Vaping addiction is a growing concern among youth, fueled by appealing flavors, sleek devices, and social media marketing. Unlike cigarettes, vaping can deliver higher nicotine doses discreetly, increasing dependence while seeming safer. To combat this, the U.S. and other countries have enacted age limits, flavor bans, ad restrictions, and school-based prevention programs, but youth remain highly vulnerable due to peer influence and aggressive marketing.
Vaping Addiction: Understanding the Risks, Signs, and How to Quit
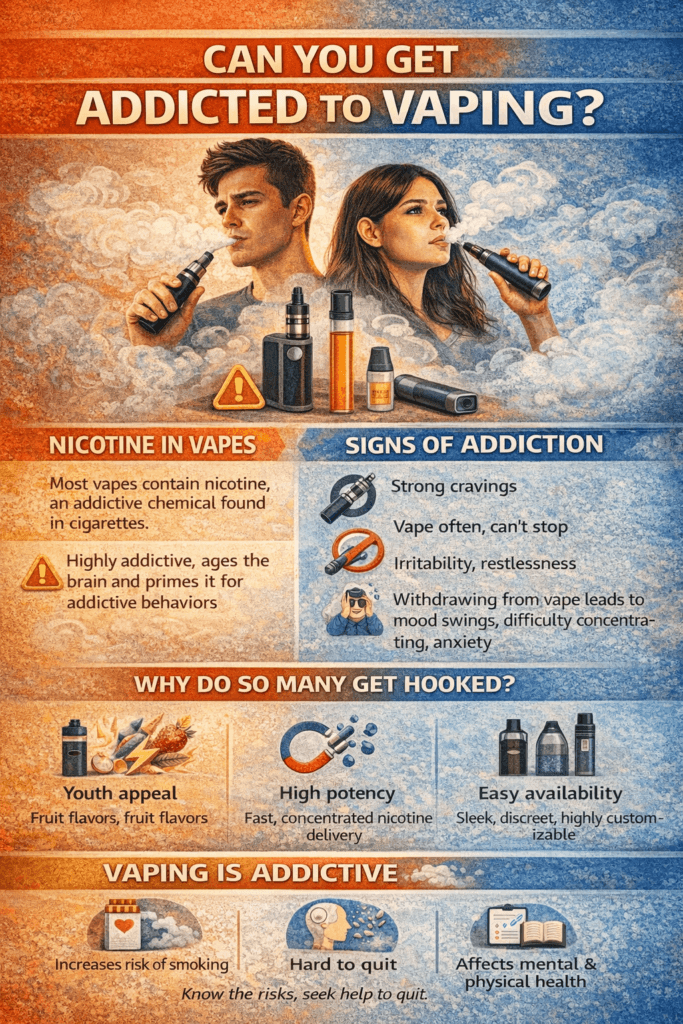
Vaping addiction is the compulsive use of electronic cigarettes (e-cigarettes) or vape devices, most often driven by their nicotine content. Like traditional cigarettes, many vapes deliver nicotine—a highly addictive substance that changes brain chemistry by stimulating dopamine release, the brain’s “reward” neurotransmitter. Over time, the brain adapts, leading to cravings, dependence, and withdrawal symptoms when vaping stops.
🔹 Why Vaping Can Be Addictive
- Nicotine content: Many vapes contain nicotine levels equal to—or even higher than—cigarettes. New “nicotine salts” allow more substantial doses to be inhaled smoothly.
- Fast absorption: Nicotine from vaping reaches the brain in seconds, reinforcing the habit quickly.
- Flavors & ease of use: Fruity, sweet, or minty flavors mask harshness and encourage repeated use.
- Behavioral reinforcement: Stress relief, social acceptance, or boredom often strengthens the cycle.
🔹 Signs of Vaping Addiction
- Craving or feeling restless without vaping.
- I need to vape frequently throughout the day.
- Withdrawal symptoms like irritability, anxiety, headaches, or trouble concentrating when not vaping.
- Continuing to vape despite negative health, financial, or social effects.
🔹 Health Risks of Vaping Addiction
- Nicotine effects: raises heart rate and blood pressure, and increases the risk of cardiovascular disease.
- Brain impact: In teens and young adults, nicotine disrupts memory, learning, and impulse control.
