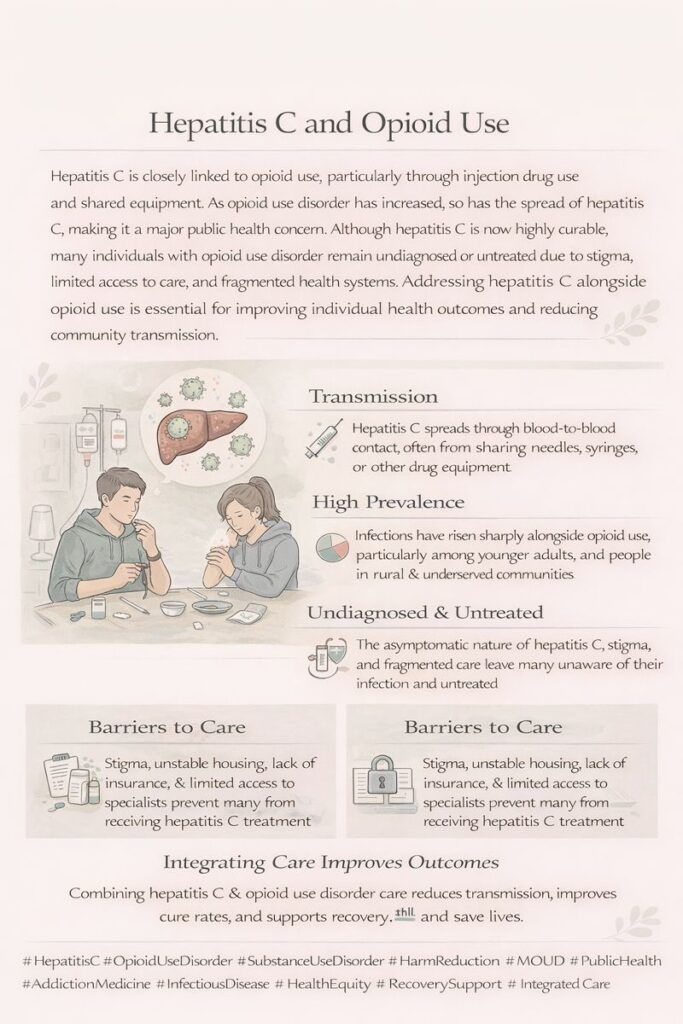
The dual epidemics of Hepatitis C (HCV) and Opioid Use Disorder (OUD) pose a significant public health challenge, especially among intravenous drug users. Tackling these interconnected issues requires a comprehensive approach that includes government action, healthcare integration, community support, and societal change. Collaborative efforts across these areas can lead to significant progress in addressing both epidemics.
“The Government’s Role in Combating Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) and Opioid Use Disorder (OUD)”
As the dual crises of Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) and Opioid Use Disorder (OUD) continue to impact communities worldwide, the role of government in addressing these intertwined public health challenges has never been more critical. A multifaceted approach focused on expanding access to treatment, enhancing harm reduction programs, and reducing stigma is essential for creating practical solutions
1. Expanding Access to Treatment
Governments must prioritize expanding access to treatment for both HCV and OUD. This involves scaling up harm reduction programs that provide essential services to vulnerable populations. Programs such as needle exchange and supervised consumption sites are proven to reduce the transmission of HCV and facilitate access to addiction treatment. By increasing funding for these initiatives, governments can ensure they reach those most in need.
2. Scaling Up Harm Reduction Programs
Harm reduction programs are vital in managing the health and safety of individuals who use drugs. These programs provide safe spaces where individuals can consume substances under supervision, significantly reducing the risk of overdose and infectious disease transmission. Needle exchange programs, for instance, allow individuals to access sterile syringes while also providing opportunities for education and outreach on HCV and OUD treatment options. Governments should work to scale these programs to meet demand and address public health concerns effectively.
