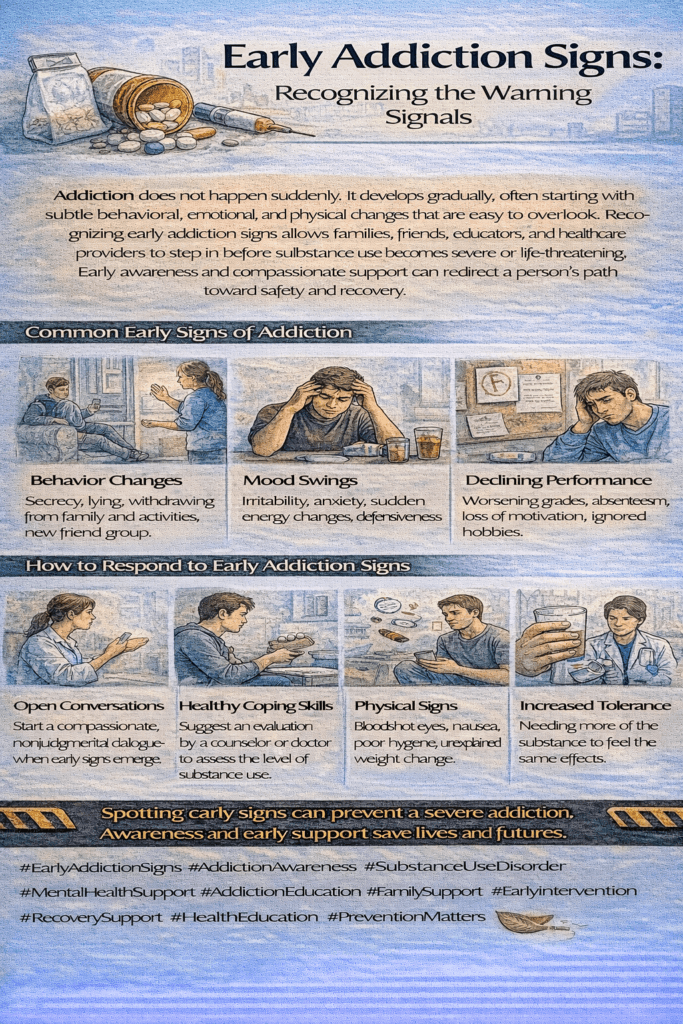
Understanding early signs of addiction is crucial for timely intervention and support. Addiction can manifest in various forms, from substance use disorders like alcohol and opioids to behavioral addictions such as gambling or internet gaming. Recognizing these signs early involves awareness of behavioral, physical, and psychological changes. Self-management strategies empower individuals to take proactive steps toward recovery, while family support systems offer emotional encouragement and practical assistance. Community strategies provide accessible resources, education, and supportive networks, forming a comprehensive approach to addressing addiction and promoting community recovery.
Recognizing Early Signs of Addiction: A Guide to Timely Intervention and Support
Early recognition of addiction can make a world of difference in helping individuals on the path to recovery. By paying close attention to changes in behavior, physical appearance, social interactions, and overall well-being, you can spot the early warning signs and take action to provide support. Prompt intervention not only improves outcomes but can also prevent further complications. Below are some tips for identifying potential signs of addiction:
1. Changes in Behavior
- Mood Swings: Sudden and noticeable mood changes, such as irritability, agitation, or unexplained euphoria, may indicate substance use.
- Withdrawal from Activities: When someone suddenly loses interest in activities, hobbies, or responsibilities they used to enjoy, it could be a sign of addiction.
- Secretive Behavior: Being secretive about daily routines, whereabouts, or spending excessive time alone may signal substance use.
2. Physical Signs
- Changes in Appearance: A decline in personal hygiene, sudden weight fluctuations, or neglect of grooming are common indicators of substance misuse.
- Health Issues: Unexplained health problems, frequent illnesses, or unusual physical symptoms that don’t have a clear medical explanation can be signs of addiction.
3. Psychological Signs
- Poor Concentration: If someone begins having difficulty focusing on tasks or maintaining attention, it could be due to substance use affecting their cognitive abilities.
- Memory Issues: Frequent forgetfulness or difficulty recalling recent events is often linked to the cognitive impairment caused by addiction.
4. Social and Interpersonal Signs
- Strained Relationships: Substance use often leads to changes in relationships, creating tension between family members, friends, or colleagues.
- Isolation: Spending more time alone or with a new social group that might be associated with substance use can indicate a developing addiction.
