Navigating the terrain of recovery from addiction involves a multifaceted journey guided by principles that extend beyond the conventional therapeutic approaches. The 12 spiritual principles of recovery serve as a compass for individuals seeking healing, emphasizing faith, courage, and service. While these principles offer advantages such as fostering personal growth and community support, ethical dilemmas concerning inclusivity and cultural sensitivity may arise. Self-management strategies aligned with these principles empower individuals on their journey, emphasizing hope and perseverance. Additionally, family support strategies play a pivotal role in fostering a nurturing environment aligned with spiritual principles. In this exploration, we delve into the nuances of the 12 spiritual principles, examining their benefits, ethical considerations, and practical strategies for self-management and family support, acknowledging the diverse terrain of recovery.
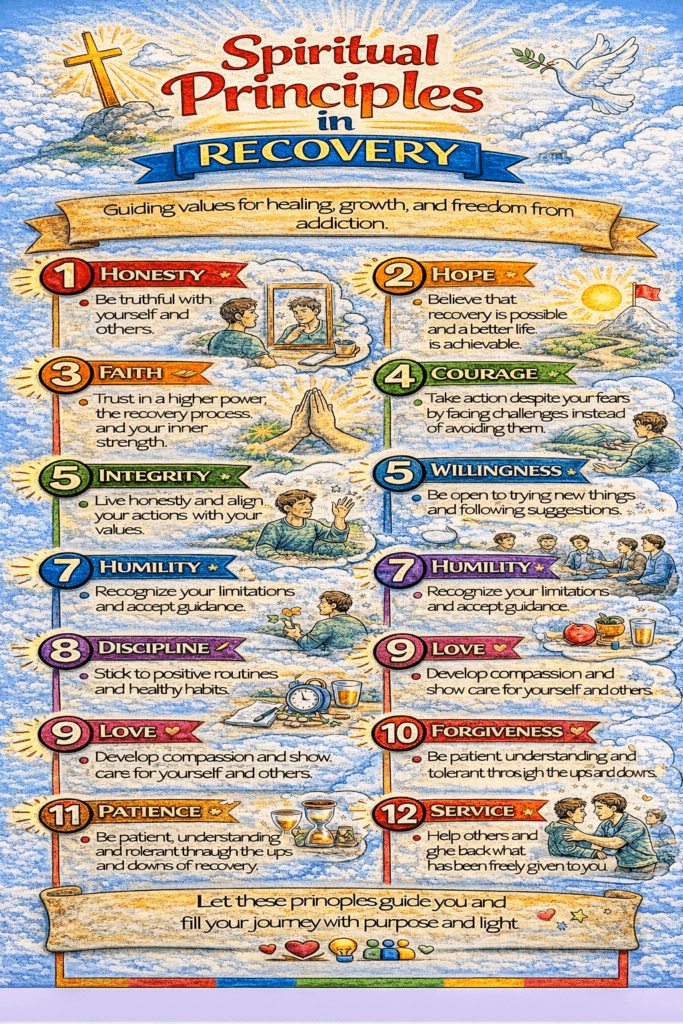
The 12 Spiritual Principles of Recovery: A Path to Healing and Transformation
The 12 spiritual principles of recovery form the core foundation of many 12-step programs and serve as guiding tenets for individuals seeking freedom from addiction. These principles provide a spiritual framework that encourages personal growth, self-discovery, and connection to something greater than oneself, whether that be a higher power, community, or an individual’s internal sense of purpose. Though not tied to religious doctrine, they offer a pathway toward healing and transformation.
1. Hope:
Recovery begins with the belief that change is possible. Hope is the light that keeps individuals moving forward, especially in the darkest times. It inspires belief in recovery and the potential for a better future, no matter how long the road to healing may seem.
2. Faith:
Faith is often centered around trust—whether in a higher power, the collective strength of a recovery group, or one’s inner capacity for change. This trust forms the foundation for letting go of control and embracing the recovery journey with openness.
3. Surrender:
Acknowledging powerlessness over addiction is a fundamental step toward recovery. Surrendering doesn’t mean giving up; it means accepting that some things are beyond control and seeking guidance and support from a higher power, whatever that may be for the individual.
