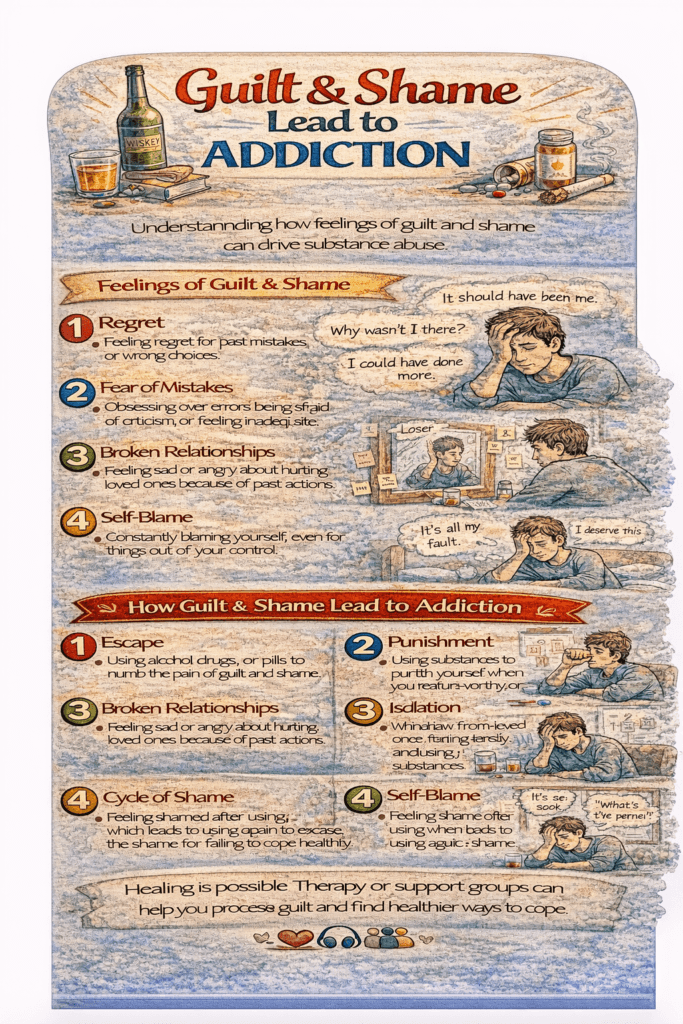
In addiction prevention, acknowledging the potent impact of guilt and shame is essential. Stemming from a sense of responsibility and inadequacy, these emotions significantly contribute to addiction development. This exploration delves into how guilt and shame act as precursors to addictive behaviors, highlighting the need for preventive strategies. We’ll uncover self-management techniques for empowerment, explore the crucial role of family support, and scrutinize community resources fostering a supportive societal foundation for those dealing with these emotions. Together, these approaches provide a comprehensive perspective on addiction prevention by addressing the root causes of guilt and shame at personal, familial, and community levels.
Understanding the Link Between Guilt, Shame, and Addiction
Guilt and shame are powerful emotions that can profoundly influence an individual’s mental health and behavior. When left unaddressed, these emotions often play a significant role in the development and perpetuation of addiction. Understanding how guilt and shame contribute to addiction is crucial for effective intervention and recovery.
