When discussing ways to support personal and professional growth, two approaches often come into play: enabling and empowering. Both methods aim to help individuals and groups overcome challenges, but work differently. Understanding these differences is crucial for selecting the appropriate method for each situation.
Enabling typically means offering immediate help that removes obstacles. It often involves stepping in and resolving issues directly. In contrast, empowering is about giving people the tools and confidence to handle challenges independently. While both approaches share the goal of providing support, their long-lasting effects differ significantly.
Overview of the Concepts
What is Enabling?
Enabling means providing direct assistance and removing barriers to short-term success. This method can include offering resources, handling tasks for someone, or quickly managing a crisis. Although enabling is very useful in emergencies or when immediate help is needed, it may also limit an individual’s opportunity to learn from challenges because the solution is provided rather than discovered independently.
What is Empowering?
Empowering is a process that enables individuals to address problems independently. Instead of taking over the issue, this approach focuses on building confidence and developing essential skills. Methods such as mentoring, sharing practical knowledge, and offering valuable tools are all part of empowering someone. In the long run, this practice helps resolve the present difficulty and paves the way for sustained personal and professional progress.
Who Benefits from Each Approach?
Who Benefits from Enabling?
- Individuals facing immediate crises need fast and effective solutions.
- People who, at the moment, cannot handle specific tasks on their own.
- Situations where quick intervention is more important than long-term skill building.
Who Benefits from Empowering?
- Those aiming to build lasting confidence and self-reliance.
- Individuals in settings that value independent decision-making.
- Scenarios where long-term growth and learning are prioritized over immediate fixes.
Pros and Cons: Enabling vs Empowering
Enabling: Pros & Cons
Pros:
- Offers immediate relief in critical situations.
- Quickly removes obstacles to deliver fast solutions.
- Is essential during emergencies when time is of the essence.
Cons:
- Can lead to dependency if applied too frequently.
- May hinder the development of critical problem-solving skills.
- Sometimes masks deeper issues that need long-term attention.
Empowering: Pros & Cons
Pros:
- Builds long-term self-reliance and personal confidence.
- Encourages the development of valuable skills and independent problem-solving.
- Fosters an environment of ongoing growth and resilience.
Cons:
- Takes longer to produce measurable benefits, which may not be suitable for emergencies.
- Demands significant effort and commitment from both supporters and recipients.
- Progress can be gradual as new habits and skills develop.
Detailed Comparisons: Key Features of Both Approaches
- Immediate Impact vs Long-Term Growth
Certain situations require a fast fix, while others benefit from a more gradual, steady approach. Enabling focuses on short-term actions that quickly address problems, whereas empowering is about building lasting skills that lead to sustainable development. This fundamental difference is crucial in determining which method is most appropriate. - Fostering Independence vs Creating Dependence
Encouraging autonomy is essential for long-term success. Enabling can provide quick relief but might inadvertently encourage reliance on external help. On the other hand, empowerment emphasizes self-sufficiency and helps individuals develop the confidence to solve future challenges independently. - Time and Resource Investment
Enabling typically requires fewer immediate resources and yields fast results, which is beneficial during crises. Empowering, however, requires a more significant investment of time and effort in activities such as mentoring and skill development. While its benefits take longer to materialize, they tend to offer more enduring solutions. - Cultural and Organizational Fit
The effectiveness of each approach can depend heavily on the environment in which it is applied. Some cultures value quick problem resolution and may favor enabling methods. Others, particularly those that encourage innovation and continuous learning, are more likely to see success with empowering strategies. - Long-Term Emotional Impacts
Both methods influence how people perceive themselves, but in distinct ways. While enabling might temporarily reduce stress, it can also create feelings of inadequacy if people become too reliant on outside help. Empowerment, conversely, tends to boost self-esteem and provide a sense of achievement that contributes to long-term well-being.