4. Courage:
Recovery requires immense courage to face fears, confront past mistakes, and deal with the emotional and psychological wounds that fuel addiction. It takes bravery to step into the unknown and embrace the challenges that come with breaking free from the cycle of addiction.
5. Integrity:
Living with integrity means aligning one’s actions with moral values and principles. In recovery, it involves cultivating honesty in relationships and being accountable for one’s choices, creating a foundation of trustworthiness and reliability.
6. Willingness:
Being open-minded and willing to embrace new perspectives, experiences, and approaches to recovery is crucial. Willingness signals readiness for change and the ability to step outside one’s comfort zone to seek growth.
7. Humility:
Recovery teaches individuals the importance of humility—recognizing their limitations and embracing the wisdom and experiences of others. Humility encourages a mindset of continual learning and openness to growth.
8. Self-Discipline:
Self-discipline is about developing the strength to resist urges and control one’s thoughts and actions. It plays a vital role in managing triggers, avoiding relapse, and fostering a balanced, healthier lifestyle.
9. Love:
Recovery fosters love and compassion—both for oneself and for others. Building positive relationships based on love, kindness, and mutual support creates a nourishing environment for healing and personal growth.
10. Perseverance:
The journey to recovery is rarely linear. Perseverance is essential in helping individuals navigate setbacks, challenges, and moments of self-doubt. Even when difficult, staying committed to the process is critical to lasting recovery.
11. Spiritual Awareness:
Spiritual awareness involves recognizing the deeper meaning of life and developing a connection to something more significant than the self. This could be a higher power, the universe, or a broader sense of purpose and interconnectedness.
12. Service:
One of the most potent aspects of recovery is giving back to others. Engaging in acts of service and helping others on their recovery journey reinforces a sense of community, purpose, and shared growth. Service allows individuals to contribute to something greater while reinforcing their healing.
The 12 spiritual principles of recovery serve as a holistic framework for individuals seeking to overcome addiction. By embracing hope, faith, surrender, courage, and other principles, individuals can transform their lives, develop a spiritual awareness, and build a foundation for lasting recovery. These principles encourage self-reflection, community, and a deep connection to personal and spiritual growth, vital to overcoming addiction and living meaningfully. Whether interpreted through a religious or secular lens, these spiritual principles guide healing, self-discovery, and personal transformation.
The Advantages of the 12 Spiritual Principles in Addiction Recovery
The 12 spiritual principles of recovery offer invaluable advantages to individuals seeking to overcome addiction. These principles, often associated with 12-step recovery programs, provide a holistic approach that addresses various dimensions of well-being, from the physical to the spiritual. By integrating these principles into their recovery journey, individuals can experience transformative growth and long-lasting change.
1. Holistic Well-Being
The 12 spiritual principles encourage a holistic approach to recovery, recognizing that addiction affects not only the body but also the mind, emotions, and spirit. Individuals cultivate a more balanced and healthy life by focusing on spiritual, mental, emotional, and physical well-being. This holistic focus helps them heal from the inside out, addressing the root causes of addiction, not just the symptoms.
2. Personal Growth
Embracing these spiritual principles fosters personal growth and self-awareness. As individuals reflect on their actions, beliefs, and values, they better understand themselves and their purpose in life. This growth is not just about quitting substances; it’s about evolving into a better version of oneself, one that is capable of navigating life’s challenges without turning to addiction.
3. Supportive Community
The principles often serve as the foundation for supportive communities, such as 12-step programs. Within these communities, individuals find solidarity and encouragement by sharing experiences with others who understand the challenges of addiction. The sense of belonging and mutual support is a powerful motivator for sustained recovery.
4. Resilience
Recovery is rarely a straightforward process, and setbacks can occur. However, spiritual principles promote resilience by helping individuals recover from these challenges. By instilling hope, faith, and perseverance, the principles provide a framework for individuals to continue moving forward, even after moments of difficulty.
