Perfectionism, when we aim for perfect standards and fear making mistakes, can lead to challenges, including a higher risk of addiction. In this introduction, we’ll explore how perfectionism connects to addiction, looking at the difficulties it brings. We’ll discover ways to manage it personally, see how family support is crucial, and check out community resources that help prevent addiction. By understanding how perfectionism affects us, we can create supportive environments that focus on well-being and provide strong support for ongoing recovery.
The Hidden Link Between Perfectionism and Addiction: Understanding the Risk Factors
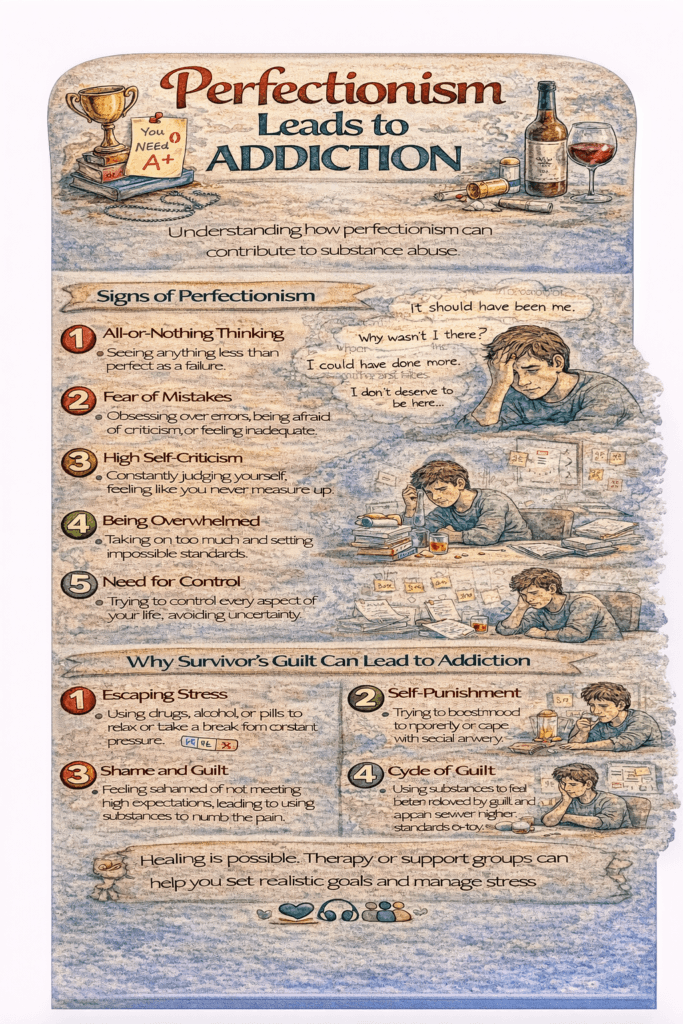
Perfectionism, defined by an unyielding drive for flawlessness and excessively high self-imposed standards, may seem like a trait that fosters success. However, it often carries significant emotional challenges that can contribute to the development of addiction. Recognizing the ways perfectionism can lead to harmful behaviors is vital for prevention and recovery.
How Perfectionism Contributes to Addiction
- Escapism from Pressure
The relentless pressure to meet unrealistic standards can overwhelm perfectionists. This stress may drive them to seek solace in substances or behaviors that temporarily numb the burden of their pursuit. - Self-Medication for Anxiety
Perfectionists often grapple with anxiety and a fear of failure. Substances such as alcohol or drugs may provide a temporary escape from the self-critical thoughts that accompany their perfectionism. - Coping Mechanism
Addiction can serve as a way to cope with the chronic sense of inadequacy that perfectionists feel when they perceive they haven’t met their goals. The temporary relief offered by addictive behaviors may create a cycle of dependency. - Impaired Stress Coping
When perfectionists encounter setbacks, their inability to manage stress constructively may lead them to substances or addictive behaviors as a maladaptive way to cope. - Social Isolation
Fear of judgment and unmet social expectations can lead to social withdrawal. This isolation increases vulnerability to addiction as individuals may turn to substances for comfort. - Risky Behaviors to Sustain Perfection
To maintain their perceived standards of excellence, perfectionists might engage in unhealthy or extreme behaviors, such as overworking or substance use, to sustain their performance. - Negative Self-Talk
The constant self-criticism and harsh inner dialogue of perfectionists take a heavy emotional toll. This negativity can push them toward substances or addictive behaviors to escape feelings of unworthiness. - Impaired Decision-Making
The all-consuming focus on achieving perfection can cloud judgment, leading to impulsive and risky choices, including engaging in addictive behaviors without fully considering the consequences.
