Navigating the journey of recovery from addiction presents unique challenges at different stages of life. Individuals face obstacles from early to late adulthood, shaped by age, circumstances, and experiences. Understanding and addressing these challenges is crucial for fostering resilience and sustainable recovery. Let’s explore the recovery challenges encountered at different life stages and identify strategies to overcome them, empowering individuals to thrive toward sobriety and well-being.
Navigating Recovery Challenges Across Life Stages
Recovery from addiction presents unique challenges that can vary significantly at different stages of life. Understanding these challenges can help individuals develop tailored strategies for maintaining sobriety and well-being. Here’s a closer look at the recovery challenges faced across various life stages:
Early Adulthood (18-25)
- Transitioning to Independence: Young adults often experience newfound freedom, which can make managing responsibilities overwhelming. The transition may include moving out, starting college, or entering the workforce, all while striving to maintain sobriety.
- Peer Pressure: This age group frequently encounters social settings where substance use is present every day, leading to heightened peer pressure and potential relapse triggers.
- Balancing Responsibilities: The struggle to balance academic or career goals with recovery efforts can create stress and temptations, making it difficult to cope.
- Establishing Relationships: Navigating relationships and setting healthy boundaries can be challenging for young adults as they learn to cultivate supportive connections that encourage sobriety.
Mid-Adulthood (26-55)
- Work-Life Balance: Juggling work responsibilities, family obligations, and social commitments can strain recovery efforts. Managing stress while remaining sober becomes crucial.
- Coping with Life Changes: Major life events—such as marriage, parenting, divorce, or career changes—can trigger relapse, necessitating proactive strategies to manage stress and emotions.
- Unresolved Trauma: Individuals in this stage may need to address past trauma or emotional issues, as these can resurface during periods of high stress, complicating recovery.
Late Adulthood (55+)
- Physical Health Issues: Aging brings physical health challenges that can complicate recovery. Individuals may need to navigate medication management and health conditions while maintaining sobriety.
- Adjusting to Retirement: Retirement can bring significant lifestyle changes, which may lead to feelings of aimlessness or boredom that can trigger relapse.
- Dealing with Loss: Late adulthood often involves coping with grief from the loss of loved ones, which can bring about feelings of isolation and sadness, making recovery more complex.
- Loneliness: As social networks diminish with age, individuals may struggle with loneliness, emphasizing the need for social support and connection.
Post-Retirement (65+)
- Lifestyle Adjustments: Adapting to a new daily routine and finding purpose can be challenging. Engaging in meaningful activities becomes essential for emotional well-being.
- Coping with Boredom: Without the structure of work, individuals may experience boredom, prompting them to explore hobbies and interests to stay engaged.
- Chronic Health Management: Managing chronic conditions and potential complications from years of substance use can add layers of complexity to recovery.
- Existential Reflections: This stage may prompt deeper questions about life’s meaning and purpose, which can affect mental health and recovery.
Recovery Later in Life (After 50)
- Long-Standing Patterns: Confronting entrenched behaviors and long-standing patterns of substance use requires significant self-reflection and commitment to change.
- Consequences of Addiction: Individuals may deal with the accumulated consequences of addiction, including strained relationships and financial instability, complicating their recovery journey.
- Social Circle Changes: Adjusting to changes in social circles can be challenging, requiring individuals to seek new sources of support and connection.
- Health Management: Managing chronic health conditions while addressing potential complications from past substance abuse is vital for overall well-being.
Regardless of the stage of life, individuals in recovery face unique challenges that necessitate tailored support and coping strategies. Seeking professional help, engaging in support groups, and building a solid support network are essential steps in overcoming these challenges and fostering long-term sobriety and well-being. By acknowledging the specific challenges at each life stage, individuals can better navigate their recovery journey and create a fulfilling life in sobriety.