5. Guidance and Direction
The 12 spiritual principles offer a moral and spiritual compass, guiding individuals through the complex recovery journey. These principles provide clarity and direction, helping individuals make decisions that align with their values and long-term recovery goals.
6. Increased Self-Esteem
Living aligned with spiritual principles fosters integrity and self-discipline, increasing self-esteem. As individuals make positive choices and stay committed to their recovery, they develop a stronger sense of self-worth and confidence in their ability to maintain a healthy lifestyle.
7. Emotional Healing
Addiction often stems from unresolved emotional pain, and the principles encourage individuals to confront and heal from these wounds. By fostering self-awareness, honesty, and emotional vulnerability, the spiritual tenets facilitate emotional healing, helping individuals address the root causes of their addiction.
8. Positive Relationships
One of the most powerful aspects of the spiritual principles is their emphasis on love, humility, and service to others. By practicing these values, individuals learn to build and nurture positive relationships within the recovery community and in their personal lives. Healthy relationships are a cornerstone of long-term recovery, providing support and accountability.
9. Life Meaning and Purpose
Addiction often leaves individuals feeling lost and disconnected from a sense of purpose. The spiritual principles help individuals find deeper meaning in life beyond their addiction, contributing to a sense of fulfillment and purpose beyond mere sobriety.
10. Coping Mechanisms
Instead of relying on substances to cope with stress or emotional pain, individuals in recovery learn healthier coping mechanisms through spiritual principles. Practices such as mindfulness, meditation, and participation in a supportive community become vital tools for managing life’s challenges.
11. Sense of Connection
The principles foster a sense of connection to something greater than oneself, whether it be a higher power, a supportive community, or a shared purpose. This connection gives individuals strength, comfort, and a sense of belonging during their recovery journey.
12. Sustained Recovery
The most significant advantage of integrating these spiritual principles is their contribution to sustained recovery. By addressing the spiritual, emotional, and social aspects of addiction, the principles offer a comprehensive framework for long-term healing, helping individuals avoid relapse and maintain a healthier lifestyle.
The 12 spiritual principles of recovery provide a multidimensional approach to overcoming addiction. By fostering personal growth, emotional healing, and a sense of community, these principles help individuals navigate the complex challenges of recovery with resilience and purpose. Ultimately, they offer a path toward sobriety and a more meaningful and fulfilling life, contributing to a more sustained recovery.
Challenges of the 12 Spiritual Principles in Addiction Recovery
While the 12 spiritual principles of recovery have proven beneficial for many individuals seeking to overcome addiction, it’s essential to recognize that they may not be suitable for everyone. Here, we explore potential disadvantages of these principles, highlighting the need for a more inclusive approach to recovery.
1. Religious and Cultural Variability
One significant disadvantage is that the principles may be deeply rooted in spiritual concepts that align with specific religious or cultural beliefs. Individuals from diverse backgrounds may find it challenging to connect with these ideas, leading to feelings of exclusion or discomfort. A more universal approach to recovery is necessary to ensure that everyone feels included and supported.
2. Lack of Universality
The spiritual principles may not be universally applicable. Individuals with different belief systems, particularly those who identify as atheists or agnostics, might struggle to relate to the spiritual aspects of these principles. This disconnect can create barriers to engagement and commitment to recovery programs that emphasize spirituality.
3. Incompatibility with Secular Approaches
Some individuals may prefer or benefit more from secular approaches to recovery. The spiritual nature of the 12 principles might not align with their philosophies, potentially hindering their progress. Recovery programs should offer a range of options that cater to spiritual and secular preferences to support diverse needs.
4. Potential for Guilt and Shame
The emphasis on moral principles and self-discipline may inadvertently lead to feelings of guilt or shame if individuals perceive themselves as failing to align with these values. This pressure can be counterproductive, causing individuals to internalize negative feelings rather than focusing on growth and healing.
5. Resistance to Surrender
Surrendering to a higher power can be particularly challenging for individuals who resist relinquishing control over their lives or those with differing views on personal empowerment. This resistance may create additional stress or conflict during the recovery process, making it essential to consider individuals’ beliefs about personal agency.