3. Improving Funding and Accessibility
Policy initiatives should focus on securing increased funding for harm reduction and treatment programs. Governments can allocate resources to establish and maintain clinics that offer comprehensive care for individuals facing HCV and OUD. Ensuring these services are accessible to all, regardless of socioeconomic status or geographic location, is crucial for achieving equitable health outcomes.
4. Supporting Innovative Research
Governments can play an active role in supporting research into innovative treatment approaches for HCV and OUD. This includes investing in studies that explore new medications, therapies, and delivery models to enhance treatment efficacy and reach underserved populations. By prioritizing research, governments can ensure that the healthcare system adapts to emerging challenges and uses the most effective strategies to manage these conditions.
5. Advocating for Reduced Stigma
Reducing the stigma associated with addiction and infectious diseases is critical for encouraging individuals to seek help. Governments can lead efforts to educate the public about HCV and OUD, dispelling myths and promoting understanding. Public awareness campaigns that highlight the importance of treatment and harm reduction can foster a more compassionate approach to those affected by these crises.
6. Collaborative Approaches
Collaboration among government agencies, healthcare providers, and community organizations is essential for a comprehensive response. By working together, these stakeholders can create a unified strategy to address the complexities of HCV and OUD. Interdisciplinary teams can develop integrated care models that combine medical treatment, mental health support, and social services to meet the diverse needs of individuals in recovery.
Governments have a vital role in addressing the dual crises of HCV and OUD. Expanding access to treatment, enhancing harm reduction programs, supporting research, and advocating for stigma reduction can create a more effective and compassionate healthcare landscape. Together, these efforts can lead to improved health outcomes for individuals and communities, ultimately breaking the cycle of addiction and disease. A proactive government approach will save lives and foster healthier, more resilient communities for future generations.
“The Importance of Integrating Hepatitis C and Opioid Use Disorder Screening and Treatment in Healthcare Systems”
The intertwining crises of the Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) and Opioid Use Disorder (OUD) pose significant public health challenges, necessitating a comprehensive approach within healthcare systems. Integrating screening and treatment for both conditions is essential and a critical step toward improving patient outcomes and promoting overall community health.
1. Routine Screening as Standard Care
Routine screening for Hepatitis C should become a fundamental component of standard care for individuals diagnosed with Opioid Use Disorder. Many individuals with OUD are at a higher risk of contracting HCV due to the methods of drug use, such as sharing needles. Early detection of Hepatitis C is crucial, as it allows for timely intervention, potentially leading to more effective treatment and significantly better health outcomes. Integrating screening into the regular assessment process ensures that HCV is not overlooked and that individuals receive the care they need.
2. Training Healthcare Providers
Healthcare providers play a pivotal role in managing both HCV and OUD. They must receive training to concurrently understand the complexities of treating these interconnected conditions. This training should include the latest treatment protocols, the potential interactions between HCV therapies and OUD medications, and strategies for addressing the psychological aspects of both conditions. Equipped with this knowledge, providers can offer a coordinated approach that supports their patients’ physical and mental health.
3. Coordinated Care for Improved Outcomes
Integrating HCV and OUD treatment can streamline care, reducing fragmentation often experienced by patients. A coordinated approach means that healthcare providers can address both conditions simultaneously, ensuring that individuals do not have to navigate separate systems for their care. This integration is particularly beneficial for patients with complex needs, as it allows for holistic treatment plans that consider the interplay between physical health, addiction, mental health, and social support.
4. Addressing Psychological Aspects
Both HCV and OUD can have profound psychological effects, including anxiety, depression, and stigma. By integrating care, healthcare providers can offer comprehensive mental health support alongside medical treatment. This can involve counseling, support groups, and resources that address the emotional and psychological challenges faced by individuals dealing with these conditions. Acknowledging the mental health component is essential for fostering recovery and promoting overall well-being.
