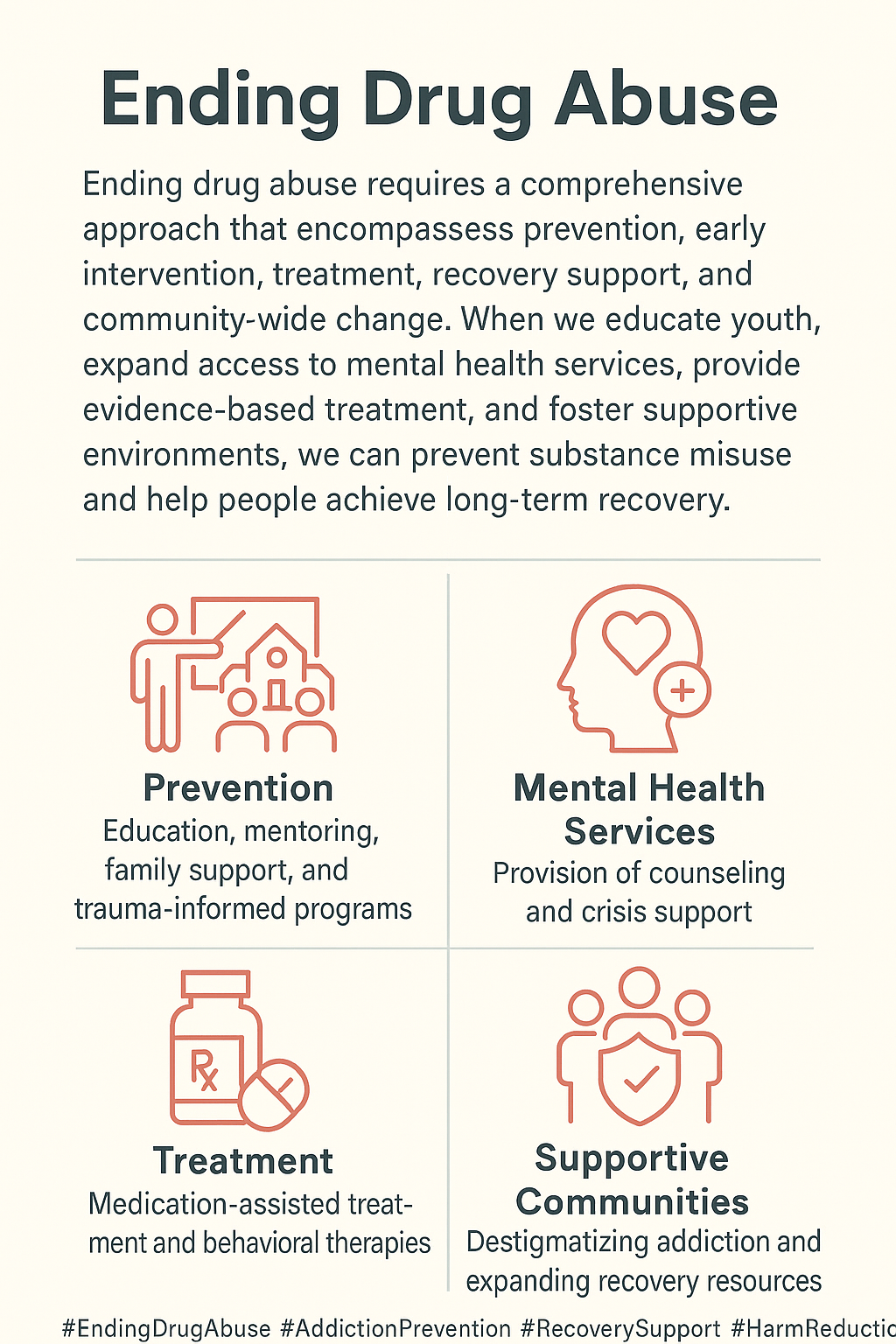
Ending drug abuse requires a multifaceted approach, including practical strategies like seeking professional help and building supportive networks. Challenges such as limited access to treatment and stigma can hinder progress. Family support is vital, offering encouragement and setting boundaries, while community resources, such as treatment programs and prevention initiatives, provide essential support. Combining these elements creates a comprehensive strategy for overcoming drug abuse and fostering long-term recovery.