- Respiratory issues: May cause chronic cough, lung irritation, and even vaping-related lung injury (EVALI).
- Gateway effect: Increases the likelihood of transitioning to cigarettes or other substances.
🔹 Treatment & Support Options
- Self-management: Set limits, track usage, and use healthier stress-relief alternatives like exercise or mindfulness.
- Nicotine replacement therapy (NRT): Patches, lozenges, or gum can help taper nicotine gradually.
- Behavioral therapy: Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) or motivational interviewing helps change thought patterns.
- Support systems: Family support, peer groups, or national quitlines (like 1-800-QUIT-NOW in the U.S.) encourage.
- Digital tools: Apps and text-based programs are emerging resources for vaping cessation.
In summary, vaping addiction is nicotine dependence reinforced by both biology and behavior. While often marketed as a “safer” alternative to smoking, vaping carries serious health risks and a strong potential for addiction—especially among youth. The good news: with the right tools, support, and strategies, breaking free from vaping is possible.
Why Vaping Addiction Hits Young People the Hardest
Vaping addiction is especially common among teens and young adults because of a mix of biological, psychological, and social factors that make them more vulnerable. Unlike older adults, youth are navigating brain development, peer influence, and targeted marketing—all of which increase the risk of nicotine dependence.
🔹 1. Brain Development
The brain continues developing until about age 25. Nicotine disrupts circuits linked to reward, learning, impulse control, and stress regulation, which makes young people more likely to become addicted quickly.
🔹 2. High Nicotine Delivery
Popular vape products like JUUL or disposable vapes often use nicotine salts, which allow very high doses to be inhaled smoothly. A single pod may contain as much nicotine as a whole pack of cigarettes—accelerating dependence.
🔹 3. Appealing Flavors & Marketing
Sweet, fruity, and candy-like flavors disguise nicotine’s harshness and make vaping feel harmless. Marketing campaigns and social media often frame vaping as trendy, fun, and safer than smoking—an appealing message for youth identity and belonging.
🔹 4. Social Influences
Peer pressure, group norms, and influencer culture make vaping appear socially acceptable. The small, discreet design of vape devices also makes them easy to use at school, parties, or social gatherings without detection.
🔹 5. Misconceptions About Risk
Many young people mistakenly believe vaping is “just water vapor” or significantly safer than smoking. In reality, most products contain addictive nicotine and harmful chemicals. These misconceptions lower barriers to experimentation and increase the likelihood of regular use.
🔹 6. Stress & Coping
Teens often turn to vaping for stress relief, anxiety management, or boredom. Since nicotine provides short-term calming effects, it reinforces the cycle and makes quitting more difficult.
In summary, vaping addiction is widespread among youth because their developing brains are susceptible to nicotine, while vape devices deliver it in potent, appealing forms. Add in flavors, peer influence, marketing, and misconceptions about safety, and young people face a perfect storm of vulnerability. Recognizing these risks is the first step toward prevention and support.
How Vaping Companies Target Youth: Marketing Tactics That Hook the Next Generation
Public health experts have raised serious concerns because vaping companies repeatedly use tactics that appeal to youth—even while claiming their products are “for adults only.” These strategies lower the perception of risk and make vaping seem trendy, fun, and harmless.
🔹 1. Flavor Variety
Flavors like cotton candy, gummy bear, mango, mint, and bubblegum directly appeal to younger taste preferences. Surveys show that flavors are one of the top reasons teens first try vaping.
🔹 2. Youth-Friendly Packaging
Bright colors, flashy designs, and sleek disposable vapes mimic candy wrappers, energy drinks, or tech gadgets. Some devices even look like USB drives, pens, or highlighters—making them easy to hide from parents and teachers.
🔹 3. Social Media & Influencer Marketing
Vaping companies have tapped into Instagram, TikTok, and YouTube by sponsoring influencers who make vaping look stylish. Viral hashtags, memes, and challenges normalize vaping as part of youth culture. Even without official ads, companies benefit from user-generated content created by teens.
🔹 4. Music, Fashion, and Lifestyle Branding
Sponsorship of concerts, festivals, and youth-centered events positions vaping as part of a rebellious, cool, or fashionable lifestyle. This mirrors the old playbook once used by cigarette companies.