5. Streamlining Care Pathways
The integration of screening and treatment can lead to more efficient care pathways. Patients will benefit from a unified approach that reduces the number of appointments and the burden of navigating multiple providers. By creating streamlined diagnosis, treatment initiation, and follow-up processes, healthcare systems can enhance patient engagement and adherence to treatment plans, ultimately leading to improved health outcomes.
6. Enhancing Public Health Initiatives
Integrating screening and treatment within healthcare systems also supports broader public health initiatives. By identifying and treating individuals with HCV and OUD, healthcare providers can help reduce the prevalence of these conditions in the community. Early treatment of HCV can prevent the progression to chronic liver disease and lower transmission rates. At the same time, effective management of OUD can reduce overdose deaths and improve the quality of life for individuals and families.
Integrating screening and treatment for Hepatitis C and Opioid Use Disorder within healthcare systems is essential for addressing the complex relationship between these two public health issues. By prioritizing routine screening, training healthcare providers, and offering coordinated care, we can improve patient outcomes and promote holistic health. This integrated approach not only supports individuals on their path to recovery but also enhances the overall health of our communities, paving the way for a healthier future. As we progress, healthcare systems must embrace this integration to ensure all individuals receive the comprehensive care they deserve.
“Empowering Communities to Combat the Dual Epidemics of Hepatitis C and Opioid Use Disorder”
As the dual epidemics of Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) and Opioid Use Disorder (OUD) continue to challenge public health, communities are stepping up to play a pivotal role in education and support. Community-based programs are uniquely positioned to provide critical resources, information, and a supportive environment that can significantly impact at-risk populations.
1. Education and Awareness
One of the primary responsibilities of communities is to educate their members about the realities of HCV and OUD. Many individuals at risk for these conditions may lack essential knowledge about their significance, the importance of screening, and the available treatment options. Communities can disseminate accurate information and debunk myths surrounding these health issues by organizing workshops, seminars, and informational campaigns. This education helps individuals understand the risks associated with opioid use and the potential consequences of Hepatitis C infection, empowering them to take proactive steps toward their health.
2. Accessible Screening and Treatment Resources
Communities can facilitate access to screening and treatment services by establishing partnerships with local healthcare providers. Providing convenient and confidential screening options can encourage individuals to get tested for HCV, particularly those who may be hesitant to seek care due to stigma or fear. Community health events can be organized to offer these services in a welcoming, nonjudgmental environment, ensuring individuals feel comfortable seeking the help they need.
3. Support Services and Peer Support Groups
Support services are essential for individuals navigating the challenges of HCV and OUD. Counseling services can provide mental health support, helping individuals cope with the emotional aspects of their conditions. Additionally, peer support groups can offer a safe space for individuals to share their experiences, learn from others, and build a network of encouragement. These groups foster a sense of community and belonging, benefiting those who feel isolated or stigmatized.
4. Empowering Individuals to Seek Help
By fostering a supportive environment, communities can empower individuals to seek help and adhere to treatment plans. This empowerment can take many forms, from providing resources and information to encouraging individuals to advocate for their health. Community leaders and organizations can significantly promote messages of hope and recovery, emphasizing that individuals can lead fulfilling lives while managing HCV and OUD.
5. Reducing Stigma
The stigma surrounding HCV and OUD often prevents individuals from seeking the care they need. Communities can take active steps to reduce this stigma by promoting open conversations about these health issues and normalizing discussions around addiction and infectious diseases. Awareness campaigns can highlight the stories of individuals who have successfully managed their conditions, showcasing the importance of compassion and understanding.
6. Collaboration and Partnership
Addressing the dual epidemics effectively requires collaboration among various stakeholders, including healthcare providers, local government, non-profit organizations, and community members. By working together, communities can create comprehensive programs that address the multifaceted needs of individuals affected by HCV and OUD. This collaborative approach ensures that resources are maximized and individuals receive holistic support.