Tailoring Self-Management Strategies for Recovery Across Life Stages
Navigating recovery from addiction involves a unique set of challenges at different stages of life. Self-management strategies can empower individuals to address these challenges effectively. Here’s a look at tailored self-management strategies for various life stages:
Early Adulthood (18-25)
- Structured Routine: Establishing a structured daily routine that includes time for self-care, academic or career responsibilities, and sobriety-related activities can help provide stability during this transitional period.
- Assertiveness Skills: Developing assertiveness skills is crucial for resisting peer pressure and setting boundaries in social situations. Practice saying no and prioritizing personal well-being.
- Sober Social Activities: To build a healthy social life, seek out sober social activities and support networks. Engaging in sober events can foster connections with like-minded peers.
- Stress Management Techniques: To cope with academic or career pressures, practice mindfulness, meditation, or regular exercise. These practices can help mitigate feelings of anxiety and stress.
Mid-Adulthood (26-55)
- Prioritize Self-Care: Incorporate regular exercise, healthy eating, and adequate sleep into your routine. These practices are vital for managing stress and maintaining overall well-being.
- Time Management: Utilize time-management skills to balance work, family obligations, and recovery-related activities. Effective planning can reduce stress and help maintain sobriety.
- Open Communication: Communicate with family and loved ones about recovery goals and needs. Seeking their support can strengthen relationships and foster a supportive environment.
- Coping Strategies: Develop coping strategies to handle stressors related to career changes, relationship dynamics, and financial pressures. This might include seeking professional help or engaging in support groups.
Late Adulthood (55+)
- Positive Mindset: Embrace a positive mindset and cultivate gratitude for blessings. Focus on the present moment and avoid dwelling on past regrets.
- Engage in Meaningful Activities: Participate in hobbies and activities that provide a sense of purpose and fulfillment. This engagement can enhance emotional well-being.
- Stay Socially Connected: Combat loneliness and isolation by joining community groups, volunteering, or attending senior centers. Social connections are crucial for emotional support.
- Prioritize Physical Health: Attend regular medical check-ups, maintain a healthy diet, and engage in physical activities suited to your capabilities. Prioritizing health supports overall well-being.
Post-Retirement (65+)
- Explore New Interests: Discover new hobbies or interests to maintain a sense of fulfillment and purpose in retirement. This exploration can provide opportunities for personal growth.
- Practice Adaptability: Embrace flexibility and adapt to changes in routine and lifestyle. This mindset can help ease transitions during retirement.
- Continued Learning: Seek opportunities to learn through classes, workshops, or hobbies. Engaging in lifelong learning can enhance cognitive function and satisfaction.
- Cultivate Resilience: Focus on personal strengths and past successes. Embrace new challenges with a positive attitude, reinforcing resilience in the face of change.
Recovery Later in Life (After 50)
- Address Past Trauma: Acknowledge and address past trauma or unresolved emotional issues through therapy or support groups. This step is essential for healing and moving forward.
- Coping Skills for Health Conditions: Develop coping skills to manage chronic health conditions and age-related limitations while maintaining sobriety. This approach supports both physical and emotional health.
- Holistic Wellness Approach: Embrace a holistic approach to wellness by prioritizing physical, mental, and emotional health needs. Balance in all areas contributes to overall well-being.
- Build a Support Network: Create a support network of peers, professionals, and loved ones who understand the unique challenges of recovery later in life. Having a solid support system can provide encouragement and resources.
Self-management strategies tailored to recovery challenges at different life stages emphasize prioritizing self-care, setting boundaries, seeking support, and developing coping skills. By actively managing these challenges, individuals can navigate their recovery journey with resilience, fostering long-term sobriety and overall well-being. Embracing change and being proactive in recovery can lead to a fulfilling and healthier life.
Essential Family Support Strategies for Recovery at Different Life Stages
Family support is a critical component in helping individuals navigate the challenges of recovery from addiction. The dynamics of family support can change significantly across life stages, and it’s essential to tailor strategies to effectively meet individuals’ needs as they progress through these stages. Here are crucial family support strategies for each stage of life:
Early Adulthood (18-25)
- Emotional Support: Provide consistent emotional support and encouragement as the individual establishes independence and navigates new responsibilities. Celebrate their achievements and validate their struggles.