Effective Strategies for Ending Drug Abuse and Achieving Long-Term Recovery
Ending drug abuse requires a comprehensive approach tailored to individual needs. Here are key strategies for overcoming addiction and sustaining recovery:
1. Seek Professional Help
- Medical and Psychological Support: Consult healthcare professionals for detoxification, medication-assisted treatment, and psychological counseling to address the physical and mental aspects of addiction.
- Addiction Specialists: Work with specialists who can develop a personalized recovery plan based on your unique situation and needs.
2. Build a Strong Support Network
- Support Groups: Participate in groups like Narcotics Anonymous (NA) or Alcoholics Anonymous (AA) to share experiences and connect with others facing similar struggles.
- Family and Friends: Engage supportive family members and friends who can provide encouragement, accountability, and help during challenging times.
3. Develop a Personalized Treatment Plan
- Assessment: Undergo a comprehensive evaluation to determine the severity of addiction and any co-occurring mental health conditions.
- Tailored Plan: Collaborate with professionals to create a treatment plan that addresses your needs, goals, and preferences.
4. Address Underlying Issues
- Therapy: Participate in individual or group therapy to uncover and address the root causes of drug abuse, such as trauma, stress, or mental health disorders.
- Skill Building: Learn coping skills, stress management techniques, and strategies for emotional regulation to reduce the risk of relapse.
5. Make Lifestyle Changes
- Healthy Habits: Adopt a healthy lifestyle with regular exercise, a balanced diet, and adequate sleep to improve physical and mental well-being.
- Avoid Triggers: Identify situations, people, or environments that may trigger cravings and take steps to avoid them.
6. Set Realistic Goals
- Short-Term and Long-Term Goals: Establish achievable goals, such as gradually reducing drug use or reaching specific recovery milestones.
- Celebrate Progress: Recognize and celebrate small successes to stay motivated and maintain a positive outlook on recovery.
7. Utilize Community Resources
- Local Services: Access community resources, including addiction treatment centers, counseling, and educational programs to support your recovery journey.
- Public Health Programs: Participate in public health initiatives that provide information and resources for substance abuse prevention and recovery.
8. Stay Committed to Recovery
- Ongoing Support: Continue attending therapy, support groups, and follow-up appointments to maintain progress.
- Adapt and Adjust: Be open to adjusting your treatment plan and seeking additional help when challenges arise.
9. Focus on Relapse Prevention
- Develop a Plan: Create a relapse prevention plan that outlines coping strategies and support mechanisms to stay on track.
- Monitor Warning Signs: Be aware of relapse warning signs and have a strategy to address them quickly.
10. Educate Yourself
- Understanding Addiction: Learn about addiction, recovery strategies, and available treatment options to make informed decisions.
- Stay Informed: Keep up with the latest research and resources to support long-term recovery.
Implementing these strategies can significantly enhance the chances of successfully overcoming drug abuse and achieving lasting recovery. By seeking professional help, building a support network, and making lifestyle changes, individuals can reclaim their lives and sustain sobriety.
Overcoming Barriers to Ending Drug Abuse: A Path to Recovery
Successfully implementing strategies for ending drug abuse can be challenging due to various barriers that hinder individuals’ recovery journeys. These obstacles can stem from personal circumstances, societal factors, and systemic issues. Here are some of the most common barriers:
1. Limited Access to Professional Help
- Cost: Addiction treatment can be prohibitively expensive, and not everyone has health insurance that covers rehabilitation, therapy, or medication-assisted treatment.
- Availability: In many rural or underserved areas, specialized addiction treatment providers or facilities may be scarce.