🔹 5. “Safe” or “Healthier” Messaging
Ads frame vaping as “cleaner,” “smoke-free,” or “better for you than cigarettes.” Many youth still believe it’s “just water vapor,” a misconception that downplays the dangers of nicotine and chemical exposure.
🔹 6. Price Promotions
Coupons, discounts, and multipack deals make vaping affordable for teens with limited income. Disposable vapes are often cheaper than cigarettes, creating an easy entry point for experimentation.
🔹 7. Targeted Ads
Despite regulations, online advertising algorithms still reach younger demographics. Vape ads slip through social media platforms and websites, making underage exposure difficult to avoid.
In summary, vaping companies attract youth through flavors, flashy packaging, influencer campaigns, lifestyle branding, and misleading claims of safety. These tactics make vaping affordable, accessible, and socially desirable among teens—fueling a public health crisis of nicotine addiction in the next generation.
Government Strategies to Prevent Youth Vaping Sales
Public health officials worldwide are working to curb the rise of youth vaping. Since vaping products are often marketed in ways that appeal to teens, governments have introduced strong policies aimed at reducing access, limiting appeal, and enforcing accountability.
1. Age Restrictions
- Sales prohibited under age 18 or 21 (varies by country).
- Retailers risk fines, license suspension, or closure if they sell to minors.
- Digital ID checks are increasingly required for online sales.
2. Flavor Bans
- Flavors like mango, bubblegum, and mint are a top driver of youth vaping.
- Countries such as the U.S., EU, Canada, and Australia have restricted or banned flavored products, especially disposables.
3. Advertising & Marketing Restrictions
- Ban on youth-oriented ads across TV, radio, print, and social media.
- Prohibition on sponsoring sports, festivals, or cultural events.
- Crackdowns on influencer campaigns targeting teens on TikTok, Instagram, and YouTube.
4. Packaging & Labeling Rules
- Move toward plain packaging to reduce flashy, candy-like designs.
- Prominent nicotine addiction warnings are required on boxes.
- Prohibition on devices disguised as USB drives, toys, or school supplies.
5. Retail Restrictions
- Limiting sales to pharmacies or adult-only shops.
- Licensing systems for sellers make it easier to track and penalize violators.
- Some countries ban sales in gas stations or convenience stores.
6. Taxation & Pricing Controls
- Higher taxes on vaping products to make them less affordable.
- Elimination of discounts, coupons, and multipack promotions that target youth buyers.
7. Online Sales Regulation
- Verified government ID required for online purchases.
- No shipping to P.O. boxes to prevent hiding deliveries.
- Stricter monitoring of third-party sellers like Amazon, eBay, and social platforms.
8. School & Community Prevention Programs
- Education campaigns in schools on the risks of vaping.
- Teacher and parent training on recognizing signs of addiction.
- Quitline and text-based support programs are designed for teens.
9. Enforcement & Penalties
- Sting operations using undercover youth buyers.
- Severe penalties for companies that intentionally target minors.
- Seizure of illegal imports and counterfeit products.
In summary, governments are fighting youth vaping with a three-pronged approach:
- Restrict access through age limits, retail rules, and flavor bans.
- Reduce appeal with plain packaging, ad bans, and taxation.
- Educate & enforce through school prevention programs and penalties for violators.
Together, these strategies aim to protect the next generation from nicotine addiction and reduce the long-term public health burden of vaping.
Self-Management Strategies to Avoid Vaping Addiction
Avoiding vaping addiction starts with personal awareness and intentional choices. By combining self-discipline, healthy coping skills, and supportive resources, people can lower the risk of becoming dependent on nicotine.
1. Build Awareness
- Learn about the health risks: lung damage, nicotine dependence, and mental health effects.
- Track vaping urges in a journal—note triggers like stress, boredom, or peer influence.
2. Strengthen Coping Skills
- Practice stress management techniques such as deep breathing, mindfulness, or stretching.
- Replace vaping with healthy outlets like exercise, music, or creative hobbies.
3. Set Clear Limits
- Create personal rules (e.g., “No vaping at home” or “I won’t vape with friends”).
- Delay the urge—wait 10–15 minutes and distract yourself; most cravings fade quickly.
4. Social Support
- Share your goal with supportive friends or family.