How Guilt and Shame Lead to Addiction
- Coping Mechanism
Guilt and shame can be overwhelming emotions, leading individuals to seek temporary relief through substances or addictive behaviors. This reliance provides a momentary escape from emotional pain, making addiction an appealing coping mechanism. - Self-Medication
Often rooted in trauma, past mistakes, or unresolved conflicts, guilt and shame can drive individuals to self-medicate. Substances or addictive behaviors act as emotional anesthetics, numbing the discomfort these feelings bring. - Cycle of Escapism
Addiction can create a vicious cycle of escapism. The initial relief from guilt and shame reinforces continued use, while the resulting behaviors often generate more guilt and shame, perpetuating dependence on the addictive substance or activity. - Low Self-Esteem
Guilt and shame are closely tied to low self-esteem and negative self-perception. Feeling unworthy of forgiveness or redemption can lead to hopelessness, with addiction providing a fleeting sense of relief or self-worth. - Social Isolation
Fear of judgment or stigma may cause individuals to withdraw from others, exacerbating feelings of loneliness. In isolation, addictive behaviors can become a sole means of coping, further entrenching the addiction. - Maintaining Secrecy
Guilt and shame often drive individuals to conceal their struggles. This secrecy creates an environment where addiction can flourish unchecked, as the behavior is hidden from potential support networks. - Negative Coping Patterns
Guilt and shame disrupt healthy problem-solving skills, paving the way for addiction as a maladaptive coping strategy. Instead of addressing the root causes, individuals may turn to substances or behaviors that provide quick, temporary relief. - Cycle of Self-Destruction
For some, guilt and shame lead to a self-destructive mindset. They may feel they deserve the negative consequences of addiction, reinforcing the belief that they are unworthy of change or happiness.
Breaking the Cycle: Addressing Guilt and Shame in Addiction Recovery
- Explore Root Causes
Therapy provides a safe space to uncover and address the origins of guilt and shame, helping individuals gain clarity and perspective on their emotions. - Promote Self-Forgiveness
Encouraging self-forgiveness is essential in breaking free from guilt and shame. Learning to accept past mistakes as part of the human experience fosters healing and growth. - Build Healthy Coping Mechanisms
Therapy and support groups can teach individuals healthier ways to manage emotions, such as mindfulness, journaling, or engaging in positive activities. - Foster Resilience and Self-Esteem
Programs focused on building self-worth and resilience can help individuals replace negative self-perceptions with a more balanced, compassionate view of themselves. - Create Support Networks
Overcoming guilt and shame often requires a supportive environment where individuals feel accepted and understood. Community support and group therapy can play a critical role.
By addressing the interplay between guilt, shame, and addiction, individuals can break the destructive cycle and pave the way for meaningful recovery. Emphasizing self-compassion, resilience, and healthier coping strategies is key to lasting change.
Self-Management Strategies to Address Guilt and Shame and Prevent Addiction
Guilt and shame are intense emotions that, when left unmanaged, can contribute to unhealthy coping mechanisms such as addiction. By addressing these emotions proactively, individuals can cultivate a healthier mindset and reduce the risk of reliance on addictive behaviors. Here are self-management strategies to cope with guilt and shame effectively:
1. Self-Reflection
- Take time to reflect on the sources of guilt and shame.
- Identifying underlying issues helps address root causes, fostering clarity and growth.
2. Mindfulness and Meditation
- Practice mindfulness to stay grounded in the present moment.
- Techniques like deep breathing or meditation can reduce self-judgment and detach from negative thoughts.
3. Positive Affirmations
- Combat negative self-talk by repeating affirmations that emphasize self-worth and resilience.
- Regularly remind yourself of your capacity for growth and healing.
4. Set Realistic Goals
- Establish achievable, smaller goals that build toward larger objectives.
- A sense of accomplishment can counteract feelings of inadequacy and foster motivation.
5. Seek Professional Support
- Reach out to therapists or counselors for guidance in exploring guilt and shame.
- Professional support offers tools for coping and a safe space for emotional exploration.
6. Practice Forgiveness
- Acknowledge past mistakes and allow yourself to learn from them.
- Self-forgiveness helps break free from cycles of guilt and shame, promoting emotional liberation.
7. Develop Healthy Coping Mechanisms
- Engage in activities like exercise, art, or hobbies that bring joy and relaxation.
- Healthy outlets can replace harmful behaviors and reduce emotional distress.
8. Build a Support System
- Surround yourself with a trusted network of friends, family, or support groups.
- Sharing your emotions diminishes isolation and reinforces a sense of belonging.
9. Educate Yourself
- Learn about addiction and emotional health to gain insight into practical strategies for managing guilt and shame.
- Understanding empowers informed decision-making and resilience.