Breaking the Cycle: Prevention and Intervention
Understanding the connection between perfectionism and addiction is critical for creating effective support strategies:
- Address Root Causes: Therapy and counseling can help individuals uncover and challenge the beliefs driving their perfectionism.
- Develop Healthy Coping Mechanisms: Teaching stress management techniques, such as mindfulness and relaxation exercises, can reduce reliance on addictive behaviors.
- Foster Self-Compassion: Encouraging self-compassion helps individuals accept their imperfections and view setbacks as part of the human experience.
- Strengthen Social Support: Building strong, nonjudgmental relationships provides a buffer against isolation and reinforces healthy choices.
Perfectionism does not have to lead to addiction. By recognizing its risks and implementing healthier ways to manage its challenges, individuals can pursue personal growth without sacrificing their well-being.
Managing Perfectionism: Strategies to Prevent Addiction
Perfectionism, while often admired for its association with high achievement, can lead to significant stress and anxiety. If left unchecked, this pursuit of flawlessness may increase vulnerability to addiction as individuals seek relief from the emotional toll. Adopting healthier self-management strategies can help mitigate these risks and promote a more balanced life.
Practical Approaches to Manage Perfectionism
- Set Realistic Goals
Break large tasks into smaller, achievable steps. Realistic goal-setting helps reduce the overwhelming pressure of striving for perfection and encourages progress over perfection. - Practice Self-Compassion
Treat yourself with kindness and understanding. Recognize that mistakes and imperfections are part of the human experience, and offer yourself the grace you would extend to others. - Challenge Negative Thoughts
Reframe self-critical and perfectionistic thoughts. Replace irrational beliefs with balanced perspectives that acknowledge effort and progress over unattainable standards. - Embrace Mistakes as Learning Opportunities
Shift your mindset to view mistakes as valuable lessons rather than failures. Understand that setbacks can foster growth and contribute to long-term success. - Establish Healthy Boundaries
Avoid overcommitting by setting clear boundaries. Prioritize tasks and learn to say “no” when necessary to protect your time and energy. - Prioritize Self-Care
Focus on physical and mental well-being through adequate sleep, regular exercise, and relaxation techniques. Self-care is essential for managing the stress often linked to perfectionism. - Celebrate Achievements
Take time to acknowledge and celebrate even small accomplishments. Shifting focus to what you’ve achieved rather than where you fall short can boost self-esteem and satisfaction. - Seek Support
Share your feelings and challenges with trusted friends, family, or a support network. Open communication can provide emotional relief and fresh perspectives on managing perfectionism. - Mindfulness and Meditation
Practice mindfulness to stay present and let go of excessive worry about past failures or future expectations. Meditation can help calm the mind and foster a sense of balance. - Professional Assistance
Engage with therapists or counselors specializing in perfectionism. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and other approaches can address perfectionistic tendencies and provide tailored strategies for managing them. - Develop Healthy Coping Mechanisms
Replace harmful habits with constructive outlets like hobbies, exercise, or creative pursuits. These activities offer positive ways to manage stress and channel energy.
Building Resilience and Balance
By implementing these strategies, individuals can manage perfectionism in healthier ways, reducing its emotional toll and preventing the risk of addiction. A balanced approach not only promotes well-being but also fosters resilience and the ability to enjoy life’s imperfections. Embrace progress over perfection, and let self-compassion guide your journey toward a healthier mindset.
The Role of Family Support in Managing Perfectionism and Preventing Addiction
Perfectionism can take a toll on individuals, leading to stress, anxiety, and even addiction as a coping mechanism. Family support plays a pivotal role in addressing these challenges, fostering a healthier mindset, and reducing the risk of maladaptive behaviors. By creating a nurturing environment, families can empower each other to embrace imperfection and prioritize well-being.
Family Support Strategies for Managing Perfectionism
- Open Communication
Cultivate an atmosphere of open and non-judgmental communication. Encourage family members to share their feelings, challenges, and experiences with perfectionism without fear of criticism or judgment. - Set Realistic Expectations
Help establish attainable expectations for each family member. Emphasize that perfection is unrealistic and that mistakes are a regular and valuable part of growth and learning. - Provide Emotional Support
Reinforce unconditional love and acceptance, regardless of achievements or perceived failures. Knowing they are valued for who they are, not just what they accomplish, can alleviate pressure on perfectionists. - Encourage Healthy Coping Mechanisms
Introduce positive outlets for stress, such as exercise, mindfulness, or creative hobbies. These activities can help family members develop constructive ways to manage anxiety and frustration. - Model Healthy Behavior
Demonstrate self-compassion and acceptance of imperfections in your own life. Children and other family members often mirror observed behaviors, making it essential to embody a balanced approach to success and setbacks. - Celebrate Effort, Not Just Results
Shift the focus from outcomes to effort. Acknowledge and celebrate the hard work and dedication that go into tasks, emphasizing that personal growth matters more than achieving perfection. - Seek Family Counseling
Engage in family therapy to address perfectionism together. A therapist can provide tools and techniques to navigate perfectionist tendencies and foster healthier relationships within the family. - Promote Individuality
Celebrate the unique strengths and qualities of each family member. Emphasize individuality and encourage members to appreciate their distinct attributes and talents. - Encourage Balanced Lifestyles
Advocate for a lifestyle that balances work, relaxation, and recreation. Avoid overburdening family members with expectations to excel in every domain of their lives. - Supportive Academic Environment
Work with educators to ensure a supportive school environment that values effort and resilience over unattainable standards. Encourage a growth mindset in academic settings. - Recognize Warning Signs
Stay alert for signs of stress or perfectionist tendencies in family members. Early recognition of warning signs allows families to intervene with additional support, such as professional counseling or therapy, when needed.