6. Reliance on External Guidance
Some individuals may feel uncomfortable relying on external sources, such as a higher power, for guidance in their recovery journey. This reliance can detract from their sense of autonomy and empowerment, potentially leading them to prefer more self-directed approaches to healing.
7. Stigmatization of Non-Believers
Within specific recovery communities that strongly emphasize spiritual principles, individuals who do not embrace these aspects may feel stigmatized or excluded. This marginalization can create barriers to support and connection, making it difficult for non-believers to fully engage in the recovery process.
8. Interpretation Variability
The spiritual principles can be open to interpretation, leading to variability in understanding and implementation. This inconsistency can cause confusion or conflict within recovery groups, emphasizing the need for clear communication and shared understanding among participants.
9. Overemphasis on Personal Responsibility
While personal responsibility is a crucial aspect of recovery, overemphasizing it may inadvertently lead to self-blame or judgment. This mindset can hinder individuals’ ability to cope with setbacks and discourage them from seeking support when needed.
10. Limited Cultural Sensitivity
The principles may lack cultural sensitivity, potentially overlooking the diverse backgrounds and cultural beliefs of individuals seeking recovery. A more inclusive framework that respects and incorporates cultural differences can enhance the effectiveness of recovery programs.
11. Dependency on Group Dynamics
Some individuals may feel pressured to conform to group dynamics within recovery communities, leading to a lack of authenticity in their journey. Encouraging individuality and personal exploration can help create a more supportive environment.
12. Challenges for Non-Theistic Individuals
For those who do not adhere to theistic beliefs, the spiritual nature of the principles may present unique challenges and hinder their engagement in specific recovery programs. Tailoring recovery options to accommodate non-theistic individuals can promote inclusivity and support.
Recognizing the potential disadvantages of the 12 spiritual principles in addiction recovery is crucial to fostering an inclusive, practical approach to healing. Every individual has unique needs, beliefs, and preferences that must be considered in their recovery journey. By embracing a more tailored approach, we can better support a diverse range of individuals in their quest for well-being, ultimately leading to more successful and sustainable recovery outcomes.
Navigating Ethical Dilemmas in the Application of the 12 Spiritual Principles of Recovery
The application of the 12 spiritual principles of recovery offers significant benefits for many individuals seeking to overcome addiction. However, it also raises various ethical dilemmas that require careful consideration. It’s vital to ensure that all individuals are treated with respect and that their diverse beliefs are acknowledged throughout recovery. Here are some critical ethical dilemmas to consider:
1. Cultural Sensitivity
Dilemma: Cultural sensitivity is paramount when applying spiritual principles rooted in specific cultural or religious contexts. Ethical considerations arise when individuals from diverse backgrounds encounter practices that conflict with their beliefs, potentially leading to feelings of exclusion or discomfort.
2. Inclusivity for Non-Believers
Dilemma: Creating an inclusive environment for individuals who do not identify with spiritual or religious beliefs can be challenging. Ethical dilemmas may surface when recovery programs inadvertently exclude or marginalize non-believers, undermining their recovery experience.
3. Respecting Individual Autonomy
Dilemma: Balancing the encouragement of spiritual principles with respect for individual autonomy is essential. Ethical concerns emerge when individuals feel pressured to conform to specific spiritual practices that conflict with their personal beliefs, potentially impacting their commitment to recovery.
4. Avoiding Proselytization
Dilemma: There is a fine line between providing spiritual guidance and proselytizing. Ethical challenges can arise when recovery programs unintentionally promote a specific religious agenda, infringing on an individual’s right to choose their own beliefs.
5. Consent and Informed Decision-Making
Dilemma: Ensuring informed consent regarding the spiritual nature of recovery programs is crucial. Ethical dilemmas occur when individuals are not adequately informed about the spiritual aspects of programs and may feel pressured to conform without fully understanding the implications.
6. Addressing Diversity in Group Settings
Dilemma: In group settings, discussions about spiritual matters can create discomfort or conflict. Ethical considerations involve managing these conversations respectfully to honor the diverse beliefs of all participants and foster a supportive environment.