Real-Life Insights & Impact
In addiction settings, both enabling and empowering behaviors play critical roles, but they can have very different impacts. Here are examples of each:
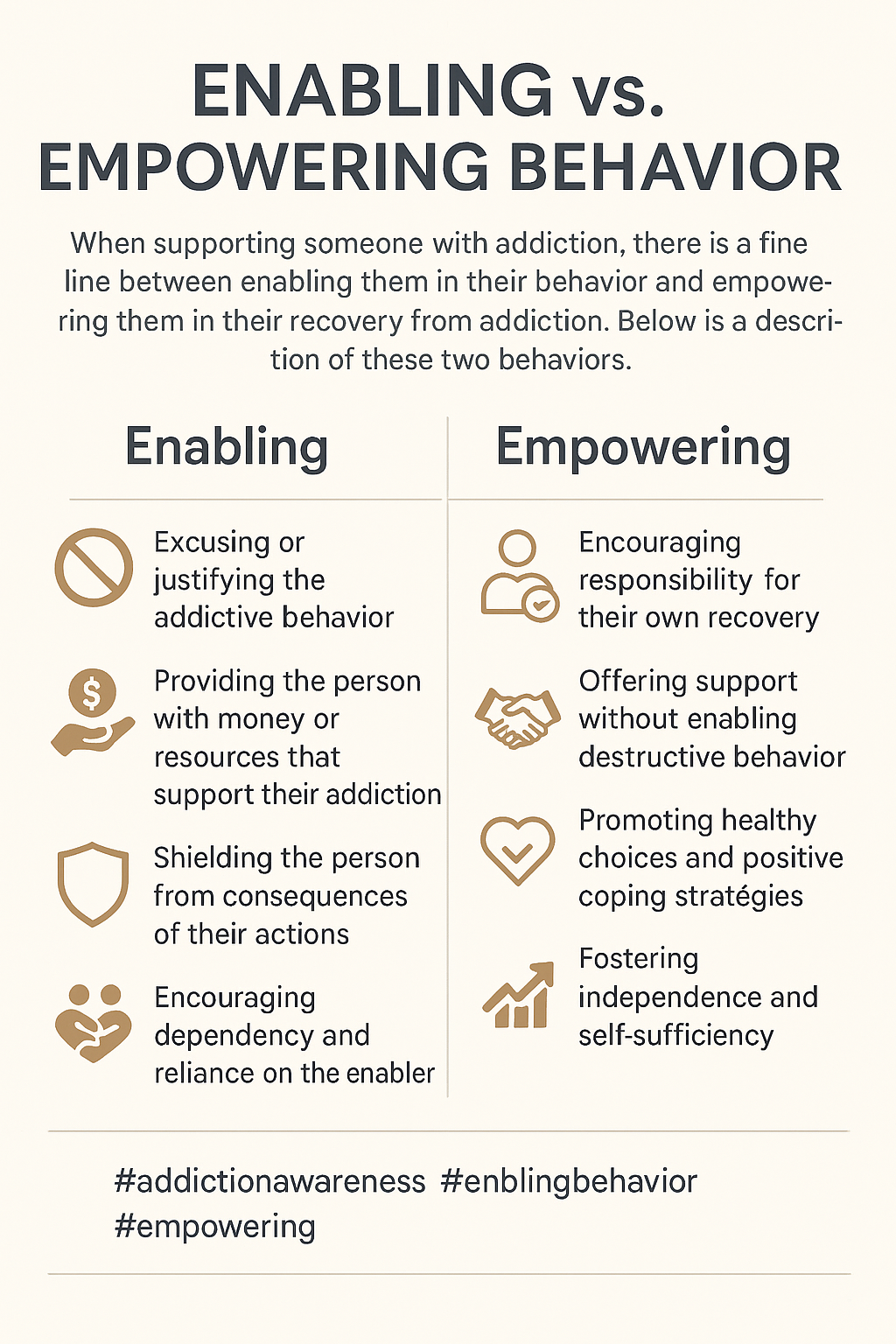
Enabling in Addiction Settings:
Enabling behaviors often contribute to an individual’s addiction by protecting them from the consequences of their actions. This can prevent them from experiencing the full impact of their behavior, thereby discouraging them from making a change.
- Bailing out a loved one: A family member constantly bails out someone with an addiction by paying their bills, legal fees, or covering up their mistakes.
- Covering up harmful behaviors: A parent might make excuses for a child’s substance use or lie to others to protect them from consequences (e.g., “They’re just going through a tough time”).
- Providing financial support despite harmful behavior: Continuing to give money to someone struggling with addiction, even when it is clear they are using it to fund their substance use.
- Allowing destructive behavior: Not setting boundaries or tolerating aggressive or abusive behavior from the person with an addiction because you don’t want to confront them or cause more conflict.
- Ignoring clear signs of relapse: A loved one may deny that someone has relapsed or downplay it, avoiding any serious discussion about treatment or recovery.
Empowering in Addiction Settings:
Conversely, empowering behaviors focus on supporting the person’s ability to take control of their recovery and make healthier choices.
- Providing emotional support: Encouraging someone to make their own treatment decisions, supporting their autonomy, and acknowledging their ability to change.
- Encouraging participation in therapy: Motivating someone to attend counseling, join a support group, or pursue other avenues of treatment by emphasizing their strengths and potential for growth.
- Setting healthy boundaries: Loving but firm boundaries help the individual understand that certain behaviors, such as substance abuse or harmful actions, will not be tolerated. This can help them understand the concepts of accountability and responsibility.
- Offering resources for self-improvement: Helping the person access tools for personal development, such as job training programs, educational opportunities, or fitness activities, that empower them to regain their independence.
- Celebrating small victories: Acknowledging and celebrating even the smallest progress helps build confidence and motivation for continued recovery.
- Encouraging self-reliance: Rather than taking over problems, guiding someone to find solutions independently fosters resilience and problem-solving skills.
In essence, enabling often leads to perpetuating the addiction, while empowering supports the individual in taking ownership of their recovery and well-being.
Final Thoughts: Which Approach to Choose?
Choosing between enabling and empowering is not always straightforward. The best approach depends on the specific circumstances, the nature of the challenges, and the long-term goals of those involved. If quick intervention is essential, enabling may be the best approach. However, if building the capacity to overcome future challenges is the priority, empowering provides a more sustainable solution.
A mix of both methods can be the most effective strategy. For instance, during an emergency, enabling techniques can help stabilize the situation, while transitioning later to an empowering strategy can build the skills needed to prevent future dependency. This shift ensures that immediate issues are resolved without sacrificing the potential for long-term growth and independence.
Ultimately, understanding the benefits and limitations of each approach is crucial. Whether facing a crisis or planning for future success, the choice between quick fixes and sustainable growth will shape how challenges are managed and overcome. Reflect on how applying these ideas might impact your personal or professional life, and consider sharing your experiences. Opening discussions about effective support strategies can lead to better decisions and help more people thrive independently.
What are your thoughts on this balance? Reflect on whether providing immediate help or investing in long-term skill development has had a significant impact on your experiences. The insights shared here will encourage you to carefully assess each situation and choose an approach that meets current needs and lays the groundwork for ongoing success.
Video: How to Stop Enabling Bad Habits Fast!