10. Gratitude Practice
- Focus on positive aspects of life through daily gratitude exercises.
- Gratitude helps shift attention away from negative emotions and enhances well-being.
11. Journaling
- Write down your thoughts, emotions, and experiences regularly.
- Journaling provides a constructive outlet for processing and understanding your emotional state.
12. Celebrate Progress
- Recognize even small achievements as steps toward self-improvement.
- Celebrating progress fosters pride and reinforces positive self-image.
By combining these self-management strategies with professional guidance, individuals can effectively address the emotional burdens of guilt and shame. Creating a healthier emotional foundation not only improves overall mental health but also reduces the likelihood of turning to addiction as a means of coping.
The Role of Family Support in Managing Guilt and Shame to Prevent Addiction
Guilt and shame are powerful emotions that can lead individuals to seek unhealthy coping mechanisms, including addiction. Family support plays a crucial role in helping individuals healthily manage these emotions, fostering resilience, and preventing the onset or escalation of addictive behaviors. Here are some family support strategies to consider:
1. Open Communication
- Create an environment where family members feel safe to express their feelings, mistakes, and struggles.
- A non-judgmental space for honest discussions about guilt and shame encourages emotional transparency and healing.
2. Empathy and Understanding
- Practice empathy by genuinely listening to the person experiencing guilt or shame.
- Offer emotional support without criticism or judgment, helping them feel understood and accepted.
3. Normalize Mistakes
- Reinforce the idea that making mistakes is a natural part of being human.
- Share personal stories of challenges and growth, showing that errors can lead to valuable lessons and growth.
4. Encourage Professional Help
- If guilt and shame become overwhelming, suggest seeking professional help such as therapy or counseling.
- Offer to assist in finding resources or support networks to ensure the individual receives the help they need.
5. Participate in Family Therapy
- Consider family therapy sessions to address dynamics and create a shared space for healing.
- Family therapy can foster understanding, improve communication, and provide collective support in managing guilt and shame.
6. Educate the Family
- Educate all family members about the impact of guilt and shame on mental health and addiction.
- Understanding these issues can reduce stigma and encourage compassion, strengthening the family’s support network.
7. Set Healthy Boundaries
- Establish clear, respectful boundaries within the family.
- Ensure that each member’s needs and expectations are communicated and honored, fostering mutual respect.
8. Promote Forgiveness
- Emphasize the importance of self-forgiveness and forgiving others within the family.
- Forgiveness helps break the cycle of guilt and shame, creating a healthier, more supportive family atmosphere.
9. Participate in Support Groups
- Explore support groups for individuals and families coping with guilt and shame.
- Support groups provide shared experiences, resources, and a sense of community that can alleviate feelings of isolation.
10. Celebrate Achievements
- Acknowledge and celebrate personal and family achievements, no matter how small.
- Positive reinforcement helps boost self-esteem and counters the feelings of inadequacy that often accompany guilt and shame.
11. Model Healthy Coping Mechanisms
- Demonstrate effective coping strategies within the family, such as stress management and emotional regulation.
- By modeling healthy behavior, family members can learn to address negative emotions constructively.
12. Encourage Self-Care
- Promote self-care practices like exercise, hobbies, and relaxation techniques.
- Encouraging self-care helps manage stress and enhances mental well-being, making it less likely that individuals will turn to unhealthy coping strategies.
By implementing these family support strategies, families can create a nurturing environment where individuals feel heard, supported, and empowered. This approach not only helps in managing guilt and shame but also reduces the risk of turning to addiction as a means of escape or coping. A compassionate, open, and understanding family dynamic is essential in breaking the cycle of addiction and fostering long-term emotional healing.
Community Resource Strategies for Preventing Addiction by Addressing Guilt and Shame
Guilt and shame are powerful emotions that can fuel addiction, often serving as coping mechanisms for individuals struggling with these intense feelings. To prevent addiction on a larger scale, communities can play a crucial role in addressing these emotions through accessible resources and support systems. Here are some effective community-based strategies to help prevent addiction related to guilt and shame:
1. Educational Programs
- Implement community-wide educational programs focused on mental health, emotional well-being, and coping strategies.