- Clear Expectations and Boundaries: Set clear expectations regarding substance use, emphasizing the importance of sobriety. Support their sobriety goals through understanding and accountability.
- Resource Guidance: Help them find sober social activities and peer support groups. Connect them with communities that promote a healthy lifestyle.
- Open Communication: Foster an environment of open communication. Encourage the individual to share their experiences and challenges without fear of judgment. Active listening can strengthen trust and connection.
Mid-Adulthood (26-55)
- Practical Support: Help with balancing work, family, and recovery-related responsibilities. Offer practical support, such as childcare or household help, to alleviate stress.
- Family Therapy Participation: Consider attending family therapy or support groups together. These sessions can address relationship dynamics and improve communication, both vital to recovery.
- Celebrate Achievements: Regularly express pride in their sobriety and personal growth. Recognizing milestones reinforces their motivation and commitment to recovery.
Late Adulthood (55+)
- Stay Connected: Maintain a strong connection with the individual by offering companionship and emotional support as they navigate retirement and the changes of aging.
- Encourage Social Engagement: Help them maintain social connections by encouraging participation in fulfilling activities that promote well-being and sobriety. This can include community groups or hobbies.
- Assist with Practical Needs: Provide practical support, such as transportation to medical appointments, and help with day-to-day tasks. This assistance can alleviate stress and allow them to focus on their recovery.
- Share Wisdom: Use your life experience to provide perspective and encouragement during challenging times. Sharing wisdom can help them see their journey in a broader context.
Post-Retirement (65+)
- Emotional Support During Transition: Offer emotional support as the individual transitions into retirement. Encourage them to express their feelings about changes in routine and lifestyle.
- Facilitate Social Connections: Help the individual stay socially connected by engaging in community activities or volunteering. This involvement can combat feelings of isolation.
- Healthcare Navigation: Help navigate healthcare systems and manage chronic health conditions while supporting sobriety goals. Be present at medical appointments when possible.
- Reflect on Achievements: Offer emotional support as the individual reflects on their achievements and transitions. Encourage positive dialogue about their contributions and experiences.
Recovery Later in Life (After 50)
- Empathy and Understanding: Show empathy as the individual addresses past trauma or unresolved emotional issues that may affect their recovery. Listening and understanding can provide comfort.
- Encourage a Healthy Lifestyle: Encourage nutritious eating, regular exercise, and stress-management techniques tailored to their abilities to maintain a healthy lifestyle.
- Practical Support for Health Management: Help manage medications, attend medical appointments, and access community resources for older adults. Your involvement can significantly ease their burden.
- Stay Informed: Educate yourself about the unique challenges of recovery later in life. This knowledge enables you to offer tailored support and encouragement, showing that you understand their needs.
Family support strategies are essential at different life stages. They focus on providing emotional support, practical assistance, and encouragement tailored to the individual’s needs. By fostering a supportive, nurturing family environment, loved ones can play a pivotal role in helping individuals overcome challenges during recovery and promote long-term sobriety and well-being. In doing so, families can strengthen their bonds and contribute to their loved ones’ healing and growth on the road to recovery.
Community Resource Strategies for Supporting Recovery at Different Life Stages
Community resources play a vital role in helping individuals overcome the challenges of addiction recovery. Tailored support at various life stages can significantly enhance the recovery experience. Here are community resource strategies for each stage of life, designed to provide assistance and foster long-term well-being.
Early Adulthood (18-25)
- Local Support Groups: Connect young adults with local support groups, such as Young People in Recovery (YPR) or university-based recovery programs. These groups offer peer support and shared experiences that can be crucial during this transitional period.
- Youth-Focused Treatment Programs: Provide access to addiction treatment and counseling services tailored to the needs of young adults. These services often understand the unique pressures this age group faces.
- Sober Living Arrangements: Provide resources and supportive housing options for young adults transitioning from treatment programs. Safe, substance-free environments can facilitate recovery and stability.
- Educational and Vocational Resources: Connect individuals with resources that support academic and career goals while maintaining sobriety. This may include tutoring programs, career counseling, and job placement services.
Mid-Adulthood (26-55)
- Community-Based Treatment Programs: Provide access to local treatment programs that offer counseling, therapy, and support groups tailored to recovering adults. These programs can help address the complexities of adult life while promoting sobriety.
- Employment Assistance Programs: Connect individuals with employment resources, vocational training, and job placement services to foster career goals and financial stability. Financial independence can enhance self-esteem and reduce stress.
- Practical Resource Access: Offer resources for affordable housing, financial assistance, and transportation services to help individuals overcome barriers to recovery. Addressing these practical needs is critical for sustaining long-term sobriety.
- Community Wellness Programs: Facilitate access to community wellness programs, recreational activities, and fitness facilities to promote overall well-being. Physical activity can be a powerful tool for managing stress.
Late Adulthood (55+)
- Senior-Specific Treatment Programs: Provide access to addiction treatment and counseling services for older adults, acknowledging their unique life experiences and challenges.
- Social Connections: Offer resources for senior centers, social clubs, and recreational activities that encourage social engagement and combat isolation. A supportive community can play a crucial role in recovery.
- Healthcare Resources: Connect individuals with healthcare resources, including senior specialists, support groups for older adults, and Medicare/Medicaid assistance programs. Ensuring access to comprehensive healthcare is essential for recovery.
- Practical Support Services: Provide transportation, home care assistance, and other helpful support options to help older adults maintain independence and well-being during recovery.
Post-Retirement (65+)
- Retirement Communities: Offer information about retirement communities and assisted living facilities that provide supportive environments for individuals in recovery. These settings can foster a sense of community.
- Senior-Specific Addiction Programs: Provide access to addiction treatment and support services tailored to the needs and challenges of retirees.
- Volunteer and Learning Opportunities: Connect individuals with volunteer opportunities, lifelong learning programs, and creative arts classes. Engaging in meaningful activities can enhance fulfillment and purpose in retirement.
- Healthcare Access: Facilitate access to healthcare resources, including medical specialists, home health services, and prescription assistance programs to support health management.
Recovery Later in Life (After 50)
- Tailored Treatment Programs: Offer access to addiction treatment programs designed for older adults, focusing on issues such as chronic pain management and polypharmacy.
- Peer Support Resources: Provide information about peer support groups, counseling services, and wellness programs specifically for older adults in recovery. These resources can foster connection and understanding.
- Legal Assistance Programs: These programs connect individuals with legal assistance, estate planning services, and elder abuse prevention resources to address legal and financial concerns.
- Practical Support Services: Offer access to transportation, meal delivery programs, and home modification services to support aging in place and independent living.