5. Financial and Legal Issues
- Money Problems: Individuals struggling with addiction may have unexplained financial difficulties, frequently borrow money, or even sell personal belongings to fund their substance use.
- Legal Troubles: Legal issues such as arrests or charges for driving under the influence (DUI) may arise as a result of substance-related behaviors.
6. Changes in Routine
- Sleep Disturbances: Significant changes in sleep patterns, such as insomnia or excessive sleep, may be signs of substance use disrupting their routine.
- Decline in Work/School Performance: A sudden drop in performance at work or school, increased absenteeism, or difficulty meeting responsibilities may signal an issue.
7. Drug-Related Paraphernalia
- Presence of Paraphernalia: If you discover items such as needles, pipes, pill bottles, or foil in personal spaces, these could be clear signs of substance use.
8. Behavioral Patterns
- Increased Tolerance: Needing larger quantities of a substance to achieve the same effect is a hallmark of addiction.
- Withdrawal Symptoms: Physical or psychological withdrawal symptoms when the substance is not used indicate a dependence on the substance.
9. Denial and Defensiveness
- Lack of Insight: Individuals struggling with addiction may deny having any issues and become defensive if the topic is raised. This resistance to acknowledging a problem is common in addiction.
10. Trust Your Gut
- Intuition: If you have a strong feeling that someone may be struggling with addiction, trust your instincts. Reach out for professional help, whether by contacting a counselor, healthcare professional, or a support group.
Recognizing the signs of addiction early can lead to timely intervention, offering the chance for support and recovery before the situation worsens. Whether you are concerned about a friend, family member, or yourself, don’t hesitate to take action—early detection can make all the difference.
Recognizing Early Signs of Addiction: The Power of Education, Observation, and Empathy
Staying informed, observant, and proactive is critical for identifying the early signs of addiction. Early recognition allows for timely intervention, significantly improving the chances of successful recovery. Whether you are concerned about a friend, family member, or colleague, approaching the situation with empathy and understanding is essential in offering meaningful support. Here are strategies to help identify addiction at an early stage:
1. Education and Awareness
- Understand Common Signs: Start by educating yourself about the behavioral, physical, and psychological signs of addiction. Knowing what to look for will help you recognize them more easily.
- Learn about Specific Substances: Different substances have unique effects. Understanding the signs associated with alcohol, opioids, stimulants, and others can help you detect substance-specific issues.
2. Observe Changes in Behavior
- Monitor Mood Swings: Unexplained irritability, mood swings, or extreme highs and lows can be signs of substance use.
- Watch for Withdrawal: Notice if someone is withdrawing from hobbies, social activities, or responsibilities they previously enjoyed.
3. Physical Signs and Symptoms
- Notice Changes in Appearance: Sudden changes in appearance, such as weight loss, poor hygiene, or neglect of personal grooming, may indicate a problem.
- Recognize Health Issues: Substance use can worsen health problems or cause frequent infections or illnesses that seem out of the ordinary.
4. Interpersonal and Social Changes
- Assess Relationships: Addiction often strains relationships. Look for increased conflict, isolation, or a shift in social circles toward people who may be involved in substance use.
- Monitor Social Activities: Avoidance of usual gatherings or events can be a sign that something is wrong.
5. Financial and Legal Issues
- Notice Financial Strain: Frequent borrowing of money or sudden financial instability may suggest that someone is struggling with addiction.
- Be Aware of Legal Troubles: Substance use often leads to legal issues like arrests, DUIs, or other legal consequences.
6. Changes in Routine and Performance
- Monitor Work or School Performance: A decline in work or school performance, absenteeism, or lack of productivity may be linked to substance use.
- Watch for Sleep Disturbances: Changes in sleep patterns, such as insomnia or excessive sleeping, could indicate a deeper issue.
7. Observation of Drug-Related Behaviors
- Recognize Drug Paraphernalia: The presence of items such as needles, pipes, or pill bottles may point to substance use.
- Observe Patterns of Use: Pay attention to the need for larger quantities of a substance or withdrawal symptoms when it isn’t used.
8. Trust Your Instincts
- Intuition: Trust your gut if you feel something is off. Even if the signs are subtle, it’s essential to seek guidance if you suspect addiction.
9. Open Communication
- Maintain Dialogue: Create a space for open, non-judgmental communication. If you suspect addiction, encourage the individual to talk about their experiences and feelings without fear of criticism.
