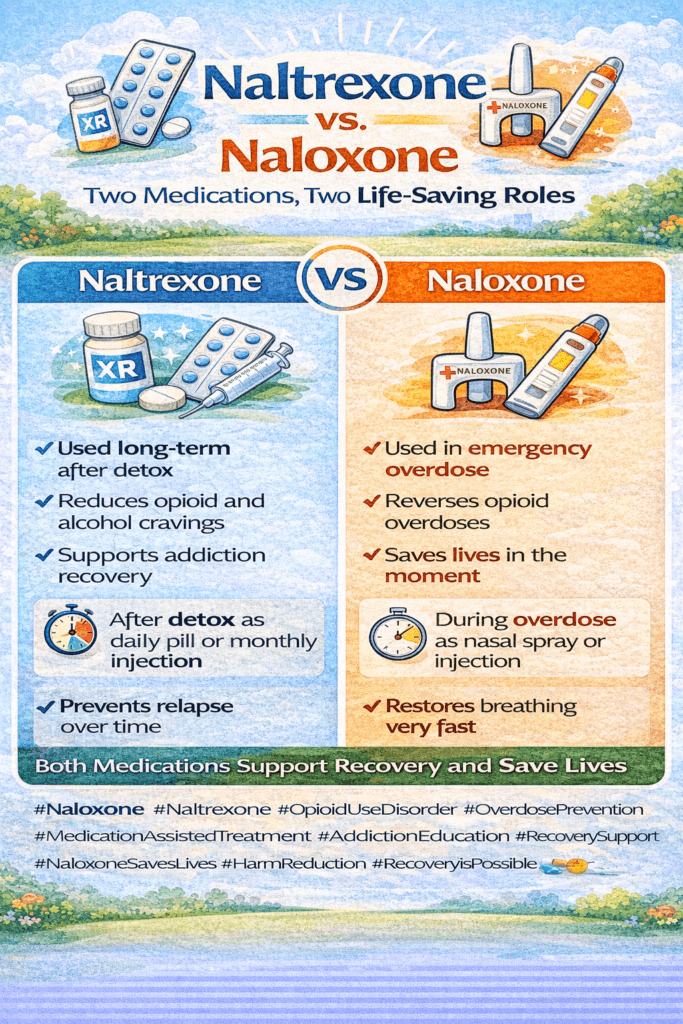
Naltrexone and naloxone are vital for managing opioid dependence and preventing overdose. Naltrexone aids long-term addiction management, while naloxone reverses overdoses. However, stigma surrounds their use. This introduction explores their differences, usage, stigma, and the importance of community and family support strategies to help individuals facing opioid challenges. With understanding and support, communities can better address opioid issues and support those affected.
Naltrexone vs. Naloxone: Understanding the Differences in Opioid Antagonists
Opioid addiction and overdose are critical public health concerns, and two medications—naltrexone and naloxone—play pivotal roles in addressing these issues. While both are opioid antagonists, they serve very different purposes. Understanding their distinctions can help demystify their roles in opioid treatment and overdose intervention.
Naltrexone: A Tool for Long-Term Addiction Management
Naltrexone is primarily used for the long-term management of opioid and alcohol dependence. It functions by blocking the euphoric effects that these substances produce, helping individuals maintain abstinence. Naltrexone comes in two forms: oral pills and an extended-release injectable version, commonly known as Vivitrol, which is administered once a month.
The medication works by occupying opioid receptors in the brain, preventing opioids from activating them. This long-term blockade is beneficial for individuals who have completed detoxification and need support to avoid relapse. Importantly, patients must be opioid-free for 7-10 days before starting naltrexone to prevent withdrawal symptoms.
Naltrexone is prescribed and administered under medical supervision, forming part of a comprehensive treatment plan that may also include counseling and behavioral therapies. It’s also effective in reducing alcohol cravings, making it a dual-purpose medication in addiction management.
Naloxone: A Life-Saving Emergency Intervention
Naloxone, on the other hand, is a rapid-response medication designed for the emergency reversal of opioid overdoses. It works by quickly displacing opioids from their receptors, restoring normal breathing in individuals experiencing an overdose. Unlike naltrexone, naloxone has a short duration of action—typically 30 to 90 minutes—but it acts quickly—often within minutes.
