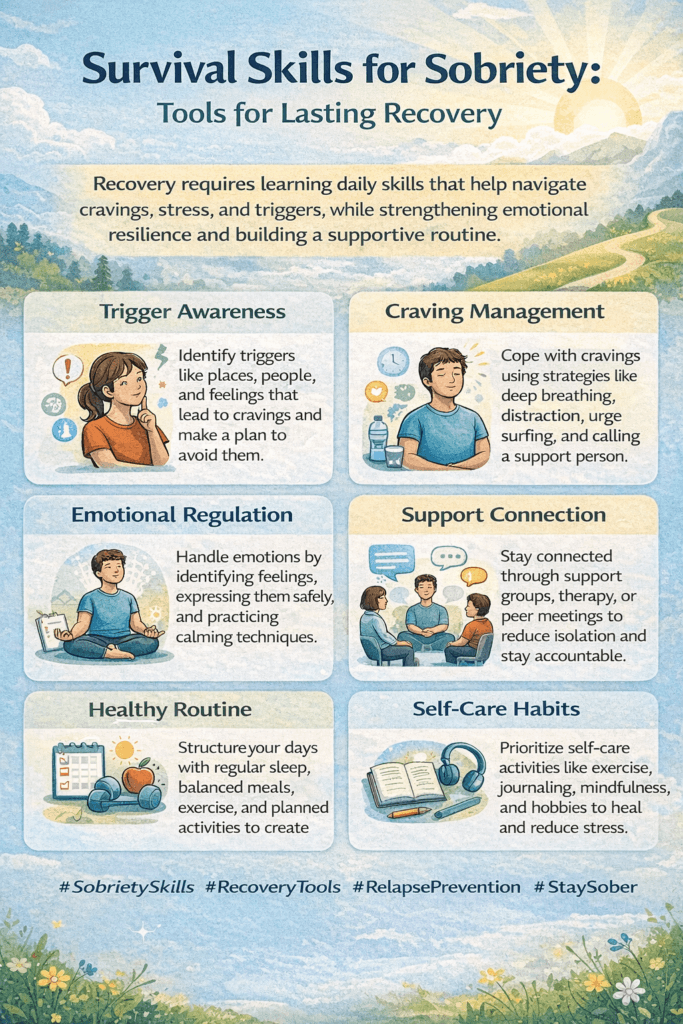
1. What are survival skills in sobriety?
They are practical coping tools that help manage cravings, emotions, triggers, and stress without returning to substance use.
2. Why are survival skills important in early recovery?
In early sobriety, the brain and body are adjusting. Without healthy coping tools, relapse risk is higher. Survival skills fill that gap.
3. What is trigger awareness?
Trigger awareness means recognizing people, places, emotions, or situations that spark cravings so you can plan ahead and stay safe.
4. How can I handle cravings when they hit suddenly?
Use deep breathing, delay and distract techniques, urge surfing, or contact a support person until the craving passes.
5. Why is emotional regulation important in sobriety?
Many people used substances to escape emotions. Learning to identify and manage feelings prevents emotional overload and relapse.
6. How does daily structure support recovery?
Routines reduce boredom, chaos, and stress — common relapse triggers — and help rebuild stability in daily life.
7. Why is social support considered a survival skill?
Connection reduces isolation, increases accountability, and provides encouragement during difficult moments.
8. What role does self-care play in sobriety?
Exercise, sleep, nutrition, mindfulness, and hobbies strengthen physical and mental health, reducing the likelihood of relapse.
9. How do boundaries protect sobriety?
Setting boundaries prevents exposure to high-risk people or environments and protects emotional well-being.
10. Can survival skills prevent relapse completely?
No skill guarantees perfect protection, but consistent practice greatly reduces the risk of relapse and strengthens long-term recovery.
Conclusion
A combination of survival skills and a detailed relapse prevention plan fortifies the journey to sustained sobriety. Individuals can better navigate recovery challenges by understanding triggers and developing healthy coping mechanisms. Creating a personalized relapse prevention plan offers a clear roadmap for maintaining sobriety, while family support provides crucial emotional and practical assistance. Additionally, leveraging community resources, such as support groups and counseling services, can bolster recovery efforts. Together, these strategies create a robust support system that empowers individuals to achieve and maintain a fulfilling, sober life.
Video: The Craving Defense Kit Nobody Talks About #sobriety #recovery #lifechanging