10. Seek Professional Help
- Consult Professionals: If you suspect addiction, reach out to healthcare professionals or addiction specialists for advice on intervention and support. Early professional involvement can make a significant difference.
Recognizing the signs of addiction early and taking action can change the course of someone’s life. By combining education, observation, and empathy, you can support those who need it most.
Understanding the Diagnosis and Treatment of Addiction: Key Insights into Substance Use and Behavioral Disorders
The diagnosis of addiction requires a thorough assessment by healthcare professionals, who evaluate symptoms, history of substance use or behavior, and how these factors affect daily life. Timely diagnosis and intervention are essential for adequate recovery. Treatment typically includes therapy, medications (for specific substance use disorders), and support programs tailored to the individual’s particular needs and circumstances.
Addiction presents itself in various forms, and its impact can differ based on the type of substance or behavior involved. Here are the most common diagnoses related to addiction:
1. Substance Use Disorders (SUDs)
- Alcohol Use Disorder (AUD): Characterized by a problematic pattern of alcohol consumption that leads to significant distress or impairment in daily life. Symptoms can include a loss of control over drinking, withdrawal symptoms, and unsuccessful attempts to reduce alcohol use.
- Opioid Use Disorder (OUD): Involves compulsive opioid use, tolerance, withdrawal symptoms, and failed attempts to stop, leading to severe impairment or distress.
- Stimulant Use Disorder: Associated with stimulant drugs like cocaine or methamphetamine. Users may develop tolerance, experience withdrawal symptoms, and continue to use despite adverse consequences.
- Cannabis Use Disorder: Involves persistent cannabis use that results in clinically significant impairment or distress, similar to other substance use disorders.
- Other Substance Use Disorders: This category includes dependence on sedatives, hallucinogens, inhalants, and other substances with addictive potential. Each disorder comes with unique symptoms and challenges.
2. Behavioral Addictions
- Gambling Disorder: Involves compulsive gambling behaviors that lead to significant harm, such as financial losses, strained relationships, and emotional distress.
- Internet Gaming Disorder: Defined by persistent and excessive engagement with online games, resulting in negative impacts on social, personal, or academic life.
- Sexual Addiction: Characterized by compulsive engagement in sexual activities that cause personal or relational problems and loss of control.
- Shopping Addiction: Compulsive buying behavior that results in financial strain and personal or social issues, often driven by an inability to resist the urge to shop.
3. Dual Diagnosis (Co-occurring Disorders)
- Co-occurring Mental Health Disorders: Addiction often coincides with mental health conditions such as depression, anxiety, bipolar disorder, or post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). This dual diagnosis requires integrated treatment to address both addiction and mental health issues simultaneously for a better recovery outcome.
4. Other Related Conditions
- Impulse Control Disorders: These include conditions like kleptomania (compulsive stealing) and pyromania (compulsive fire-setting), where individuals struggle to control destructive impulses that negatively affect themselves and others.
Treatment Approaches
Once a diagnosis is made, treatment typically combines multiple approaches to ensure holistic care:
- Therapy: Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT), Dialectical Behavioral Therapy (DBT), and Motivational Interviewing (MI) are often used to address both the psychological and behavioral aspects of addiction.
- Medication: Medications, such as methadone or buprenorphine for OUD or naltrexone for AUD, may be prescribed to reduce cravings, prevent withdrawal symptoms, or maintain recovery.
- Support Programs: Peer support groups like Alcoholics Anonymous (AA) or Narcotics Anonymous (NA) provide community and accountability, which can be critical elements in long-term recovery.
Importance of Early Diagnosis
Early identification of addiction improves the chances of successful recovery. If symptoms of addiction are detected early, whether they involve substance use or behavioral patterns, intervention can prevent the problem from escalating. It is essential to approach individuals struggling with addiction with empathy, provide access to professional support, and encourage them on the path to recovery.
By understanding the various forms of addiction and the importance of timely diagnosis and treatment, individuals and their loved ones can better navigate the challenges of addiction and pursue healthier, substance-free lives.
Empowering Families: Strategies for Recognizing and Responding to Early Signs of Addiction
Addiction can be a challenging and complex issue, impacting not only the individual but also their family and loved ones. By employing effective family strategies, you can play a proactive role in recognizing early signs of addiction and supporting your loved one in seeking the help they need. Your involvement, understanding, and supportive approach can significantly enhance their recovery and well-being.
Here are some essential family strategies for identifying and responding to early signs of addiction effectively:
1. Open Communication
- Create a Supportive Environment: Foster open, non-judgmental communication within the family. Encourage honest discussions about feelings, challenges, and concerns related to substance use or behavioral changes.
- Listen Actively: Pay close attention to what your loved one says and validate their feelings. Create opportunities for them to express their struggles without fear of criticism or judgment.
2. Educate Yourself
- Learn About Addiction: Educate yourself and your family members about the signs and symptoms of addiction, including behavioral changes, physical symptoms, and psychological effects associated with substance use or compulsive behaviors.
- Understand Risk Factors: Be aware of common risk factors for addiction, such as family history, mental health disorders, trauma, and environmental influences.
3. Observe Changes in Behavior
- Be Observant: Stay attuned to changes in behavior, mood swings, withdrawal from social activities, sleep patterns, and overall demeanor that may indicate a problem.
- Document Concerns: Track concerning behaviors or patterns to provide concrete examples when discussing concerns with your loved one or seeking professional help.
4. Establish Boundaries and Consequences
- Set Clear Boundaries: Establish clear and consistent rules regarding substance use or problematic behaviors within the household. Communicate expectations and consequences for violating boundaries.
- Enforce Boundaries: Follow through with consequences when necessary while supporting and encouraging positive behavior changes.
5. Seek Professional Guidance
- Consult with Healthcare Professionals: If you notice signs of addiction or are concerned about your loved one’s behavior, seek guidance from healthcare professionals, counselors, or addiction specialists.
- Family Therapy: Consider participating in family therapy to improve communication, address underlying family dynamics, and learn effective strategies to support your loved one in recovery.
6. Encourage Healthy Activities and Support Systems
- Promote Healthy Habits: Encourage participation in positive, healthy activities that can serve as alternatives to substance use or addictive behaviors, such as exercise, hobbies, and socializing with supportive peers.
- Build Support Networks: Help your loved one establish connections with supportive individuals and community resources, such as support groups, peer networks, or religious/spiritual communities.
7. Be Patient and Supportive
- Show Empathy: Approach discussions with empathy and understanding, recognizing that addiction is a complex issue that may involve underlying emotional or psychological challenges.
- Offer Support: Be a source of emotional support and encouragement throughout the recovery process, demonstrating your commitment to their well-being and recovery journey.
Addiction is a multifaceted challenge that requires understanding and compassion from family members. You can create a supportive environment that encourages recovery by fostering open communication, educating yourself, observing behavioral changes, and seeking professional help. Your proactive involvement can significantly impact your loved one’s journey toward a healthier, substance-free life. Together, you can navigate the complexities of addiction and promote lasting change.
Empowering Communities: Strategies for Supporting Early Signs of Addiction
Addiction is a pervasive issue that affects individuals and families across communities. By implementing effective community resource strategies, communities can play a crucial role in supporting individuals showing early signs of addiction. These initiatives provide essential services and support, promote awareness, reduce stigma, and encourage early intervention, ultimately contributing to improved outcomes and healthier communities.
Here are several community resource strategies to help address early signs of addiction:
1. Education and Awareness Programs
- Public Awareness Campaigns: Launch campaigns to educate community members about the signs and symptoms of addiction, risk factors, and available support resources. This can empower individuals to recognize issues in themselves or others and seek help.
- School-Based Education: Implement educational programs in schools to inform students, teachers, and parents about substance use disorders and behavioral addictions. Early education can significantly influence attitudes and behaviors related to substance use.
2. Access to Screening and Assessment Services
- Community Health Clinics: Offer screening and assessment services for addiction-related concerns, facilitating early detection and intervention. Making these services accessible can encourage individuals to seek help before issues escalate.
- Mobile Health Units: Deploy mobile health units to provide outreach services, including screenings and referrals, in underserved or remote areas. This approach can bridge gaps in healthcare access.
3. Support Groups and Peer Networks
- Support Group Meetings: Facilitate regular support group meetings for individuals struggling with addiction and their families. These gatherings allow participants to share experiences, receive peer support, and access community resources.
- Peer Mentorship Programs: Establish programs in which individuals in recovery serve as mentors to those experiencing early signs of addiction, offering guidance and encouragement. Peer support can be instrumental in fostering hope and resilience.
4. Harm Reduction Services
- Naloxone Distribution Programs: Provide training and distribute naloxone kits to community members to effectively reverse opioid overdoses. Ensuring easy access to this life-saving medication can reduce fatalities associated with opioid use.
- Needle Exchange Programs: Implement programs that offer clean syringes and safe disposal options to reduce the spread of infectious diseases among individuals who inject drugs. These initiatives promote health and safety within the community.