Naloxone is available in several forms, including injectables and nasal sprays, with Narcan being the most well-known nasal spray brand. Because opioid overdoses can happen anywhere and at any time, naloxone is widely distributed in harm reduction programs, carried by first responders like paramedics, and available over-the-counter in many regions. This accessibility has made it a crucial tool in the fight against the opioid overdose epidemic.
Critical Differences Between Naltrexone and Naloxone
- Purpose: Naltrexone is used for long-term addiction treatment, while naloxone is used for emergency overdose reversal.
- Formulation: Naltrexone is available in oral and injectable forms, whereas naloxone is available in injectable and nasal spray forms.
- Mechanism of Action: Naltrexone provides a long-term blockade of opioid receptors, whereas naloxone works quickly to reverse opioid effects in an overdose.
- Usage: Naltrexone is part of a preventive treatment plan for those who have already detoxed, while naloxone is used in life-threatening, acute overdose situations.
- Accessibility: Naltrexone requires a prescription, while naloxone is often available over the counter or through community programs.
Both naltrexone and naloxone play vital roles in addressing the opioid crisis, but serve very different purposes. Naltrexone helps individuals maintain long-term recovery, while naloxone provides life-saving intervention during an opioid overdose. Understanding the differences between these two medications is essential for healthcare providers, patients, and the public in tackling opioid addiction and overdose.
Gender Differences in the Use of Naltrexone and Naloxone: Tailoring Addiction Treatment and Overdose Prevention
Addiction treatment and overdose prevention strategies must account for various factors, including gender. Gender differences can influence how medications like naltrexone and naloxone work in treating addiction and reversing opioid overdoses. These differences affect their effectiveness, side effects, and overall outcomes, making it essential to consider gender-specific needs when developing treatment plans. Let’s take a closer look at how these gender dynamics impact the use of naltrexone and naloxone.
Naltrexone: Gender-Specific Considerations in Addiction Treatment
Naltrexone is used to help individuals maintain abstinence from opioids and alcohol by blocking the pleasurable effects of these substances. While it is effective for both men and women, gender differences can influence outcomes.
Effectiveness
- Alcohol Dependence: Research suggests that naltrexone may be slightly more effective in reducing alcohol cravings and consumption in men. However, women also experience significant benefits, particularly in reducing heavy drinking days. The differences in outcomes may be subtle, but they underscore the need for individualized treatment plans tailored to a person’s gender.
- Opioid Dependence: Naltrexone’s effectiveness in treating opioid addiction appears to be consistent across genders. Both men and women can benefit from its ability to block opioid effects and prevent relapse, although individual responses may vary.
Side Effects
- Hormonal Interactions: Women may experience different side effects from naltrexone due to hormonal fluctuations. For instance, side effects such as nausea and headaches may be more pronounced at specific points in the menstrual cycle, affecting women’s overall treatment experience.
- Body Composition: The differences in body fat composition between men and women can influence how naltrexone is metabolized. Women, who typically have a higher percentage of body fat, may experience a slower breakdown of the drug, potentially affecting both effectiveness and side effects.
Adherence and Retention
- Psychosocial Factors: Men and women face different challenges in adhering to long-term addiction treatment. Women, for instance, may encounter barriers related to childcare or stigma around seeking treatment, which can impact retention in programs using naltrexone. Understanding these barriers is essential for improving treatment outcomes for women.
Naloxone: Gender Considerations in Overdose Reversal
Naloxone is an opioid antagonist used to reverse opioid overdoses rapidly. While it is highly effective across genders, gender-specific social and behavioral factors can influence its use and access.
Effectiveness
- Overdose Reversal: The physiological response to naloxone is similar in men and women, and it works equally well in reversing opioid overdoses. However, gender can influence the context in which naloxone is administered.
Access and Utilization
- Social Factors: Men are statistically more likely to overdose in public spaces, where first responders or bystanders can administer naloxone. Women, on the other hand, are more likely to experience overdoses in private settings, potentially delaying the administration of naloxone. This disparity underscores the importance of ensuring naloxone is readily available in all settings and of educating individuals on how to administer it.