- Stigma: Societal stigma surrounding addiction often discourages individuals from seeking help due to fear of judgment or discrimination.
2. Weak or Unsupportive Social Networks
- Lack of Support: Family and friends may not fully understand addiction or may not provide the necessary support, undermining the recovery process.
- Enabling Relationships: Being surrounded by individuals who use drugs or alcohol can make it more challenging to maintain sobriety and avoid relapse.
3. Reluctance to Seek Treatment
- Denial: Many individuals struggling with substance use may not recognize the severity of their addiction or may deny the need for help.
- Fear of Withdrawal: The fear of experiencing withdrawal symptoms can deter individuals from seeking detox and treatment.
4. Co-Occurring Mental Health Issues
- Dual Diagnosis: Many individuals with substance use disorders also have underlying mental health issues, such as depression or anxiety, complicating recovery efforts if not adequately addressed.
- Lack of Integrated Care: Treatment programs that fail to address both addiction and mental health may not provide the comprehensive support necessary for recovery.
5. Environmental and Social Triggers
- Exposure to Triggers: Being in environments where drugs are easily accessible or associating with people who use drugs can hinder recovery efforts.
- Stress and Trauma: Ongoing stress, unresolved trauma, or socioeconomic challenges, like unemployment or housing instability, can trigger cravings or lead to relapse.
6. Lack of Knowledge or Education
- Misinformation: A lack of understanding about addiction and recovery can prevent individuals from seeking appropriate help.
- Underestimating Addiction: Some individuals and their families may not fully grasp the complexity of addiction and the need for long-term treatment and support.
7. Inadequate Relapse Prevention
- No Support Post-Treatment: Many individuals relapse after completing treatment due to a lack of continued support or follow-up care.
- High Expectations: Unrealistic expectations of a quick fix can lead to discouragement when recovery takes longer than anticipated.
8. Cultural and Societal Barriers
- Cultural Stigma: In certain cultures, addiction is perceived as a moral failing, which can deter individuals from seeking help.
- Lack of Culturally Competent Care: Treatment programs that are not tailored to diverse cultural needs can make it challenging for individuals from diverse backgrounds to feel understood and supported.
9. Legal and Systemic Barriers
- Criminalization: Often, addiction is treated as a criminal issue rather than a health issue, resulting in incarceration instead of treatment.
- Policy Gaps: Inconsistent policies regarding addiction treatment, such as restrictions on medications like methadone or buprenorphine, can hinder access to adequate care.
10. Personal Motivation and Resistance
- Lack of Motivation: Some individuals may not feel ready or motivated to quit, making it difficult to engage fully in treatment.
- Fear of Change: The challenge of changing deeply ingrained behaviors can be intimidating, leading to resistance against treatment.
Addressing these barriers to ending drug abuse requires a comprehensive approach that improves access to treatment, education, and support systems while advocating for a societal shift in how addiction is perceived and treated. Individuals can find the support and resources needed to embark on their recovery journeys by recognizing and working to overcome these challenges. We can create an environment that fosters healing, understanding, and long-term success.
Supporting Recovery: Effective Strategies for Families of Individuals Struggling with Drug Abuse
Family support plays a pivotal role in helping individuals overcome drug abuse and achieve long-term recovery. A loving and understanding family can provide the necessary foundation for healing and growth. Here are some effective strategies for family members to support their loved ones on their recovery journey:
1. Educate Yourself
- Understanding Addiction: Learn about the nature of addiction, its effects on behavior, and the treatment options available. A deeper understanding will enable you to provide informed support.
- Stay Informed: Keep up to date with the latest research and resources on addiction and recovery to better assist your loved one.
2. Foster Open Communication
- Non-Judgmental Approach: Approach conversations with empathy and understanding, avoiding blame or criticism. This creates a safe space for your loved one to share their thoughts and feelings.
- Active Listening: Listen actively to your loved one’s concerns and emotions without interrupting or making assumptions, showing that you value their perspective.