7. Navigating Conflicts of Belief Systems
Dilemma: Conflicts between individuals with differing belief systems within recovery groups can lead to ethical challenges. Ensuring a respectful and inclusive environment becomes vital in managing these conflicts and promoting understanding.
8. Avoiding Stigmatization
Dilemma: Spiritual principles should not contribute to stigmatizing individuals who do not embrace such beliefs. Ethical considerations arise when judgment or bias is directed toward those who approach recovery from a secular perspective, potentially hindering their participation.
9. Ensuring Non-Discrimination
Dilemma: Recovery programs must ensure non-discrimination on the basis of religious or spiritual beliefs. Ethical dilemmas arise when individuals feel excluded or judged for their beliefs, which can significantly impact their recovery journey.
10. Balancing Spirituality and Professionalism
Dilemma: Professionals in recovery settings must balance the incorporation of spiritual principles and professionalism. Ethical concerns arise when personal beliefs unduly influence the therapeutic relationship, potentially affecting treatment effectiveness.
11. Accounting for Individual Trauma
Dilemma: Some individuals may have experienced trauma related to religious or spiritual contexts. Ethical challenges involve recognizing and addressing these traumas to provide a safe and supportive recovery environment free from triggers.
12. Ensuring Equal Access
Dilemma: Recovery programs must ensure equal access to support regardless of an individual’s beliefs. Ethical considerations arise when individuals feel marginalized or face barriers due to their spiritual or non-spiritual stance, limiting their opportunities for recovery.
Addressing these ethical dilemmas requires ongoing awareness, cultural competence, and a commitment to creating inclusive and respectful recovery environments. By honoring the diverse beliefs and experiences of individuals seeking support, we can foster a recovery process that is effective and ethically sound, providing a holistic path toward healing and well-being for everyone involved.
Empowering Recovery: Self-Management Strategies Aligned with the 12 Spiritual Principles
Self-management strategies aligned with the 12 spiritual principles of recovery can significantly empower individuals on their journey toward healing and well-being. By integrating these strategies into daily life, individuals can foster personal growth, resilience, and a greater sense of control over their recovery process. Here are self-management strategies corresponding to each spiritual principle:
1. Hope
Strategy: Cultivate hope by regularly reflecting on positive changes, past achievements, and growth potential. Focus on the possibilities that arise from a commitment to recovery, using visualizations or journaling to reinforce your optimism.
2. Faith
Strategy: Develop faith by exploring and deepening your personal spiritual beliefs. Engage in practices that resonate with your understanding of a higher power, including prayer, meditation, or reading spiritual texts, to foster a sense of connection and trust.
3. Surrender
Strategy: Practice surrender by letting go of the need for control over every aspect of your life. Embrace surrender as a willingness to accept support and guidance from a higher power or a supportive community, recognizing that seeking help is a strength, not a weakness.
4. Courage
Strategy: Cultivate courage by facing challenges head-on. Break larger recovery goals into smaller, manageable steps, and celebrate the courage it takes to confront and overcome obstacles. Journaling about your fears and successes can help build confidence.
5. Integrity
Strategy: Strengthen integrity by aligning your actions with your values. Regularly assess your behavior and make amends when necessary. Consider keeping a personal code of ethics to guide your decisions and strive to live in unity with your moral principles.
6. Willingness
Strategy: Foster willingness by maintaining an open mind. Be willing to explore new perspectives and try different approaches to recovery. Embrace change as essential to personal growth, perhaps by joining workshops or support groups that introduce novel ideas.
7. Humility
Strategy: Practice humility by acknowledging your limitations and being open to learning from others. Cultivate a continuous improvement mindset by seeking feedback from peers or mentors and valuing the experiences and wisdom shared by those around you.
8. Self-Discipline
Strategy: Develop self-discipline by establishing healthy routines and habits. Set clear, achievable goals, create a structured daily routine, and exercise self-control in your decision-making to support your recovery journey. Consider using a planner or app to track your progress.
9. Love
Strategy: Embrace love as a guiding principle by fostering positive relationships. Practice self-love and compassion, recognizing your worth, and extending these qualities to others in your support network. Engage in acts of kindness towards yourself and those around you.