Implementing community resource strategies tailored to the different stages of life is essential for supporting individuals facing recovery challenges. By accessing these resources, individuals can find the support they need to overcome obstacles, achieve long-term sobriety, and enhance their overall well-being. A strong community network can provide the foundation for a successful recovery journey, ensuring no one has to navigate it alone.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some common questions:
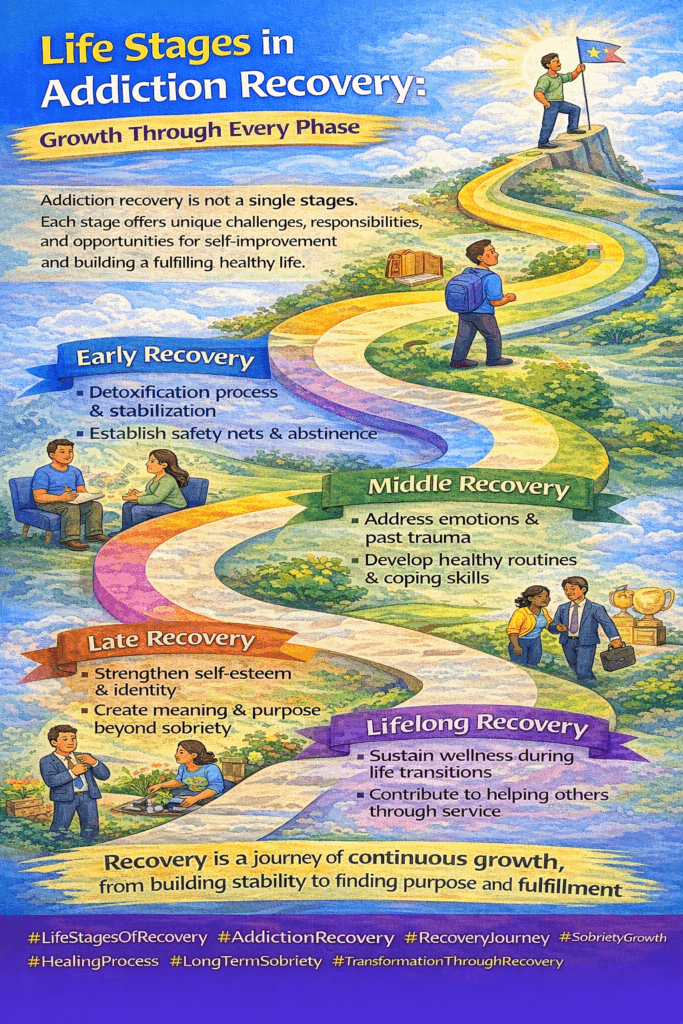
What are the life stages in addiction recovery?
Life stages in recovery refer to the evolving phases individuals move through as they progress from initial sobriety to long-term personal growth and sustained wellness.
What happens in early recovery?
Early recovery focuses on detoxification, physical stabilization, managing cravings, and establishing abstinence through treatment and support systems.
What is the focus of middle recovery?
Middle recovery emphasizes emotional healing, therapy, trauma processing, relationship repair, and rebuilding daily life routines and responsibilities.
What occurs in late recovery?
Late recovery centers on identity development, building self-esteem, exploring life purpose, and strengthening long-term relapse-prevention strategies.
What is maintenance or lifelong recovery?
This stage involves sustaining sobriety through life changes, continued personal growth, community connection, and the ongoing development of recovery skills.
Are the stages of recovery linear?
No. Recovery stages are cyclical. Individuals may move forward and backward between stages as they encounter new stressors or challenges.
Why is understanding recovery stages helpful?
Knowing what to expect reduces fear, increases motivation, and helps individuals prepare for new challenges at each phase of recovery.
Do support needs change across recovery stages?
Yes. Early recovery often needs intensive clinical support, while later stages rely more on peer networks, personal growth, and lifestyle balance.
Can someone stay in one recovery stage for a long time?
Yes. Each person progresses at their own pace. Staying engaged in recovery practices matters more than moving quickly through stages.
Does long-term recovery require ongoing effort?
Yes. Recovery is a lifelong process that involves continuous self-awareness, the use of coping skills, and support to maintain wellness.
Conclusion
Recovery from addiction is a journey marked by distinct challenges at each stage of life. From the tumultuous transitions of early adulthood to the unique stressors of late adulthood, individuals face obstacles shaped by their age, circumstances, and experiences. However, by understanding and addressing these challenges with tailored support and resources, individuals can foster resilience and navigate their journey toward sobriety and well-being. Through self-management strategies, family support, and community resources, individuals can overcome obstacles, build life skills, and achieve lasting recovery. By recognizing the diversity of challenges across different stages of life and implementing targeted interventions, we can empower individuals to thrive in their recovery journey and reclaim their lives from addiction.
Video: The hidden stages of addiction recovery nobody talks about #sobriety #transformation #facts