3. Encourage Professional Help
- Support Treatment: Encourage your loved one to seek professional help and actively participate in their treatment process.
- Assist with Logistics: Help schedule appointments, find treatment facilities, or arrange transportation to ensure they receive the support they need.
4. Create a Supportive Environment
- Positive Atmosphere: Foster a positive and supportive home environment that promotes recovery and reduces stress.
- Healthy Lifestyle: Encourage and participate in healthy activities together, such as exercise, hobbies, and nutritious eating, to create a wellness-oriented household.
5. Set Boundaries
- Clear Limits: Establish and maintain boundaries regarding acceptable behavior and consequences for relapses or other issues.
- Consistent Rules: Enforce boundaries consistently to create a stable, predictable environment that fosters trust and security.
6. Promote Accountability
- Supportive Monitoring: Help your loved one stay accountable to their treatment plan and recovery goals without being overly controlling.
- Encourage Self-Responsibility: Encourage your loved one to take responsibility for their actions and for their progress in recovery, fostering independence.
7. Participate in Family Therapy
- Joint Counseling: Engage in family therapy to address underlying issues, improve communication, and strengthen family dynamics.
- Shared Goals: Work with a therapist to set common goals and develop strategies to support your loved one’s recovery.
8. Manage Your Well-Being
- Self-Care: Prioritize your physical and emotional health to maintain the strength to support your loved one effectively.
- Seek Support: Consider joining support groups for families of individuals with substance use disorders to share experiences and gain additional support.
9. Encourage Healthy Coping Strategies
- Stress Management: Help your loved one develop healthy coping mechanisms for managing stress and emotional challenges.
- Skill Building: Support them in building life skills, such as problem-solving and emotional regulation, to enhance their resilience.
10. Celebrate Progress
- Acknowledge Achievements: Recognize and celebrate milestones and achievements in your loved one’s recovery journey, no matter how small.
- Positive Reinforcement: Offer encouragement and positive reinforcement to motivate continued progress and foster a sense of accomplishment.
11. Be Prepared for Relapse
- Relapse Plan: Develop a plan for managing relapse, including how to offer support and re-engage in treatment if necessary.
- Stay Committed: Maintain a supportive, non-judgmental stance, even in the face of setbacks, to help your loved one stay on track.
12. Avoid Enabling Behavior
- Avoid Providing Financial Support: Refrain from providing money or resources that could fuel the addiction.
- Promote Responsibility: Encourage your loved one to take responsibility for their recovery and address any issues independently.
By implementing these strategies, families can create a supportive and effective environment that enhances the likelihood of successful recovery from drug abuse. Family members play an essential role in the recovery process, and their understanding, encouragement, and commitment can significantly impact their loved one’s journey toward healing. Together, families can foster a sense of hope and resilience that empowers individuals to reclaim their lives.
Building a Supportive Community: Key Strategies to Address Drug Abuse and Support Recovery
Community resource strategies are essential for effectively addressing drug abuse and supporting recovery efforts. By creating a comprehensive framework of services and support, communities can foster a healthier environment that promotes healing and resilience. Here are some key strategies to consider:
1. Develop Comprehensive Treatment Programs
- Integrated Services: Establish programs that offer a range of services, including detoxification, counseling, medication-assisted treatment, and aftercare. A holistic approach addresses all aspects of an individual’s recovery.
- Accessibility: To reduce barriers to care, ensure that treatment options are accessible to diverse populations, including underserved and marginalized communities.
2. Promote Prevention and Education
- Awareness Campaigns: Implement public awareness campaigns to educate the community about the risks of drug abuse and the importance of prevention. Knowledge is a powerful tool in combating addiction.
- School Programs: Develop school-based prevention programs that educate students about substance abuse and healthy coping mechanisms, fostering resilience from a young age.