- Workshops and seminars can raise awareness about the adverse effects of guilt and shame, providing community members with tools to address these emotions before they lead to harmful behaviors.
2. Community Counseling Services
- Establish accessible counseling services where individuals can seek professional help for managing guilt, shame, and related emotional struggles.
- Collaborating with mental health professionals to offer affordable or free services ensures that no one is left without support due to financial barriers.
3. Support Groups
- Facilitate support groups specifically designed for individuals dealing with guilt and shame.
- Peer support can be instrumental in reducing feelings of isolation, offering a sense of belonging, and helping individuals recognize they are not alone in their struggles.
4. Community Events
- Organize community events that focus on mental health awareness and destigmatizing discussions around guilt and shame.
- Panel discussions, guest speakers, and community activities can encourage open conversations and help create a supportive atmosphere for individuals facing these emotions.
5. Art and Expressive Therapies
- Introduce community-based art and expressive therapy programs.
- Creative outlets such as art classes, music workshops, and writing sessions provide individuals with alternative ways to process and express their emotions, offering a therapeutic way to cope with guilt and shame.
6. Community-Based Therapy Programs
- Collaborate with local mental health organizations to establish community-based therapy programs, offering group sessions and workshops for individuals struggling with guilt and shame.
- These programs can create a space for shared healing and promote collective well-being within the community.
7. Online Resources and Helplines
- Develop and promote online resources, including helplines and websites, to provide information, support, and counseling services for individuals experiencing guilt and shame.
- These resources ensure that individuals can access help remotely, making it easier for those who are hesitant or unable to seek in-person support.
8. Crisis Intervention Services
- Establish crisis intervention services that provide immediate support for individuals experiencing acute distress related to guilt and shame.
- Crisis hotlines or response teams can offer timely assistance, helping to de-escalate emotional crises and provide guidance before the situation worsens.
9. Community Awareness Campaigns
- Launch awareness campaigns to challenge stigma and encourage open conversations about mental health.
- Promote the understanding that seeking help is a sign of strength, not weakness, and that no one should face guilt or shame alone.
10. Collaboration with Faith-Based Organizations
- Partner with local faith-based organizations to create a supportive network for individuals dealing with guilt and shame.
- Faith communities can offer spiritual guidance, counseling, and a sense of belonging, providing additional layers of support for those in need.
11. Employment Assistance Programs
- Collaborate with local businesses and employers to implement mental health-friendly employment assistance programs.
- By acknowledging and addressing the mental health needs of employees, businesses can create a work environment that supports individuals dealing with guilt, shame, and other emotional struggles.
12. Recreation and Leisure Programs
- Develop recreation and leisure programs within the community, such as sports teams, fitness classes, and hobby groups.
- These activities promote positive mental health by providing healthy outlets for stress, enhancing social connections, and reducing the likelihood that individuals will turn to unhealthy coping mechanisms.
By implementing these community resource strategies, communities can foster a supportive and understanding environment that helps address the root causes of guilt and shame. Creating spaces for healing, open communication, and personal growth will not only reduce the risk of addiction but also build a stronger, more resilient community.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some common questions:
Conclusion
The intricate interplay between guilt, shame, and addiction underscores the need for comprehensive strategies to prevent the destructive trajectory that can unfold. As individuals grapple with these complex emotions, empowering self-management techniques become indispensable in fostering resilience. Equally vital is the role of familial bonds, where strong family support acts as a stabilizing force. Beyond individual and familial spheres, community resource strategies play a pivotal role in creating a supportive environment. By addressing guilt and shame at multiple levels, we can collectively build a resilient foundation that not only prevents addiction but also fosters a culture of understanding, compassion, and recovery. In this holistic approach, individuals find strength within themselves, families become pillars of support, and communities form a united front against the insidious grip of addiction.
Video: