Nicotine is highly addictive due to its ability to release dopamine in the brain, reinforcing repeated use rapidly. This leads to physical dependence, making quitting challenging due to cravings and withdrawal symptoms. Nicotine cessation therapies, like patches, gum, and lozenges, provide controlled doses of nicotine to ease withdrawal and cravings. These therapies help reduce dependence gradually, allowing individuals to manage both physical and behavioral aspects of addiction.
Effective Nicotine Cessation Therapies: Finding the Right Path to Quit
Nicotine addiction is a challenging habit to break, but with the right cessation therapies, quitting is entirely possible. Various approaches help individuals overcome both the physical dependence on nicotine and the behavioral aspects of addiction. Here’s an overview of some of the most effective nicotine cessation therapies available today.
1. Nicotine Replacement Therapy (NRT)
Nicotine Replacement Therapy (NRT) provides controlled doses of nicotine to ease withdrawal symptoms and reduce cravings. These products help individuals gradually wean off nicotine while avoiding the harmful chemicals in tobacco. Typical forms of NRT include:
- Patches – Provide a steady dose of nicotine through the skin.
- Gum – Helps with oral fixation and provides immediate nicotine relief.
- Lozenges – Dissolve in the mouth to curb cravings.
- Nasal sprays – Deliver fast-acting nicotine through the nasal membranes.
- Inhalers – Mimic the hand-to-mouth action of smoking while providing nicotine.
2. Prescription Medications
Certain prescription medications can significantly aid smoking cessation by targeting brain pathways involved in addiction. Two of the most commonly used medications include:
- Varenicline (Chantix) – Reduces cravings and withdrawal symptoms by partially stimulating nicotine receptors while blocking nicotine’s pleasurable effects.
- Bupropion (Zyban) – An antidepressant that also helps reduce nicotine cravings and withdrawal symptoms by influencing neurotransmitters in the brain.
3. Behavioral Therapies
Overcoming nicotine addiction involves more than just addressing physical dependence—it requires changing habits and behaviors associated with smoking. Behavioral therapies, such as Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT), help individuals:
- Identify triggers that lead to smoking.
- Develop coping strategies to manage stress and cravings.
- Build a structured plan for long-term cessation success.
4. Support Groups and Quitlines
Connecting with others who are also on a quitting journey can provide crucial encouragement and accountability. Support options include:
- Nicotine Anonymous (NicA) – A 12-step program offering peer support.
- Telephone Quitlines – Professional counseling services available through state and national quitlines.
- Local and online support groups – Provide motivation and shared experiences to stay smoke-free.
5. Digital and Mobile Apps
Technology has made nicotine cessation more accessible through apps and online programs. These digital tools offer:
- Progress tracking and goal setting.
- Motivational messages and reminders.
- Interactive exercises to manage cravings.
6. Alternative Therapies
Some individuals find relief from nicotine cravings through alternative therapies, including:
- Acupuncture – May help reduce withdrawal symptoms and cravings.
- Hypnosis – Addresses subconscious triggers associated with smoking.
- Mindfulness and meditation – Help manage stress and improve self-control.
Finding the Right Approach
There is no one-size-fits-all solution for quitting nicotine. Combining multiple therapies often leads to the best outcomes, as different approaches address various aspects of addiction. Whether using NRT, prescription medications, behavioral support, or alternative treatments, the key is persistence and finding what works best for you.
Quitting nicotine is a journey, but with the right tools and support, it is an achievable goal. If you’re ready to leave, consider reaching out to a healthcare professional or exploring available resources to take the first step toward a healthier, smoke-free life.
Why Is Tobacco So Addictive? The Science Behind Nicotine Dependence
Tobacco addiction is one of the most challenging dependencies to overcome, mainly due to the powerful effects of nicotine on the brain and body. Nicotine’s addictive potential stems from its unique chemical and pharmacological properties, which reinforce continued use and make quitting difficult. Here’s a breakdown of why tobacco is so addictive:
1. Rapid Absorption and Brain Penetration
Nicotine quickly enters the bloodstream and reaches the brain within seconds when inhaled through smoking or vaping. This rapid delivery creates an almost immediate effect, reinforcing repeated use and making nicotine one of the most habit-forming substances.