- Awareness and Training: Gender differences may also exist regarding awareness and willingness to carry naloxone. Harm reduction programs aim to educate everyone equally, but cultural and social factors can influence uptake. Women, for example, may feel less empowered to carry naloxone or administer it, whereas men may be more likely to be trained and equipped to use it in public settings.
Recovery and Follow-up
- Support Systems: Post-overdose care and follow-up can differ by gender. Women may have different social support needs after an overdose, often requiring more family or community-based assistance. Tailoring follow-up care to meet these gender-specific needs can improve recovery outcomes and reduce the risk of future overdoses.
Understanding the gender differences in the use of naltrexone and naloxone is crucial for creating more effective addiction treatment and overdose prevention strategies. While both medications are effective across genders, factors such as hormonal interactions, body composition, social dynamics, and access to care can influence outcomes. A gender-sensitive approach that addresses the unique needs of men and women will ensure that both medications are used to their fullest potential in combating addiction and saving lives.
By addressing these gender-related considerations, healthcare providers can help reduce the stigma surrounding treatment and ensure that both men and women receive the care and support they need for recovery.
Breaking the Stigma: Understanding Naltrexone, Naloxone, and Their Role in Addiction Treatment
The stigma surrounding addiction is pervasive, often extending to life-saving treatments like naltrexone and naloxone. Both of these medications play crucial roles in addressing opioid and alcohol dependence, yet societal attitudes can create barriers to their use and acceptance. Understanding the roots of this stigma and addressing it head-on is essential for supporting those in need of addiction treatment and overdose prevention.
Naltrexone: Addressing the Stigma in Long-Term Addiction Treatment
Association with Addiction
One of the primary sources of stigma around naltrexone stems from its association with addiction. For many, using naltrexone is seen as a public admission of struggling with substance use, often viewed as a personal failure rather than a treatable medical condition. This perspective overlooks the reality that addiction is a chronic illness requiring medical intervention, much like diabetes or heart disease.
Misunderstanding of Treatment
Medication-assisted treatment (MAT), which includes the use of naltrexone, is frequently misunderstood. Some people falsely believe that using medication to manage addiction is merely replacing one drug with another. In reality, naltrexone blocks the euphoric effects of opioids and alcohol, helping individuals sustain recovery. Educating the public about the science behind MAT can dispel these misconceptions.
Mental Health Stigma
Another layer of stigma comes from the co-occurrence of mental health disorders in many individuals who use naltrexone. The stigma surrounding mental illness often compounds the negative perceptions about addiction treatment, making it even harder for individuals to seek help. Dual-diagnosis treatment, where both addiction and mental health conditions are addressed simultaneously, is critical for breaking this cycle of stigma.
Visibility of Long-Term Treatment
Naltrexone treatment can be long-term, sometimes requiring ongoing medical supervision and the use of extended-release formulations like Vivitrol. For some, the need for long-term treatment is seen as a weakness, further perpetuating stigma. Unlike short-term medical interventions, addiction often requires continuous management, and this long-term approach should be normalized.
Naloxone: The Stigma of Overdose Reversal
Association with Overdose
Naloxone, commonly known by the brand name Narcan, is a life-saving medication used to reverse opioid overdoses. However, because it is often used in emergencies, the visible act of administering naloxone can attract negative attention. When people see naloxone being used, it usually highlights the issue of drug use, which can lead to public moral judgments.
Moral Judgments
Individuals who overdose are sometimes perceived as morally flawed or irresponsible, and the need for naloxone can reinforce these negative stereotypes. This moralization of addiction overshadows the reality that addiction is a medical condition that affects people from all walks of life. Naloxone should be considered an essential public health tool, not a marker of personal failure.
Misconceptions about Naloxone
A common misconception is that naloxone enables drug use by removing the fear of a fatal overdose. This belief is harmful and unsupported by evidence. Naloxone does not encourage continued drug use; instead, it provides a critical opportunity for individuals to seek treatment after surviving an overdose. Misunderstanding this point contributes to the stigma around naloxone distribution and use.
Policy and Legal Issues
In some areas, legal barriers to accessing naloxone reflect and reinforce stigma. Restrictions on naloxone distribution and inadequate insurance coverage for its purchase create unnecessary obstacles to its widespread use. These systemic barriers reflect a more significant issue—a societal stigma that continues to frame addiction as a moral issue rather than a public health concern.
Addressing the Stigma
Education and Awareness
- Public Awareness Campaigns: Broad public education campaigns are essential for shifting societal attitudes about addiction. Addiction must be recognized as a medical condition, and the use of medications like naltrexone and naloxone should be understood as legitimate medical treatments.
- Training and Outreach: Equipping healthcare providers, first responders, and community members with naloxone use training and information about the benefits of MAT can foster more supportive environments for individuals in recovery.
Policy Changes
- Legal Protections: Good Samaritan laws, which protect individuals who administer naloxone from legal consequences, are vital in reducing the stigma. These laws can encourage bystanders to act during an overdose situation without fear of punishment.
- Insurance Coverage: Ensuring that naltrexone and naloxone are widely covered can make these treatments more accessible and reduce financial barriers. Adequate coverage reflects a commitment to treating addiction as a healthcare issue.
Supportive Services
- Integrated Care: Providing integrated care, where addiction treatment is part of broader mental and physical healthcare, can help address the stigma by normalizing addiction as part of overall health. This holistic approach reduces the isolation and judgment individuals might otherwise face.
- Peer Support: Encouraging the formation of peer support and recovery communities can foster a sense of belonging among individuals. Engaging with others who have faced similar challenges reduces the stigma of addiction treatment and helps individuals build strong support networks.
Breaking the stigma around naltrexone and naloxone requires addressing the root causes of negative perceptions about addiction. By educating the public, changing harmful policies, and offering integrated care and peer support, we can promote a more compassionate and practical approach to addiction treatment and overdose prevention. The goal is to view addiction as a medical issue, not a moral failing, and recognize the value of treatments that save lives and support recovery.
Community Resource Strategies for Expanding Access to Naltrexone and Naloxone
As the opioid crisis continues to affect communities, it’s crucial to develop comprehensive strategies that increase access to life-saving medications like naltrexone and naloxone. These medications play essential roles in treating addiction and preventing overdose deaths, but many barriers—such as stigma, lack of awareness, and limited access—still stand in the way. Here are some key community resource strategies to ensure that naltrexone and naloxone reach those who need them most.
Naltrexone: Expanding Access and Support for Addiction Treatment
Naltrexone is used in medication-assisted treatment (MAT) for opioid and alcohol dependence. Community resource strategies can help increase its availability and reduce the stigma associated with its use.
1. Education and Awareness Campaigns
Many misconceptions surround naltrexone and medication-assisted treatment in general. By conducting community outreach programs, we can educate the public about the effectiveness of naltrexone in managing opioid and alcohol dependence. Dispelling myths and showing that addiction is a medical condition requiring proper treatment can help reduce stigma and encourage more people to seek help.
2. Treatment Navigation Services
Navigating the healthcare system can be challenging for individuals seeking addiction treatment. Establishing treatment navigation services can help patients more easily access naltrexone. These services can help individuals in recovery find healthcare providers, secure insurance coverage, and schedule appointments, making the treatment process smoother.
3. Support Groups and Peer Networks
Support networks are vital for people receiving naltrexone treatment. Facilitating peer support groups where individuals can share their experiences, coping strategies, and encouragement can provide a sense of community during recovery. This peer-led support helps individuals stay committed to treatment and feel less isolated.
4. Collaboration with Healthcare Providers
Integrating naltrexone into comprehensive care plans requires strong collaboration between healthcare providers, such as primary care doctors, addiction specialists, and mental health professionals. These partnerships can ensure that patients receive holistic care, addressing both addiction and any co-occurring mental health conditions.
5. Telehealth Services
Telehealth is an excellent way to improve accessibility to naltrexone treatment, particularly for people in rural or underserved areas. Virtual consultations and follow-up appointments can reduce barriers to treatment access and help individuals stay on track with their recovery, regardless of location.
6. Medication-Assisted Treatment (MAT) Programs
Expanding MAT programs that incorporate naltrexone is essential for providing comprehensive services to those battling opioid and alcohol dependence. These programs often include counseling, behavioral therapy, and medical monitoring, addressing the complex needs of individuals undergoing addiction treatment.
Naloxone: Empowering Communities to Prevent Overdoses
Naloxone is a life-saving medication used to reverse opioid overdoses, and community strategies can ensure its widespread availability and use in emergencies.
1. Distribution Programs
Naloxone should be readily available to those at risk of opioid overdose, as well as their caregivers. Implementing naloxone distribution programs in collaboration with pharmacies, healthcare facilities, and community organizations can ensure this life-saving medication is readily accessible to those who need it most.
2. Training Initiatives
Training initiatives can empower community members to act during overdose emergencies. Offering training on how to recognize overdose symptoms, administer naloxone, and perform CPR can save lives. First responders, healthcare professionals, and even laypersons should be equipped with this knowledge to prepare them to provide critical assistance.
3. Public Awareness Campaigns
Public awareness is critical to reducing the stigma associated with naloxone and opioid use disorder. Launching campaigns that highlight the importance of naloxone as a life-saving tool can encourage more people to carry naloxone kits and be prepared to use them in emergencies.
4. Community-Based Distribution Points
Establishing community-based distribution points, such as harm reduction centers, syringe exchange programs, and outreach vans, can help individuals access naloxone kits. These points can also provide training on using the medication, ensuring that access and knowledge go hand in hand.
5. Good Samaritan Laws
Good Samaritan laws protect individuals who administer naloxone during an overdose emergency from legal consequences. Advocating for the implementation and enforcement of these laws can reduce fear of legal repercussions, encouraging bystanders to intervene and save lives.
6. Integration with Harm Reduction Services
Naloxone distribution should be integrated with existing harm reduction services, such as needle exchange programs, substance use disorder treatment centers, and community health clinics. This approach ensures that individuals who are at the highest risk of overdose have regular access to naloxone and related support services, creating a comprehensive system of care.
In summary, implementing community resource strategies for both naltrexone and naloxone is essential for increasing access to these life-saving medications and providing comprehensive support for individuals affected by addiction. By addressing the barriers of stigma, lack of awareness, and accessibility, we can build more resilient communities and save lives. Community efforts that promote education, support, and policy change will ultimately lead to better public health outcomes and a more compassionate approach to addiction and overdose prevention.
Family Support Strategies for Individuals Using Naltrexone and Naloxone in Addiction Treatment
Family plays a critical role in the recovery process for individuals facing opioid and alcohol dependence. The support of loved ones can be a powerful tool for the success of treatments involving medications such as naltrexone and naloxone. These medications are vital for managing dependence and preventing overdose, but having a solid family support system can significantly enhance treatment outcomes. Here are essential strategies families can adopt to help their loved ones recover.
Naltrexone: Family Support in Long-Term Addiction Management
Naltrexone is used to treat opioid and alcohol dependence by reducing cravings and preventing relapse. For individuals taking this medication, family support can make all the difference in maintaining sobriety and adhering to treatment.
1. Education and Communication
Family members must understand how naltrexone works and the role it plays in managing addiction. By educating themselves on the medication’s effectiveness and purpose, families can help dispel misconceptions and offer meaningful support. Open communication about treatment goals, expectations, and potential challenges can create a safe space where individuals feel supported rather than judged.
2. Emotional Support
Recovery from addiction is a challenging process that often involves emotional ups and downs. Providing consistent emotional support, empathy, and encouragement can help alleviate feelings of shame, guilt, or stigma associated with addiction. Being a non-judgmental listener and a source of positive reinforcement can help individuals stay motivated and committed to their recovery journey.
3. Practical Assistance
Families can assist in practical ways by helping with everyday tasks that reduce stress, which, in turn, can lower the risk of relapse. Offering to help with transportation to medical appointments, childcare, household chores, or medication reminders can significantly ease the burden on individuals in recovery and improve adherence to naltrexone treatment.
4. Boundaries and Self-Care
Family members must establish healthy boundaries and practice self-care while supporting a loved one’s recovery. Setting limits on how much you can give emotionally can prevent burnout and resentment. Encouraging family members to prioritize their own needs and seek external support—such as counseling or peer groups—helps ensure they are emotionally equipped to provide sustained support.
5. Participation in Therapy
Encouraging family participation in therapy or counseling can strengthen the overall recovery process. Attending therapy sessions together helps address underlying family dynamics and communication patterns that may have contributed to addiction. A family-centered approach to therapy can foster healing and provide a foundation for stronger relationships and better treatment outcomes.
Naloxone: Family Support in Overdose Prevention and Emergency Response
Naloxone is a life-saving medication used to reverse opioid overdoses. While it is effective in emergencies, families must be prepared and informed to ensure timely intervention.
1. Education and Training
Family members should be educated on how to recognize the signs of an opioid overdose and trained on how to administer naloxone. Providing CPR training can also be valuable in emergencies. Understanding naloxone’s role as a life-saving intervention can empower families to act quickly and confidently when needed.
2. Access to Naloxone Kits
Ensure family members have easy access to naloxone kits and know where they are stored. Encourage family members to carry naloxone at all times, especially if they live with or frequently encounter someone at risk of overdose. By making naloxone readily available, families can be better prepared for emergencies.
3. Emergency Preparedness
Developing a clear emergency response plan can save lives. Families should establish protocols for responding to overdose situations, including how to administer naloxone, when to call emergency services, and how to provide post-overdose care. Having a plan helps reduce panic and ensures everyone knows what to do in a crisis.
4. Emotional Support
The risk of overdose can be emotionally taxing for families. Providing emotional support for one another is crucial, as family members may experience anxiety, fear, or trauma related to their loved one’s opioid use disorder. Creating a non-judgmental, supportive environment for expressing feelings can help families cope with emotional strain and continue offering compassionate support.
5. Connecting with Community Resources
Families should be connected with community resources, including peer support groups, counseling, and mental health services. These resources can provide valuable guidance and coping strategies, helping families navigate the emotional and practical challenges of supporting a loved one with opioid use disorder. Access to external support can also reinforce the family’s ability to provide consistent care and prevent burnout.
In summary, family support is a cornerstone of successful recovery for individuals using naltrexone and naloxone as part of their addiction treatment. Families can create a nurturing and supportive environment that enhances the likelihood of sustained recovery by providing emotional support, practical assistance, and access to critical resources. Whether helping manage long-term addiction treatment or being prepared to respond to overdose emergencies, families play a vital role in ensuring their loved ones receive the care they need. Together, families and communities can work to reduce the stigma of addiction and provide supportive frameworks that foster healing and recovery.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some common questions:
1. Are naltrexone and naloxone the same medication?
No. They both interact with opioid receptors, but they are used for completely different purposes.
2. What is naloxone used for?
Naloxone is an emergency medication that reverses opioid overdoses by restoring breathing.
3. What is naltrexone used for?
Naltrexone is a long-term medication used to treat opioid use disorder and alcohol use disorder by blocking the effects of these substances.
4. How fast does naloxone work?
Naloxone works within minutes and can quickly restore breathing during an opioid overdose.
5. Does naloxone last a long time?
No. Naloxone works for 30–90 minutes. Because some opioids last longer, multiple doses may be needed.
6. When is naltrexone started?
Naltrexone is started after detox, once opioids are fully cleared from the body, to prevent relapse.
7. Can naltrexone be used in an emergency overdose?
No. Naltrexone is not for emergency use. Naloxone is the medication used to reverse overdoses.
8. Are these medications addictive?
No. Neither naloxone nor naltrexone produces a “high” or causes dependence.
9. What forms do these medications come in?
Naloxone is available as a nasal spray or an injection.
Naltrexone comes as a daily pill or a monthly injection.
10. Why are both medications important in the opioid crisis?
Naloxone saves lives during overdoses. Naltrexone helps prevent relapse and supports long-term recovery.
Conclusion
Naltrexone and naloxone are essential medications in combating opioid dependence and overdose. Despite their distinct purposes, both face stigma and misconceptions within communities. Yet, with proper education and support, their efficacy can be maximized. Community resources, including education programs and distribution initiatives, coupled with family support strategies, such as emotional assistance and emergency preparedness, play crucial roles in aiding individuals affected by opioid-related challenges. By addressing stigma and implementing supportive measures, communities can create environments that foster recovery and reduce the devastating impact of opioid misuse and overdose.
Video: Naltrexone vs Naloxone Two Medications, Two Life Saving Roles