Building a Supportive Family Environment
By adopting these strategies, families can create a nurturing and empathetic space where individuals feel supported in managing perfectionism. This proactive approach helps reduce the risk of turning to addiction as a coping mechanism and promotes a healthier, more balanced outlook on life. Together, families can build resilience, foster self-acceptance, and embrace the beauty of imperfection.
Community Strategies for Managing Perfectionism and Preventing Addiction
Perfectionism, while often seen as a drive for excellence, can become a harmful mindset when it leads to chronic stress, anxiety, or maladaptive coping mechanisms such as addiction. Communities play a pivotal role in addressing perfectionism and promoting mental well-being by fostering healthy coping strategies and building resilience. Here are actionable strategies that communities can implement to address perfectionism and reduce the risk of addiction.
Community Strategies for Addressing Perfectionism
- Educational Workshops and Seminars
Host workshops and seminars to educate community members about the impact of perfectionism on mental health. These events can include expert speakers, interactive discussions, and practical exercises focused on stress management and self-compassion. - Support Groups
Create support groups where individuals dealing with perfectionism can connect with peers facing similar challenges. Sharing experiences in a safe and understanding environment can help participants feel less isolated and more empowered to manage their tendencies. - Accessible Mental Health Services
Ensure the availability of affordable and accessible mental health services—partner with local mental health professionals to provide counseling and therapy tailored to addressing perfectionistic behaviors. - Community Counseling Centers
Establish dedicated counseling centers that specialize in managing perfectionism. These centers can offer resources for individuals and families, providing tailored strategies to overcome perfectionistic tendencies. - Community Wellness Programs
Launch wellness programs that focus on holistic mental health. Include activities such as mindfulness sessions, stress reduction workshops, and self-compassion training to help community members adopt healthier mindsets. - Collaboration with Schools
Partner with local schools to integrate education on perfectionism into the curriculum. Provide workshops for students, parents, and educators on fostering resilience and understanding the dangers of unrealistic standards. - Recreation and Leisure Activities
Offer activities like art classes, sports, and nature outings to encourage relaxation and stress relief. These programs promote balance and creativity, countering the rigid thinking often associated with perfectionism. - Inclusive Community Events
Organize events celebrating diversity and individuality. Showcase stories of resilience and success that emphasize progress and effort over perfection, creating a culture that values unique strengths and contributions. - Crisis Intervention Services
Ensure that crisis intervention services are readily available for those experiencing acute stress or anxiety related to perfectionism. Helplines, drop-in centers, and crisis teams can provide immediate support. - Awareness Campaigns
Launch campaigns on social media, in local newspapers, and on community boards to educate the public about the impact of perfectionism. Share stories of recovery and resilience to inspire change and challenge societal expectations of flawlessness. - Collaboration with Employers
Work with local businesses to foster supportive workplace environments. Offer training on stress management, resilience, and work-life balance to help employees manage perfectionistic tendencies effectively.
Building a Resilient and Supportive Community
By implementing these strategies, communities can create a culture that values balance, well-being, and self-acceptance over perfection. Addressing perfectionism at the community level helps reduce the associated stress and prevents maladaptive coping mechanisms, including addiction. Together, communities can foster an environment that supports mental health and celebrates the beauty of imperfection.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some common questions:
Conclusion
The intricate link between perfectionism and the risk of addiction underscores the need for comprehensive strategies at various levels. Navigating the challenges of perfectionistic tendencies requires effective self-management, emphasizing resilience over unrealistic standards. Family support emerges as a cornerstone, fostering understanding and balance in the pursuit of excellence. Additionally, community resources play a vital role in preventing addiction, offering accessible tools, education, and a supportive environment. By integrating these strategies, we can collectively strive for a healthier approach to success, resilience, and well-being, ensuring a path toward sustained recovery that embraces progress over unattainable perfection.
Video: