Reducing overdose deaths in the US is a pressing public health issue amid the opioid epidemic. Government initiatives at the federal, state, and local levels, alongside community resources, family support strategies, and individual self-management techniques, aim to curb this crisis. Policies focus on enhancing monitoring programs, expanding naloxone distribution, and improving access to treatment. Community efforts include syringe exchange programs and education. Families provide crucial support through education and advocacy, while individuals benefit from strategies empowering them to manage health risks and seek treatment. Together, these efforts form a comprehensive approach to tackling overdose deaths and supporting affected communities.
Current Data on Overdose Deaths and the Opioid Epidemic
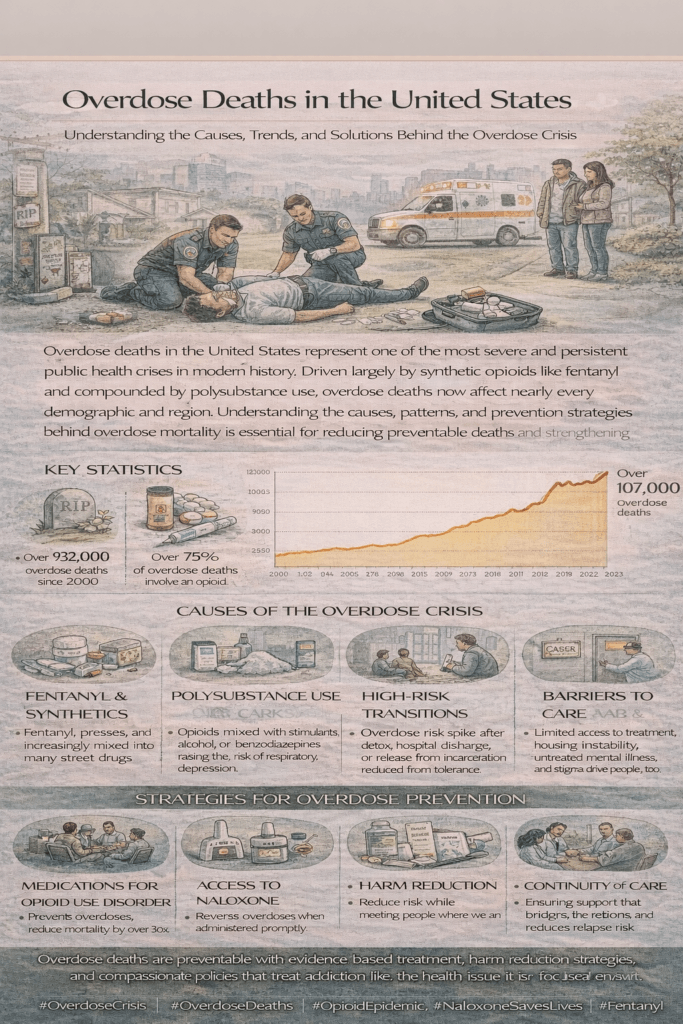
Overdose deaths in the United States remain a critical public health issue, with the opioid epidemic being a significant driver of these high rates. Here’s a snapshot of the most recent data and trends concerning overdose deaths:
Overall Trends: Recent data indicate a continued increase in overdose deaths, primarily driven by synthetic opioids such as fentanyl, alongside heroin and prescription opioids. This trend underscores the ongoing severity of the opioid crisis.
Specific Data: In 2022, approximately 107,941 drug overdose deaths were reported in the U.S., reflecting a significant rise from previous years. The COVID-19 pandemic has further exacerbated the crisis, impacting both access to addiction treatment services and increasing social stressors that contribute to substance use disorders.
Geographical Variances: The overdose crisis is not uniform across the country. Certain regions, particularly Appalachia and parts of the Midwest and Northeast, have experienced disproportionately high rates of overdose deaths. This geographic disparity highlights the need for targeted interventions and resources in these areas.
Efforts and Responses: In response to the crisis, several strategies have been implemented to mitigate the impact of overdose deaths:
- Increased Access to Naloxone: Efforts have been made to expand access to naloxone, a life-saving medication that can reverse opioid overdoses.
- Expansion of Treatment Options: There has been a push to broaden the availability of addiction treatment services, including medication-assisted treatment (MAT) and behavioral therapies.
- Harm Reduction Strategies: Programs such as syringe exchanges and supervised consumption sites are being utilized to reduce the risks associated with drug use and connect individuals with support services.
- Public Education Campaigns: Increased awareness and education efforts aim to inform the public about the dangers of drug use and the resources available for those seeking help.
Policy and Legislative Actions: At various levels of government, there are ongoing policy discussions and legislative actions designed to tackle the root causes of the epidemic and improve access to prevention and treatment services. These efforts include:
- Federal Initiatives: National strategies and funding programs to combat the opioid crisis.
- State-Level Policies: State governments implement regulations and support programs tailored to local needs.
- Local Actions: Communities are developing localized solutions to address specific challenges related to addiction and overdose.
The overdose crisis remains a pressing public health challenge, with data and responses continually evolving. Continued efforts to improve access to treatment, implement harm reduction strategies, and increase public education are vital to addressing this crisis and reducing its impact on communities across the U.S.
Federal Government Interventions in Addressing Overdose Deaths
The opioid crisis in the United States has prompted a range of federal government interventions aimed at reducing overdose deaths and mitigating the impact of opioid use disorder (OUD). Here’s a look at some key federal actions and strategies:
Expansion of Naloxone Access: Naloxone, a critical medication for reversing opioid overdoses, has seen expanded access through federal and state initiatives. Efforts include making naloxone available to first responders, community organizations, and individuals at risk of overdose. This widespread distribution aims to save lives and provide immediate intervention during an opioid overdose.
Increasing Access to Treatment: The federal government has focused on expanding access to evidence-based treatments for OUD. This includes promoting medication-assisted treatment (MAT) options such as buprenorphine, methadone, and naltrexone. Initiatives have been implemented to reduce barriers to MAT, including increasing the number of healthcare providers authorized to prescribe buprenorphine and improving access to treatment facilities.
Enhancing Prescription Drug Monitoring Programs (PDMPs): PDMPs are tools designed to monitor and track prescriptions for controlled substances, including opioids. The federal government has supported efforts to enhance these programs to prevent overprescribing, identify potential misuse or diversion, and improve prescribing practices among healthcare providers.
Supporting Harm Reduction Strategies: Federal support for harm reduction strategies includes funding syringe exchange programs and other initiatives to reduce the spread of infectious diseases among individuals who use drugs. These programs also offer support, resources, and connections to treatment services, playing a crucial role in the broader response to the opioid crisis.
Public Education and Awareness Campaigns: To address the opioid crisis, the federal government has launched public education campaigns. These campaigns focus on raising awareness about the risks of opioid use, promoting safe prescribing practices, and educating the public on recognizing the signs of opioid overdose and how to administer naloxone effectively.
Legislative and Policy Changes: Legislation has been enacted at the federal and state levels to address various aspects of the opioid crisis. These measures include improving oversight of opioid prescribing practices, increasing funding for addiction treatment and recovery services, and supporting research into alternative pain management approaches.
Interagency Collaboration: Federal agencies such as the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS), the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), and the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA) are working collaboratively to coordinate efforts and share data. This interagency approach ensures a cohesive strategy for combating opioid misuse and reducing overdose deaths.
The federal government’s multi-pronged approach to addressing the opioid crisis includes enhancing access to treatment, supporting harm reduction, and implementing legislative and policy changes. These interventions are designed to reduce overdose deaths and address the complex factors contributing to the opioid epidemic, reflecting a comprehensive effort to improve public health and safety.
State Government Interventions in Combating Overdose Deaths
State governments have taken significant steps to address the opioid crisis and reduce overdose deaths through a variety of targeted interventions. These measures reflect a commitment to improving public health and safety by tackling the multifaceted nature of the opioid epidemic. Here are some key state-level actions:
Prescription Drug Monitoring Programs (PDMPs): Many states have established or enhanced PDMPs to monitor prescriptions for controlled substances, including opioids. These programs allow healthcare providers to track prescription histories, identify potential misuse, and prevent overprescribing. By improving the ability to monitor prescription patterns, PDMPs help mitigate the risk of opioid addiction and overdose.
Expansion of Naloxone Access: In response to the overdose crisis, states have broadened access to naloxone, a life-saving medication that can reverse opioid overdoses. Initiatives include distributing naloxone to first responders, community organizations, and at-risk individuals. Some states have also enacted laws permitting pharmacists to dispense naloxone without a prescription, making it more accessible to those in need.
Enhanced Access to Treatment: States have worked to improve access to treatment for opioid use disorder (OUD) by expanding Medicaid coverage for medication-assisted treatment (MAT). This includes increasing the number of healthcare providers authorized to prescribe buprenorphine and other MAT options. These efforts aim to ensure that individuals with OUD can access effective treatment and support services.
Implementation of Good Samaritan Laws: Many states have introduced Good Samaritan laws that protect individuals who seek medical help for someone experiencing an overdose. These laws provide legal immunity to bystanders who call for emergency assistance, thereby encouraging more people to intervene in overdose situations without fear of legal consequences.
Support for Harm Reduction Programs: State governments have supported harm reduction strategies, including syringe exchange programs that provide clean syringes and resources to reduce the spread of infectious diseases among drug users. Additionally, some states fund overdose prevention education and distribute naloxone kits through these programs, further supporting harm reduction efforts.
Regulation of Opioid Prescribing Practices: To promote safer opioid prescribing, states have implemented various rules and guidelines. These include limits on the duration of opioid prescriptions, mandatory education for prescribers, and requirements for informed consent and patient monitoring. Such measures are designed to enhance prescribing practices and reduce the risk of opioid misuse.
Public Awareness Campaigns: State governments have launched public awareness campaigns to educate the public about the risks of opioids, recognize signs of overdose, and access treatment resources. These campaigns aim to reduce stigma, raise awareness about available support, and encourage individuals to seek help for substance use disorders.
Legislation and Policy Initiatives: States have enacted legislation and policy initiatives to address the opioid crisis comprehensively. This includes allocating funds for addiction treatment and recovery services, supporting law enforcement efforts against drug trafficking, and expanding mental health services. These legislative actions reflect a commitment to tackling the opioid epidemic from multiple angles.
State governments play a vital role in combating overdose deaths and addressing the opioid crisis through a range of interventions. By implementing PDMPs, expanding naloxone access, enhancing treatment options, and supporting harm reduction programs, states contribute to a broader national effort to reduce the impact of opioid use disorder and improve public health outcomes.
Community Resource Strategies to Reduce Overdose Deaths
Reducing overdose deaths requires a multifaceted approach, and community resource strategies are vital in providing support, prevention, and intervention. By leveraging local resources and fostering collaboration, communities can make significant strides in addressing the opioid crisis and other substance use disorders. Here are key community resource strategies that play a crucial role in combating overdose deaths:
Naloxone Distribution Programs: Expanding naloxone (Narcan) distribution programs is essential for overdose prevention. Naloxone is a life-saving medication that can reverse opioid overdoses. These programs distribute naloxone to first responders, community organizations, and individuals at risk of overdose, ensuring that more people have access to this critical tool for saving lives.
Syringe Exchange Programs (SEPs): Syringe exchange programs provide clean syringes and harm reduction supplies to people who inject drugs, reducing the transmission of infectious diseases. SEPs also offer education, counseling, and referrals to treatment services, helping individuals access the support they need while minimizing health risks associated with drug use.
Community Education and Training: Education and training are fundamental in equipping community members, healthcare providers, and law enforcement with the skills to recognize overdose signs, administer naloxone, and respond effectively to overdose emergencies. By raising awareness and improving response capabilities, communities can enhance their ability to manage and prevent overdose incidents.
Treatment and Recovery Support Services: Increasing access to evidence-based treatments for substance use disorders is critical. This includes medication-assisted treatment (MAT) such as buprenorphine, methadone, and naltrexone. Comprehensive support services, including counseling, peer support, and case management, are essential for facilitating long-term recovery and helping individuals achieve sustained sobriety.
Peer Support and Mutual Aid Groups: Peer support groups and mutual aid organizations, like Narcotics Anonymous (NA) and SMART Recovery, provide ongoing encouragement and accountability for those in recovery. These groups foster community and belonging, which is vital for maintaining recovery and addressing addiction challenges.
Integrated Healthcare Services: Promoting the integration of behavioral health services into primary care settings ensures that individuals with substance use disorders receive comprehensive healthcare. This integration helps address physical and mental health needs, providing a holistic approach to treatment and recovery.
Legal and Social Services Support: Access to legal and social services is essential for individuals with substance use disorders. Assisting with housing, employment, and legal challenges related to addiction can help individuals stabilize their lives and focus on recovery.
Crisis Intervention and Mobile Response Teams: Establishing crisis intervention teams and mobile response units equipped to handle overdose emergencies is crucial. These teams provide immediate medical assistance and connect individuals to appropriate treatment and support services, ensuring a swift and effective response to crises.
Community Partnerships and Collaboration: Fostering collaboration among local government agencies, healthcare providers, law enforcement, community organizations, and faith-based groups enhances the effectiveness of community resource strategies. By working together, these entities can coordinate efforts, share resources, and implement comprehensive approaches to address substance use disorders and reduce overdose deaths.
Public Awareness Campaigns: Public awareness campaigns play a crucial role in reducing stigma, educating the public about the risks of substance use, promoting safe prescribing practices, and encouraging individuals to seek help for addiction. These campaigns help foster a supportive environment and increase awareness about available resources.
Implementing these community resource strategies in a coordinated and comprehensive manner can significantly reduce overdose deaths, support individuals in recovery, and address the broader impacts of substance use disorders on public health and safety. By working together and utilizing local resources, communities can make a meaningful impact in the fight against the overdose crisis.
Family Support Strategies to Reduce Overdose Deaths
Family support is a cornerstone in combating the overdose crisis in the U.S. Families provide crucial emotional support, guidance, and advocacy for individuals struggling with substance use disorders. Implementing effective family support strategies can significantly reduce the risk of overdose and enhance recovery efforts. Here are critical strategies for families aiming to decrease overdose deaths:
1. Education and Awareness: Educate family members about substance use disorders, including the signs of overdose, risk factors, and available treatment options. Understanding these aspects equips families to recognize early warning signs and respond effectively. Knowledge is power in preventing and addressing substance use issues.
2. Open Communication: Foster open, non-judgmental communication within the family about substance use. Encourage honest conversations where individuals feel safe discussing their challenges, concerns, and treatment needs. This approach helps build trust and supports a supportive environment for recovery.
3. Supporting Treatment and Recovery: Encourage and assist individuals in accessing evidence-based treatments, such as medication-assisted treatment (MAT) and counseling. Help with logistical aspects like appointments, transportation, and follow-up care to ensure continuous support for their recovery.
4. Naloxone Training and Distribution: Educate family members on how to administer naloxone (Narcan) and provide them with naloxone kits. This training empowers families to respond promptly in the event of an opioid overdose, potentially saving lives and reducing the risk of fatal outcomes.
5. Setting Boundaries and Limits: Establish and maintain clear boundaries regarding substance use behaviors. While offering emotional support, it is crucial to limit enabling behaviors that might perpetuate substance use. Balance is critical in providing support while encouraging responsibility and recovery efforts.
6. Seeking Support for Themselves: Encourage family members to seek support through therapy, support groups, or counseling services. Coping with a loved one’s substance use can be emotionally taxing, and self-care is essential for maintaining resilience and overall well-being.
7. Reducing Access to Substances: Take proactive measures to reduce access to prescription medications and other substances that could be misused. Properly store and dispose of unused or expired medications through safe disposal programs to minimize opportunities for misuse.
8. Crisis Planning and Intervention: Develop a crisis plan with the individual struggling with substance use, outlining steps to take in case of an overdose or other emergencies. Include contact information for emergency services, treatment providers, and support networks to ensure a quick and organized response.
9. Encouraging Engagement in Positive Activities: Support and encourage participation in positive, substance-free activities and hobbies that promote mental and physical well-being. Engagement in supportive community groups or activities can foster a sense of belonging and provide constructive outlets for stress and emotions.
10. Advocacy and Empowerment: Advocate for policy changes and community resources that support individuals with substance use disorders and their families. Participate in advocacy efforts to improve access to treatment, reduce stigma, and increase awareness about overdose prevention.
By implementing these family support strategies, families can play a pivotal role in supporting their loved ones through recovery, reducing the risk of overdose, and promoting long-term health and well-being. The combined efforts of education, support, and advocacy create a strong foundation for recovery and help tackle the overdose crisis effectively.
Essential Self-Management Strategies to Decrease Overdose Deaths
Self-management strategies are vital for individuals at risk of overdose, empowering them to take control of their health and safety. Implementing effective self-management techniques can significantly reduce the risk of overdose and support long-term recovery. Here are critical self-management strategies to consider:
1. Education and Awareness: Educate yourself about the risks associated with substance use, including recognizing signs of overdose and knowing how to respond in emergencies. Stay informed about available treatment options and harm reduction strategies to make well-informed decisions about your health.
2. Medication Adherence: Adhere strictly to prescribed dosages and schedules if you are on medication for substance use disorder or other health conditions. Avoid taking higher doses or mixing medicines without consulting your healthcare provider to prevent adverse effects and reduce overdose risks.
3. Safe Use Practices: Follow safe use practices when using substances. Avoid sharing needles or other drug paraphernalia to reduce the risk of infections and complications. Using substances as prescribed or intended can minimize health risks.
4. Know Your Limits: Understand your personal tolerance levels and recognize when you might be at risk of overdose. Avoid combining substances or using them in unfamiliar or risky environments that could increase your risk.
5. Create a Safety Plan: Develop a comprehensive safety plan that includes strategies to prevent overdose. This plan should involve setting limits on substance use, using substances with others who can help in case of an emergency, and having naloxone (Narcan) readily available. Know how to use naloxone in case of an overdose.
6. Seek Support and Counseling: Engage in counseling or therapy to address underlying issues contributing to your substance use. Learning coping strategies for managing cravings, stress, and triggers can help you maintain recovery and avoid relapse.
7. Regular Health Monitoring: Regularly monitor your physical and mental health by attending medical appointments and screenings. Promptly address any health concerns to prevent complications related to substance use.
8. Avoid Risky Situations: Identify and avoid situations or triggers that might increase your risk of substance use or overdose. Develop strategies to manage stress and boredom without resorting to substances.
9. Engage in Healthy Lifestyle Choices: Adopt a healthy lifestyle by incorporating regular exercise, balanced nutrition, and adequate sleep into your routine. Avoid alcohol and other substances that could heighten your risk of relapse or overdose.
10. Build a Support Network: Surround yourself with supportive individuals who understand your challenges and can offer encouragement, accountability, and assistance during difficult times. A strong support network is crucial for maintaining motivation and recovery.
By implementing these self-management strategies, individuals can proactively reduce their risk of overdose, enhance their overall health, and support their journey toward recovery. Taking control of one’s health through education, treatment adherence, and positive lifestyle choices is essential for a successful recovery and long-term well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some common questions:
What are overdose deaths?
Overdose deaths occur when the body is overwhelmed by drugs or drug combinations, leading to respiratory failure, cardiac arrest, or organ shutdown.
Why have overdose deaths increased in the U.S.?
The rise is driven primarily by fentanyl and other synthetic opioids, along with increasing polysubstance use, limited treatment access, and social instability.
What role does fentanyl play in overdose deaths?
Fentanyl is highly potent and unpredictable. It is often mixed into heroin, cocaine, methamphetamine, and counterfeit pills, significantly increasing overdose risk.
What is a polysubstance overdose?
Polysubstance overdose involves using multiple substances together—such as opioids with stimulants, alcohol, or benzodiazepines—which significantly increases fatal risk.
Who is most at risk for overdose?
Risk is highest among people recently released from incarceration or treatment, individuals with reduced tolerance, those without stable housing, and people lacking access to care.
Why are transitions of care so dangerous?
After detox, hospitalization, or incarceration, tolerance is low. Returning to previous doses can quickly result in fatal overdose without medication or follow-up care.
Can overdose deaths be prevented?
Yes. Medications for opioid use disorder reduce mortality by more than 50%, and naloxone can reverse overdoses when used promptly.
Does harm reduction increase drug use?
No. Research consistently shows that harm reduction strategies reduce deaths and disease without increasing substance use.
What role does stigma play in overdose deaths?
Stigma discourages people from seeking treatment, carrying naloxone, or accessing harm reduction services, increasing preventable deaths.
What public health strategies reduce overdose deaths most effectively?
Expanding medication access, distributing naloxone, supporting harm reduction services, ensuring continuity of care, and treating addiction as a chronic medical condition.
Conclusion
Addressing overdose deaths in the US demands a multifaceted approach involving coordinated efforts from government, community resources, family support networks, and individual self-management strategies. Government policies have been pivotal in enhancing monitoring, expanding access to lifesaving interventions like naloxone, and improving treatment availability. Community resources, such as syringe exchange programs and education initiatives, provide essential support at the local level. Family involvement through education and advocacy strengthens support networks crucial for recovery. Meanwhile, individuals are empowered with self-management strategies to mitigate risks and seek timely care. Together, these combined efforts are essential in combating the overdose crisis, saving lives, and fostering healthier communities across the nation.
Video: How Fentanyl Became the Deadliest Threat #substanceabuse #fentanyl