Communities are on the front lines of addressing the dual epidemics of Hepatitis C and Opioid Use Disorder through education, support, and empowerment. By providing crucial information about these conditions, offering accessible screening and treatment resources, and fostering supportive environments, communities can play a transformative role in the lives of individuals affected by HCV and OUD. As we progress, communities must continue their efforts to break down barriers and promote a culture of understanding and compassion. Together, we can combat these epidemics and pave the way for healthier futures for all.
“Harnessing the Power of Social Media to Combat Stigma Around HCV and Opioid Use Disorder”
In today’s digital age, social media platforms hold immense potential to influence public perception and foster positive change. When it comes to addressing the dual challenges of Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) and Opioid Use Disorder (OUD), these platforms can be particularly effective in raising awareness, reducing stigma, and promoting a compassionate understanding of those affected by these conditions.
1. Educating the Public
Social media campaigns can serve as powerful educational tools, disseminating accurate information about HCV and OUD to a broad audience. Organizations can challenge common misconceptions and present the realities of these health issues by utilizing various formats—such as infographics, videos, and live Q&A sessions. This proactive approach informs the public and encourages conversations that can lead to increased understanding and empathy.
2. Challenging Misconceptions
Stigmas surrounding HCV and OUD often stem from misunderstanding and fear. Social media provides a platform for advocacy groups, healthcare professionals, and individuals with lived experiences to share evidence-based information and personal stories that challenge these misconceptions. By humanizing the narratives of those affected, social media can shift perspectives, illustrating that addiction and infectious diseases are complex issues that require compassion and support rather than judgment.
3. Sharing Stories of Recovery
Personal stories have the power to inspire and motivate others. Social media allows individuals to share their journeys of recovery from OUD or their experiences living with HCV. These narratives can resonate deeply with those facing similar challenges, offering hope and encouragement. Highlighting successes and milestones empowers individuals and reinforces the message that recovery is possible and worth pursuing.
4. Promoting Harm Reduction Strategies
Harm reduction strategies are essential in managing both HCV and OUD, yet they are often misunderstood or overlooked. Social media can play a pivotal role in promoting these strategies, such as safe injection practices, needle exchange programs, and medication-assisted treatment (MAT). By educating the public on the effectiveness of harm reduction, social media can shift the conversation toward evidence-based solutions that prioritize health and safety.
5. Normalizing Treatment
One of the key barriers to seeking help for HCV and OUD is the stigma attached to treatment. Social media can help normalize discussions around treatment options, emphasizing that seeking help is a courageous and essential step toward recovery. Campaigns that spotlight healthcare providers’ roles in supporting individuals can also encourage those in need to reach out for assistance, reinforcing that they are not alone in their struggles.
6. Building Community Support
Social media platforms facilitate the creation of online communities where individuals can connect, share experiences, and offer support. These spaces can be invaluable for those affected by HCV and OUD, providing a sense of belonging and understanding. Engaging with peers with similar experiences can enhance motivation to seek treatment and foster resilience.
Social media has the unique ability to transform the dialogue surrounding HCV and Opioid Use Disorder. By leveraging these platforms to raise awareness, educate the public, challenge misconceptions, and share personal stories, we can create a more compassionate understanding of these conditions. As we harness the power of social media, we pave the way for a society that supports individuals in their recovery journeys and encourages others to seek help without fear of judgment. Together, we can work toward reducing stigma and fostering a culture of understanding and healing for all.
“Fostering a Culture of Understanding: A Key to Tackling the Dual Epidemics of Addiction and Infectious Diseases”
As society grapples with the dual epidemics of addiction and infectious diseases, it becomes increasingly clear that a culture of understanding and support is essential for effective intervention and recovery. The stigma surrounding these issues can create barriers that prevent individuals from seeking the help they need. By evolving societal attitudes to prioritize empathy and support over judgment, we can foster an environment conducive to healing and recovery.