3. Supportive Housing and Rehabilitation Centers
- Rehabilitation Facilities: Create or enhance residential and outpatient rehabilitation centers that provide a supportive environment for recovery. Such facilities are crucial for individuals seeking to rebuild their lives.
- Sober Living Homes: Establish sober living homes that offer transitional housing for individuals in early recovery, allowing them to live in a drug-free environment while they adjust.
4. Community Support and Recovery Networks
- Support Groups: Facilitate support groups, such as Narcotics Anonymous (NA) or Alcoholics Anonymous (AA), to provide peer support and shared experiences. Connecting with others can be a vital component of recovery.
- Recovery Coaches: Employ recovery coaches to offer personalized support and guidance throughout recovery, helping individuals navigate challenges and stay on track.
5. Access to Healthcare Services
- Integrated Health Services: Provide access to comprehensive healthcare services, including mental health care, to address co-occurring disorders and overall well-being. Holistic health is critical for successful recovery.
- Mobile Clinics: Utilize mobile clinics to reach individuals in remote or underserved areas, ensuring that healthcare services are accessible to everyone.
6. Job Training and Employment Programs
- Vocational Training: Offer job training and educational programs to help individuals gain skills and secure employment as part of their recovery. Employment can provide stability and purpose.
- Employer Partnerships: Partner with local businesses to create job opportunities and support employment for individuals in recovery, fostering community engagement.
7. Legal and Financial Assistance
- Legal Support: Provide access to legal assistance for issues related to drug abuse, such as navigating the justice system or expunging criminal records. Legal barriers can hinder recovery efforts.
- Financial Aid: Offer financial support or assistance programs to help individuals access treatment and stabilize their lives during recovery.
8. Family and Caregiver Support
- Family Counseling: Provide family counseling and education to help families understand addiction and support their loved ones effectively. Informed families can play a critical role in recovery.
- Caregiver Resources: Support caregivers in managing stress and maintaining their well-being, recognizing their essential role in recovery.
9. Community Outreach and Engagement
- Community Events: Organize events and workshops to raise awareness about addiction and engage the community in recovery efforts. Building community solidarity strengthens support networks.
- Partnerships: Collaborate with local organizations, businesses, and faith communities to strengthen support networks and resources and create a united front against addiction.
10. Advocacy and Policy Development
- Policy Advocacy: Advocate for policies that support addiction prevention, treatment, and recovery at the local, state, and national levels. Effective policies can enhance access to care.
- Funding and Resources: Seek funding to support community-based addiction programs and services to ensure sustainability and reach.
11. Evaluation and Improvement
- Data Collection: Collect and analyze data on community addiction programs to assess effectiveness and identify areas for improvement. Continuous evaluation helps refine strategies.
- Feedback Mechanisms: Implement feedback mechanisms to gather input from individuals in recovery and their families to enhance services and ensure they meet community needs.
12. Emergency Response and Harm Reduction
- Harm Reduction Programs: Develop harm reduction initiatives, such as needle exchange programs and supervised consumption sites, to reduce the risks associated with drug use. Harm reduction can save lives.
- Emergency Services: Provide emergency services, including overdose prevention and intervention programs, to address immediate needs and promote safety.
By implementing these community resource strategies, communities can create a supportive environment that addresses the complexities of drug abuse, promotes recovery, and fosters long-term positive outcomes. Collective efforts from various sectors can make a significant difference in the lives of individuals struggling with addiction, leading to healthier, more resilient communities.
Conclusion
Effectively ending drug abuse involves a multifaceted approach that addresses practical strategies, barriers, family support, and community resources. Implementing tips such as seeking professional help and developing healthy coping mechanisms is essential, but overcoming obstacles like limited access and stigma remains a significant challenge. Strong family support, through encouragement and clear boundaries, complements these efforts, while community resources, including treatment programs and prevention initiatives, provide crucial support. By integrating these elements, we create a comprehensive framework that enhances the chances of overcoming drug abuse and achieving lasting recovery.
Video: How Can We Stop Drug Abuse Together?