2. Dopamine Release and the Pleasure Cycle
Once nicotine reaches the brain, it binds to nicotinic acetylcholine receptors, stimulating the release of dopamine, the neurotransmitter responsible for pleasure and reward. This dopamine release creates a “feel-good” sensation, reinforcing continued nicotine consumption and leading to cravings when levels drop.
3. Influence on Other Neurotransmitters
Beyond dopamine, nicotine also affects other neurotransmitters that regulate mood and cognition:
- Serotonin – Contributes to feelings of well-being and emotional stability.
- Norepinephrine – Increases alertness and focus.
- Endorphins – Produce mild pain relief and relaxation. These effects make nicotine use pleasurable and habit-forming, increasing its addictive potential.
4. Tolerance and Dependence
With repeated nicotine exposure, the brain begins to adapt by reducing its sensitivity to nicotine’s effects. This results in tolerance, meaning the user must consume more nicotine to achieve the same pleasurable sensations. Over time, this leads to dependence, where the brain relies on nicotine to function normally, and quitting causes withdrawal symptoms such as:
- Irritability
- Anxiety
- Difficulty concentrating
- Intense cravings
5. Short Half-Life and Frequent Dosing
Nicotine has a short half-life of about two hours, meaning it rapidly exits the system. As nicotine levels drop, users experience cravings and withdrawal symptoms, leading to frequent dosing throughout the day. This cycle reinforces habitual use, making it difficult to break free from nicotine dependence.
Breaking the Addiction Cycle
Understanding how nicotine affects the brain highlights why quitting tobacco is so tricky. The combination of rapid brain penetration, neurotransmitter manipulation, tolerance, dependence, and frequent dosing creates a strong addictive loop. However, effective nicotine cessation therapies, such as Nicotine Replacement Therapy (NRT), prescription medications, behavioral counseling, and support groups, can help individuals overcome dependence and achieve long-term success.
Breaking free from nicotine addiction is challenging, but with the right strategies and support, it is entirely possible.
Understanding Nicotine Replacement Therapy: A Safer Path to Quitting
Nicotine Replacement Therapy (NRT) is a widely used method to help individuals quit smoking by providing controlled doses of nicotine without the harmful chemicals found in tobacco smoke. By easing withdrawal symptoms and stabilizing nicotine levels, NRT offers a structured and gradual way to break free from nicotine dependence. Here’s how it works:
1. Reducing Withdrawal Symptoms
One of the biggest challenges of quitting smoking is dealing with withdrawal symptoms, which can include:
- Irritability
- Anxiety
- Intense cravings
- Difficulty concentrating NRT delivers nicotine in a controlled, non-inhaled form, which helps alleviate these symptoms and makes the quitting process more manageable.
2. Stabilizing Nicotine Levels
Unlike smoking, which causes rapid spikes and crashes in nicotine levels, NRT provides a steady, predictable dose of nicotine. This helps individuals feel more in control and reduces cravings, making it easier to break the cycle of addiction gradually.
3. Supporting Habit Change
NRT comes in various forms, allowing individuals to choose the best option for their needs:
- Patches – Provide a constant, slow release of nicotine throughout the day.
- Gum – Can be chewed as needed to manage sudden cravings.
- Lozenges – Dissolve slowly, providing a similar effect to gum but without chewing.
- Nasal Sprays and Inhalers – Deliver faster relief by mimicking the hand-to-mouth action of smoking.
These options allow users to address cravings as they arise, helping them transition away from both nicotine dependence and the behavioral habit of smoking.
4. Gradual Reduction for Long-Term Success
NRT is designed to be used in tapering doses over time, allowing the brain to adapt to lower nicotine levels slowly. This gradual approach reduces the likelihood of intense withdrawal symptoms and increases the chances of successfully quitting for good.
Choosing the Right NRT Plan
The effectiveness of NRT depends on using the correct method and dose for each individual. Many people benefit from combining NRT options, such as using a nicotine patch for steady relief and gum or lozenges for breakthrough cravings. Consulting a healthcare professional can help determine the best plan for a successful quit journey.
In summary, nicotine replacement therapy provides a safer, measured way to reduce nicotine dependence and increase the chances of quitting successfully. By easing withdrawal, stabilizing nicotine levels, and supporting behavioral change, NRT empowers individuals to take control of their health and move towards a smoke-free future.
How to Quit Tobacco: A Comprehensive Guide
Quitting tobacco is one of the most challenging but rewarding steps toward better health. Nicotine’s addictive properties, ingrained behavioral habits, and the brain’s adaptation to nicotine make quitting difficult. However, understanding these challenges and using effective strategies can significantly improve the chances of success. Here’s a guide to quitting tobacco and staying smoke-free.
Why Is Quitting Tobacco So Challenging?
Quitting tobacco is an arduous journey due to the powerful combination of nicotine’s addictive properties, psychological habits, and the brain’s adaptation to nicotine use. Understanding these challenges can help individuals develop effective strategies to overcome them. Here are the main reasons why quitting tobacco is so challenging:
1. Nicotine’s Addictive Power
Nicotine affects brain chemistry by rapidly releasing dopamine, a neurotransmitter associated with pleasure and reward. Over time, the brain adapts by reducing its natural dopamine production, leading to tolerance (needing more nicotine for the same effect) and dependence (experiencing withdrawal symptoms without nicotine). This cycle of dopamine release, tolerance, and withdrawal makes quitting extremely difficult.
2. Withdrawal Symptoms
When nicotine intake stops, the brain and body react with withdrawal symptoms that can include:
- Irritability
- Anxiety
- Restlessness
- Headaches
- Intense cravings. Since smoking temporarily alleviates these symptoms, many individuals struggle to resist the urge to smoke again.
3. Behavioral Habits and Triggers
Smoking often becomes deeply ingrained in daily routines and linked to specific activities, emotions, or environments. Common triggers include:
- Drinking coffee or alcohol
- Finishing a meal
- Feeling stressed or anxious
- Socializing with other smokers. These associations make it challenging to break the habit, as the brain expects nicotine in these situations.
4. Emotional Coping Mechanism
Many people use smoking as a way to cope with stress, anxiety, boredom, or social discomfort. Without an alternative coping strategy, individuals may find it challenging to manage these emotions without tobacco, increasing the likelihood of relapse.
5. Social and Environmental Influences
Being around other smokers or in environments where smoking is common makes quitting even harder. Social cues and peer pressure can reinforce smoking habits, especially in stressful or celebratory situations.
6. Nicotine’s Short Half-Life
Nicotine leaves the bloodstream quickly (within two hours), leading to frequent cravings and the need for continuous dosing. This creates a cycle of dependence, reinforcing the urge to smoke throughout the day.
7. Brain Changes Over Time
Long-term nicotine use causes structural and chemical changes in the brain, particularly in areas related to pleasure and reward. Even after quitting, these changes can persist, making former smokers more vulnerable to relapse when exposed to stress or triggers.
Strategies to Quit Tobacco Successfully
While quitting is challenging, the right approach can make it easier. Here are some effective methods:
1. Nicotine Replacement Therapy (NRT)
NRT provides controlled doses of nicotine without harmful tobacco chemicals. Options include:
- Nicotine patches – Provide a steady, slow release of nicotine.
- Gum and lozenges – Help manage cravings as they arise.
- Nasal sprays and inhalers – Offer fast-acting relief. Using a combination of NRT methods can improve success rates.
2. Prescription Medications
Certain medications help reduce cravings and withdrawal symptoms:
- Varenicline (Chantix) – Blocks nicotine’s pleasurable effects and reduces cravings.
- Bupropion (Zyban) – Alters brain chemistry to decrease nicotine dependence. A healthcare provider can determine the best option for you.
3. Behavioral Therapy and Counseling
Quitting is more than just overcoming physical dependence—it requires changing habits and thought patterns. Behavioral therapy, such as Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT), helps by:
- Identifying triggers and developing coping strategies.
- Addressing stress and emotional reliance on smoking.
- Creating a structured quit plan.
4. Support Systems
Having a strong support system increases the likelihood of quitting successfully. Options include:
- Support groups (e.g., Nicotine Anonymous)
- Quitlines (e.g., telephone counseling services)
- Online communities and mobile apps for encouragement and tracking progress
5. Healthy Lifestyle Changes
Replacing smoking with healthier habits makes quitting easier:
- Exercise to relieve stress and improve mood.
- Healthy snacks to manage oral fixation.
- Deep breathing or mindfulness techniques to reduce stress.
6. Gradual Reduction vs. Cold Turkey
Some people prefer quitting abruptly (“cold turkey”), while others find success in gradually reducing tobacco use. Choosing the method that best suits your personality and lifestyle is key.
In summary, quitting tobacco is challenging due to nicotine’s addictive properties, withdrawal symptoms, behavioral triggers, and brain adaptations. However, understanding these obstacles and utilizing a combination of therapies, behavioral strategies, and support systems can significantly improve the chances of success. With determination and the right resources, a smoke-free life is achievable.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some common questions:
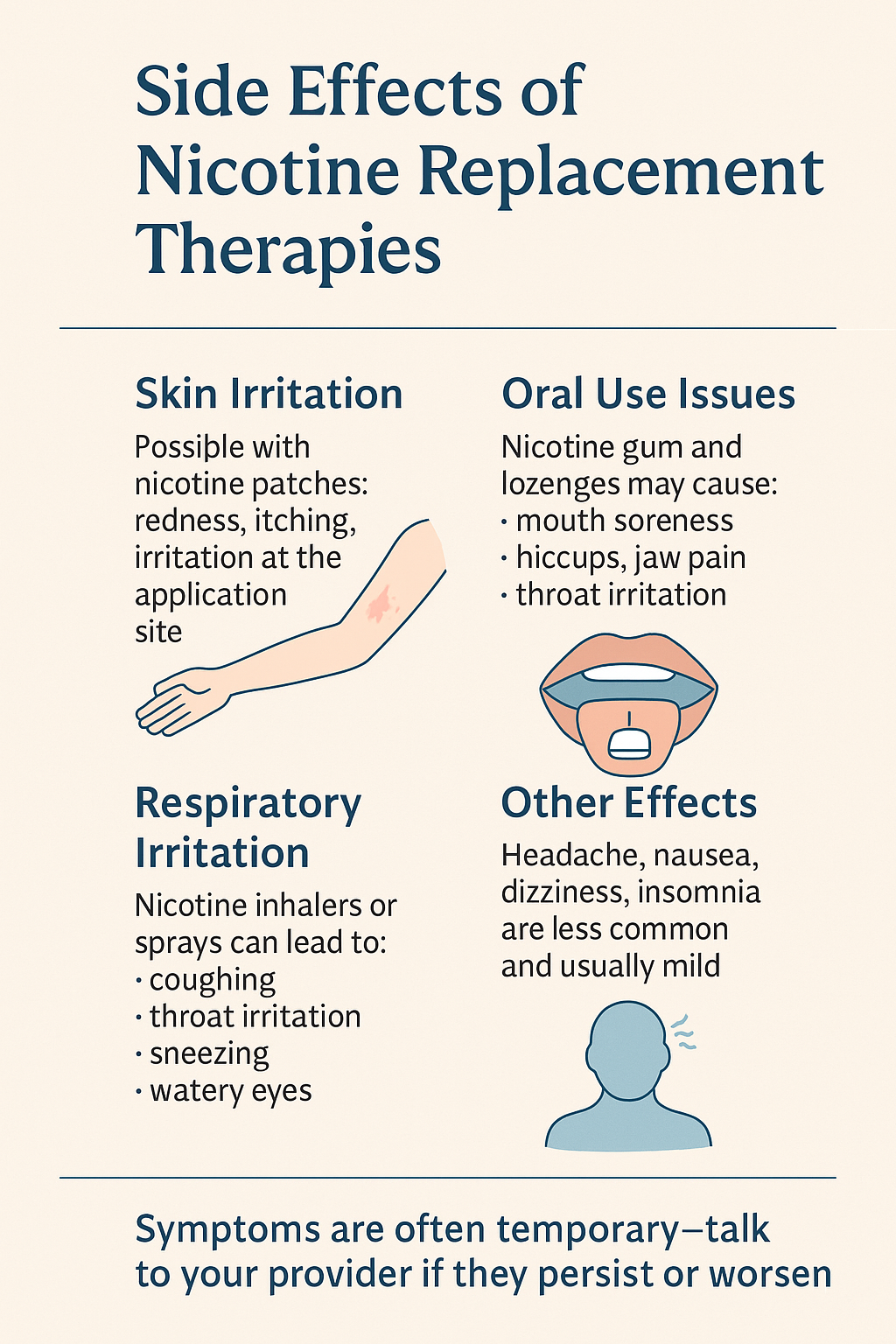
Question: What are the side effects of nicotine replacement therapies?
Answer: Nicotine Replacement Therapies (NRT), such as patches, gum, lozenges, inhalers, and nasal sprays, are generally safe and effective for quitting smoking. However, they can cause side effects, especially in the initial stages of use. Side effects vary depending on the form of NRT used.
Common Side Effects of NRT
1. Nicotine Patches