10. Perseverance
Strategy: Cultivate perseverance by maintaining a steadfast commitment to your recovery goals. Focus on your progress, even in the face of setbacks. Use challenges as opportunities for growth, perhaps by reflecting on what each challenge teaches you.
11. Spiritual Awareness
Strategy: Deepen spiritual awareness by incorporating mindfulness and contemplative practices into your daily routine. Explore different spiritual traditions and practices that resonate with you, such as yoga, meditation, or nature walks, to foster a sense of connection with the world around you.
12. Service
Strategy: Engage in service by actively participating in activities that support others in their recovery. Volunteer your time, share your experiences, and contribute to the well-being of your recovery community. Acts of service can enhance your sense of purpose and belonging.
These self-management strategies, aligned with the 12 spiritual principles, emphasize personal agency, growth, and a holistic approach to recovery. By implementing these strategies, individuals can empower themselves to actively engage in their recovery journey, fostering a sense of control and well-being. Additionally, seeking guidance from spiritual mentors, therapists, or support groups can complement these self-management efforts, creating a supportive network that enhances the recovery experience. Embrace your journey with hope, faith, and resilience, knowing each step forward is a testament to your strength and commitment to healing.
Strengthening Recovery: Family Support Strategies Aligned with the 12 Spiritual Principles
Family support is crucial in the recovery journey, providing emotional stability and encouragement. By aligning family support strategies with the 12 spiritual principles, families can create a nurturing environment that enhances the recovery experience. Here are strategies corresponding to each principle to strengthen family support:
1. Hope
Strategy: Foster hope within the family by emphasizing the positive aspects of the individual’s recovery journey. Share stories of progress and celebrate even small achievements to instill a sense of hope. Creating a family “progress board” can visually track achievements and serve as a constant reminder of growth.
2. Faith
Strategy: Respect and support the individual’s spiritual beliefs. Engage in open and non-judgmental conversations about faith, allowing each family member to express their beliefs while promoting unity. Consider family discussions around different spiritual practices or traditions that resonate with everyone.
3. Surrender
Strategy: Encourage an atmosphere of surrender within the family by promoting acceptance of things beyond control. Let go of expectations and focus on supporting each other without trying to control the individual’s recovery process. Practicing mindfulness together can help family members cultivate this sense of surrender.
4. Courage
Strategy: Support family members in cultivating courage by acknowledging and addressing challenges openly. Encourage open communication about fears and concerns to foster an environment where everyone feels safe expressing their feelings. Family meetings can provide a structured space for these discussions.
5. Integrity
Strategy: Strengthen family integrity by aligning actions with shared values. Promote honesty and accountability within the family to create an environment where everyone feels comfortable expressing themselves authentically. Establishing family agreements can help reinforce this integrity.
6. Willingness
Strategy: Foster willingness within the family by remaining open to learning and adapting. Encourage family members to be willing to explore new ways to support the individual’s recovery and to adjust approaches as needed. Family workshops or participation in support groups can facilitate this openness.
7. Humility
Strategy: Practice humility within the family by recognizing that everyone is on their unique journey. Cultivate a non-judgmental attitude and value each family member’s perspective to foster a humble, supportive environment. Sharing personal stories of growth and struggles can help build mutual understanding.
8. Self-Discipline
Strategy: Support self-discipline within the family by establishing healthy routines together. Encourage shared goals, such as maintaining a supportive home environment, and reinforce the importance of self-control. Creating family rituals, like regular family dinners, can help foster discipline.
9. Love
Strategy: Embrace love as a guiding principle within the family. Demonstrate unconditional love and support for the individual in recovery, fostering a nurturing environment that encourages personal growth. Simple acts of kindness and words of affirmation can significantly impact the individual’s morale.
10. Perseverance
Strategy: Cultivate perseverance as a family by facing challenges together. Reinforce the importance of staying committed to the recovery journey, emphasizing collective perseverance in the face of setbacks. Create a family mantra or mission statement that emphasizes resilience and togetherness.