1. Emphasizing Empathy Over Judgment
The first step in building a culture of understanding is to change the narrative around addiction and infectious diseases. Too often, individuals struggling with these issues face harsh judgment and stigmatization. Society must recognize that addiction is a complex health condition influenced by various factors, including genetics, environment, and mental health. Promoting empathy can help individuals feel seen and understood, reducing feelings of shame and isolation.
2. Encouraging Open Dialogues
Open and honest conversations about addiction and infectious diseases are vital for breaking down stigma. Schools, workplaces, and community organizations should create safe spaces for discussions that allow individuals to share their experiences and seek support without fear of repercussion. Educational programs that include information about the realities of addiction and its intersection with infectious diseases can foster a more informed community, enabling individuals to approach these topics with compassion.
3. Promoting Supportive Environments
Supportive environments are key to encouraging individuals to seek treatment. Workplaces and schools can implement policies that prioritize mental health and provide resources for those struggling with addiction or related health issues. Initiatives such as employee assistance programs, mental health days, and wellness workshops can create an atmosphere where seeking help is accepted and encouraged. Similarly, schools can integrate mental health education into their curricula, teaching students the importance of support and understanding.
4. Building Community Connections
Communities play a crucial role in fostering understanding and support. Local organizations can facilitate peer support groups, mentorship programs, and community events that promote awareness and education. By connecting individuals with shared experiences, communities can offer a sense of belonging that encourages recovery. Additionally, outreach to marginalized populations can help ensure that all individuals have access to the resources and support they need.
5. Advocating for Policy Changes
On a larger scale, advocating for policy changes that support individuals affected by addiction and infectious diseases is essential. This includes pushing for funding for treatment programs, harm reduction initiatives, and public health campaigns that raise awareness about the importance of empathy and understanding. By influencing policy, we can create systemic changes that promote recovery and support for all individuals.
The dual epidemics of addiction and infectious diseases require a comprehensive response rooted in a culture of understanding and support. By shifting societal attitudes to emphasize empathy, encouraging open dialogues, promoting supportive environments, building community connections, and advocating for policy changes, we can dismantle the stigma that keeps individuals from seeking help. Together, we can create a society where everyone feels empowered to pursue treatment and support, paving the way for healing and recovery for all.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some common questions:
Why is hepatitis C common among people with opioid use disorder?
Frequent injection, limited access to sterile supplies, unstable housing, and barriers to healthcare increase infection risk and reduce opportunities for early diagnosis and treatment.
Does hepatitis C cause symptoms right away?
Often no. Many people have no symptoms for years, which is why routine screening is critical for people with opioid use disorder.
How severe is untreated hepatitis C?
Without treatment, hepatitis C can lead to liver scarring, cirrhosis, liver failure, or liver cancer over time.
Is hepatitis C curable?
Yes. Modern antiviral medications can cure hepatitis C in over 95% of cases, usually with 8–12 weeks of oral treatment.
Can people actively using opioids be treated for hepatitis C?
Yes. Active substance use is not a contraindication. Studies show high cure rates when treatment is offered with appropriate support.
How does stigma affect hepatitis C treatment?
Stigma may prevent people from seeking testing or care and may lead providers to delay treatment unnecessarily, worsening outcomes.
How can opioid use disorder treatment help prevent hepatitis C?
Medications for opioid use disorder reduce injection frequency, lowering transmission risk. Counseling and support improve engagement in healthcare.
Conclusion
The dual epidemics of Hepatitis C and Opioid Use Disorder require a coordinated and compassionate approach to address them effectively. By enhancing government support, integrating healthcare services, leveraging community resources, utilizing social media for awareness, and fostering societal understanding, we can make meaningful progress in combating these public health challenges. Together, we can create an environment that supports individuals in their recovery journey and helps curb the impact of these interconnected epidemics.
Video: Needle Sharing Consequences That Shock People #hepatitisC #epidemic #warning