5. Crisis Intervention and Hotline Services
- Crisis Hotlines: Establish 24/7 hotlines staffed by trained professionals to provide immediate crisis intervention, support, and referrals to individuals experiencing addiction-related crises. Immediate access to help can prevent worsening situations.
- Mobile Crisis Teams: Deploy mobile crisis teams to respond to emergencies and provide on-site support and assessment for individuals in crisis due to addiction. These teams can offer immediate assistance and connect individuals to further resources.
6. Community-Based Counseling and Therapy
- Community Counseling Centers: Provide accessible counseling and therapy services tailored to individuals and families affected by addiction. Addressing underlying issues is critical to promoting long-term recovery.
- Group Therapy Sessions: Offer sessions on addiction recovery, coping skills, and relapse-prevention strategies. Group settings can foster a sense of belonging and shared understanding.
7. Legal and Financial Assistance
- Legal Aid Clinics: Partner with legal aid organizations to provide support and guidance for individuals facing addiction-related legal issues, such as criminal charges or housing disputes. Access to legal support can alleviate additional stressors.
- Financial Counseling: Offer financial counseling services to help individuals manage money effectively and address addiction-related financial challenges. This support can help individuals regain stability.
8. Collaboration with Local Organizations
- Partnerships with Nonprofits: Collaborate with local nonprofit organizations specializing in addiction treatment, mental health, and social services to expand the range of available resources and support. These partnerships can create a more integrated support network.
- Faith-Based Organizations: Engage with religious and spiritual communities to provide holistic support, counseling, and spiritual guidance for individuals and families affected by addiction.
9. Community Engagement and Advocacy
- Community Forums and Events: Host forums and community events to discuss addiction-related issues, raise awareness, and mobilize community members to support prevention and treatment efforts. Engaging the community fosters collective responsibility.
- Advocacy Campaigns: Advocate for policies and funding at the local, state, and federal levels to support addiction prevention, treatment, and recovery services within the community. Strong advocacy can lead to systemic changes that benefit those affected by addiction.
Communities play a pivotal role in addressing addiction through supportive resources and strategies. By implementing educational programs, facilitating access to services, and promoting open dialogue, communities can effectively support individuals showing early signs of addiction. Together, we can create a culture of understanding and proactive intervention, ultimately fostering healthier, more resilient communities.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some common questions:
1. What are early addiction signs?
Early addiction signs are subtle behavioral, emotional, and physical changes that appear before substance use becomes severe or uncontrollable.
2. Why is recognizing early signs important?
Early detection allows for quick support and intervention, preventing progression to a serious substance use disorder.
3. What behavioral changes are common early signs?
Secrecy, lying about activities, withdrawing from family or friends, mood swings, irritability, and sudden changes in routines.
4. Can school or work performance be affected early on?
Yes. Declining grades, missed responsibilities, loss of motivation, and poor concentration are common early warning signals.
5. What physical signs may appear?
Sleep disturbances, changes in appetite, weight fluctuations, bloodshot eyes, frequent illness, or neglect of hygiene.
6. Does needing more of a substance indicate addiction risk?
Yes. Increased tolerance — needing more to feel the same effect — is a key early sign of dependence.
7. Are withdrawal symptoms an early warning sign?
Mild withdrawal symptoms such as headaches, nausea, shakiness, or anxiety when not using can indicate growing dependence.
8. Why do people deny early addiction signs?
Denial is common because individuals may feel shame, fear judgment, or believe they still have control.
9. How should family or friends respond to early signs?
With calm, nonjudgmental conversation, expressing concern, and encouraging professional screening or counseling.
10. Can early intervention prevent full addiction?
Yes. Early support, education, counseling, and coping strategies can stop addiction before it becomes severe.
Conclusion
Early recognition of signs of addiction is vital for effective intervention and support. Whether it’s substance use disorders like alcohol or opioids or behavioral addictions such as gambling or internet gaming, understanding the diverse manifestations of addiction is essential. Self-management strategies empower individuals to initiate and sustain recovery efforts, while solid family support systems provide crucial emotional backing and practical assistance throughout the journey. Community strategies play a pivotal role by offering accessible resources, education, and supportive networks that bolster recovery efforts and promote resilience. By integrating these components, communities can enhance early detection, support individuals in navigating addiction challenges, and foster environments that promote long-term wellness and recovery.
Video: If you notice this, addiction might be starting #addictionawareness #help