11. Spiritual Awareness
Strategy: Encourage spiritual awareness within the family by exploring shared spiritual practices or traditions. Create a space where each family member can express their spiritual beliefs and experiences, promoting a sense of connection. Regular family reflections or gratitude sessions can enhance this awareness.
12. Service
Strategy: Engage in acts of service as a family by supporting each other and contributing to the community’s well-being. Encourage family members to actively participate in activities that promote the greater good, such as volunteering or community service projects, reinforcing the spirit of unity and purpose.
Implementing these family support strategies aligned with the 12 spiritual principles emphasizes unity, love, and a shared commitment to recovery within the family unit. These strategies can foster a supportive and nurturing environment that enhances the individual’s recovery journey. Additionally, seeking guidance from family therapists or support groups can provide resources and insights to ensure adequate family support. By working together, families can play a pivotal role in their loved one’s healing process, helping to create a lasting foundation for recovery.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some common questions:
1. What are spiritual principles in addiction recovery?
Spiritual principles are guiding values that support healing and personal growth. Common principles include honesty, hope, faith, courage, humility, patience, gratitude, forgiveness, and service. They help individuals rebuild meaning and purpose beyond addiction.
2. Are spiritual principles religious?
Not necessarily. Spirituality in recovery can be religious, but it can also be secular. It simply refers to connecting with something greater than oneself—such as purpose, inner values, community, or personal meaning.
3. Why are spiritual principles important in recovery?
Addiction often disconnects individuals from meaning, relationships, and self-worth. Spiritual principles restore connection, guide decision-making, and help individuals cope with stress, guilt, and cravings.
4. Do I need to believe in God to use spiritual principles?
No. Many recovery programs encourage defining a “higher power” personally. This can be nature, humanity, inner wisdom, or shared group support. The focus is on openness, not specific beliefs.
5. How do spiritual principles help prevent relapse?
They encourage self-reflection, accountability, emotional regulation, and connection to supportive communities—all of which reduce the risk of relapse.
6. What does practicing honesty mean in recovery?
It means being truthful with yourself and others about struggles, cravings, and mistakes. Honesty breaks denial and builds trust in therapy and relationships.
7. How does gratitude support recovery?
Gratitude shifts focus from loss to progress. It improves mood, reduces stress, and strengthens motivation to stay sober.
8. What role does humility play?
Humility allows individuals to accept help, admit limitations, and remain open to learning—essential steps in long-term healing.
9. How is forgiveness part of recovery?
Forgiveness—of self and others—reduces shame and resentment, emotions that often fuel substance use.
10. What does “surrender” mean spiritually in recovery?
Surrender means letting go of the belief that you must control everything on your own and becoming open to support, guidance, and growth.
11. How can I practice spiritual principles daily?
Examples include:
- Daily reflection or meditation
- Journaling gratitude
- Helping others
- Attending support groups
- Practicing patience in stressful moments
12. Can spiritual growth happen without therapy?
Spiritual principles are most effective when combined with evidence-based treatment, counseling, or peer recovery support.
13. What if I feel disconnected from spirituality?
That’s common. Spiritual connection often develops gradually through mindfulness, service, nature, or supportive relationships.
14. How do spiritual principles improve mental health?
They promote hope, emotional balance, self-compassion, and resilience—factors linked to improved mental health outcomes.
15. What is the biggest benefit of spiritual principles in recovery?
They help individuals move from surviving to meaningful living, replacing addiction with purpose, connection, and inner peace.
Conclusion
The 12 spiritual principles of recovery stand as pillars of strength for individuals on the path to healing from addiction. Their advantages, from promoting personal growth to fostering a supportive community, cannot be understated. However, a nuanced understanding demands consideration of potential disadvantages and ethical dilemmas, particularly surrounding cultural sensitivity and inclusivity. Striking a balance between self-management and adherence to these principles empowers individuals to navigate their recovery journey with resilience and hope. Family support strategies aligned with these principles create a cohesive and nurturing environment, emphasizing love and shared commitment. While recognizing the challenges, the holistic approach offered by the 12 spiritual principles continues to play a significant role in guiding individuals toward sustained recovery and a renewed sense of purpose.