- Skin irritation (redness, itching, or burning at the application site)
- Sleep disturbances (vivid dreams or insomnia)
- Dizziness or headaches
- Nausea
2. Nicotine Gum
- Jaw pain or soreness
- Hiccups
- Upset stomach, nausea
- Throat irritation
- Increased saliva production
3. Nicotine Lozenges
- Mouth or throat irritation
- Hiccups
- Nausea or heartburn
- Coughing
4. Nicotine Inhalers
- Mouth or throat irritation
- Coughing
- Runny nose
- Upset stomach
5. Nicotine Nasal Spray
- Nasal irritation (burning, runny nose, sneezing)
- Watery eyes
- Throat irritation
- Coughing
Serious But Rare Side Effects
- Irregular heartbeat or palpitations
- Severe allergic reactions (swelling, rash, or difficulty breathing)
- High blood pressure (in some cases, with excessive use)
Most side effects are mild and temporary, improving as the body adjusts to lower nicotine levels. If side effects are severe or persistent, switching to a different form of NRT or adjusting the dosage may help. Consulting a healthcare provider can ensure the safest and most effective approach.
Question: How does nicotine replacement therapy work?
Answer: Nicotine Replacement Therapy (NRT) helps people quit smoking by delivering controlled doses of nicotine without the harmful chemicals found in tobacco smoke. It reduces withdrawal symptoms and cravings, making the transition to a smoke-free life easier.
Mechanism of NRT
- Provides a Lower, Steady Dose of Nicotine
- NRT supplies nicotine in a controlled way, avoiding the rapid spikes and crashes caused by smoking.
- This helps to ease withdrawal symptoms such as irritability, anxiety, restlessness, and intense cravings.
- Reduces Dependence Over Time
- NRT gradually lowers nicotine exposure, allowing the brain and body to adjust without the shock of sudden nicotine deprivation.
- Over time, users can taper down their NRT dose until they no longer need nicotine at all.
- Breaks the Behavioral Habit of Smoking
- Since NRT does not involve inhaling smoke or using a cigarette, it helps separate nicotine addiction from smoking behavior.
- This allows individuals to focus on breaking the psychological habit of reaching for a cigarette in response to triggers.
Forms of NRT and How They Work
- Nicotine Patches – Provide a steady release of nicotine throughout the day. Used once daily.
- Nicotine Gum – Releases nicotine when chewed, helpful in managing sudden cravings.
- Nicotine Lozenges – Dissolve slowly in the mouth to provide gradual nicotine absorption.
- Nicotine Inhalers – Deliver nicotine vapor that is absorbed through the mouth and throat, mimicking the hand-to-mouth action of smoking.
- Nicotine Nasal Spray – Delivers nicotine quickly through the nasal lining, providing fast relief from cravings.
Effectiveness of NRT
- NRT doubles the chances of quitting compared to quitting without assistance.
- Works best when combined with behavioral support (e.g., counseling, quitlines, mobile apps).
- Gradual tapering of nicotine helps the body adjust and reduces the risk of relapse.
NRT works by reducing withdrawal symptoms and cravings while helping users break the smoking habit. Gradually lowering nicotine intake allows for a smoother transition to a tobacco-free life.
Question: What factors can limit the effectiveness of nicotine replacement therapy?
Answer: Several factors can limit the effectiveness of Nicotine Replacement Therapy (NRT) and reduce its success in helping individuals quit smoking. These factors include:
1. Incorrect Use of NRT
- Underuse or insufficient dosage: Using too little nicotine may not adequately control withdrawal symptoms and cravings.
- Not following recommended usage guidelines: Skipping doses or stopping NRT too early can increase relapse risk.
- Incorrect technique: For example, not chewing nicotine gum properly (chewing too fast instead of the recommended “chew and park” method) can reduce its effectiveness.
2. Severe Nicotine Addiction
- Individuals with high nicotine dependence may find that standard NRT doses do not fully relieve cravings.
- Heavy smokers might need a combination of NRT methods (e.g., patch + gum/lozenge) to maintain stable nicotine levels.
3. Psychological and Behavioral Triggers
- Smoking is not just a physical addiction but also a habit tied to daily routines, emotions, and social situations.
- If behavioral triggers (e.g., stress, drinking coffee, socializing) are not addressed, cravings may persist even with NRT.
4. Lack of Behavioral Support
- NRT is more effective when combined with counseling, support groups, or behavioral therapy.
- Without additional support, individuals may struggle to cope with triggers and relapse.
5. Unrealistic Expectations
- Some people expect NRT to eliminate cravings, but it is meant to reduce, not eliminate, withdrawal symptoms.
- Misconceptions about how NRT works can lead to frustration and discontinuation.
6. Side Effects or Discomfort
- Some users experience nausea, dizziness, headaches, or skin irritation with NRT, leading them to stop using it prematurely.
- Adjusting dosage or switching to a different NRT form can help manage side effects.
7. Continued Exposure to Smoking Triggers
- Living with smokers or being in environments where smoking is common can make quitting harder.
- Secondhand smoke exposure and social pressure can increase relapse risk.
8. Lack of Motivation or Readiness to Quit
- If an individual is not mentally prepared or fully committed to quitting, NRT alone may not be enough.
- Setting clear goals and a quit plan improves the chances of success.
To maximize the effectiveness of NRT, users should follow proper dosage, combine NRT with behavioral support, address psychological triggers, and stay committed to their quit plan. If NRT alone is not working, alternative strategies such as combination therapy or prescription medications (e.g., varenicline, bupropion) may be needed.
Conclusion
Nicotine’s chemical properties, particularly its ability to stimulate dopamine release, make it highly addictive, leading to physical dependence and significant challenges when trying to quit. Nicotine cessation therapies, such as patches, gum, and lozenges, offer controlled doses of nicotine to ease withdrawal symptoms and cravings, helping individuals gradually reduce their dependence. These therapies provide a safer alternative to smoking, allowing users to break the cycle of addiction while managing both the physical and behavioral aspects of quitting.
Videos: Simple Ways to Stop Smoking That Actually Work
Surprising Side Effects of Quitting Smoking!
The SHOCKING Truth About Nicotine Replacement Therapy