- Choose activities that don’t involve vaping (coffee meetups, sports, volunteering).
- Avoid vape-heavy environments until you feel confident.
5. Use Alternatives
- Keep sugar-free gum, mints, or water handy for oral cravings.
- Try deep breathing or stress-relief tools like a stress ball.
6. Set Goals & Rewards
- Write down your reasons for avoiding vaping (health, money, independence).
- Track your days without vaping and reward progress with small, positive incentives.
7. Digital Tools
- Use quit-vaping apps or text-based support (e.g., SmokefreeTXT for Teens in the U.S.).
- Block or unfollow vape-related accounts on social media to reduce temptation.
8. Medical & Professional Support
- If already vaping, consider nicotine replacement therapy (NRT) under medical guidance.
- Seek counseling (CBT, motivational interviewing) to manage cravings and peer pressure.
In summary, preventing vaping addiction requires awareness, coping skills, boundaries, and healthy substitutes. With the right mix of self-management, social support, and professional help, staying vape-free becomes a realistic and sustainable goal.
Family Support Strategies to Avoid Vaping Addiction
Families play a critical role in preventing and reducing vaping addiction, especially among teens and young adults. By building trust, modeling healthy habits, and providing support, parents and caregivers can help protect loved ones from nicotine dependence.
1. Open Communication
- Create a non-judgmental space where kids or relatives feel safe discussing vaping.
- Ask questions like “What do you know about vaping?” rather than lecturing.
- Share honest facts about risks such as nicotine addiction, lung damage, and mental health effects.
2. Model Healthy Behavior
- Avoid smoking or vaping around children.
- Demonstrate positive coping strategies like exercise, hobbies, or relaxation techniques instead of substances.
3. Set Clear Expectations
- Establish family rules (e.g., no vaping in the house, car, or during gatherings).
- Explain the why—emphasize health and protection, not just punishment.
4. Strengthen Monitoring & Boundaries
- Stay aware of social media, peer groups, and school environments where vaping is promoted.
- Encourage check-ins based on trust and respect rather than constant surveillance.
5. Encourage Healthy Alternatives
- Support involvement in sports, arts, volunteering, or clubs to reduce boredom and peer pressure.
- Provide outlets for stress relief, such as journaling, exercise, or creative projects.
6. Provide Education
- Share age-appropriate, fact-based information—avoid scare tactics.
- Use real-life stories or videos to make the consequences relatable.
7. Offer Emotional Support
- Acknowledge that stress and peer pressure can be overwhelming.
- If you discover vaping, respond with empathy and work together on solutions rather than punishment.
8. Seek Professional Help if Needed
- Connect with school counselors, doctors, or quit programs if vaping has already started.
- Consider family therapy if communication has broken down.
In summary, families can help prevent vaping addiction by fostering trust, open dialogue, and healthy coping strategies. Through strong communication, clear boundaries, and supportive guidance, parents and caregivers empower youth to make safer choices and resist nicotine addiction.
Community Resource Strategies to Prevent Vaping Addiction
Preventing vaping addiction requires more than just family guidance—it calls for coordinated community-wide action. Schools, healthcare providers, local governments, and youth organizations can all play a vital role in protecting young people from nicotine dependence.
1. School-Based Prevention Programs
- Implement educational lessons on vaping risks, nicotine addiction, and healthy coping skills.
- Encourage peer mentoring and leadership programs to empower students against peer pressure.
- Integrate vaping prevention into broader health and wellness curricula.
2. Public Awareness Campaigns
- Run social media campaigns, posters, and local events to spread awareness.
- Use real-life stories and testimonials to make risks relatable to young people.
3. Youth Engagement Activities
- Provide after-school programs, sports, arts, or clubs as alternatives to vaping.
- Encourage youth involvement in volunteering and leadership to foster a sense of purpose and belonging.
4. Support Services
- Ensure access to quitlines, counseling, or group therapy for youth and adults.
- Partner with clinics or community health centers for confidential support.
- Offer resources in multiple languages and culturally relevant formats.
5. Policy Advocacy & Enforcement
- Advocate for local bans on flavored tobacco products, age restrictions, and vape-free public spaces.
- Support enforcement against underage sales in retail stores and online outlets.
6. Parental & Family Support Resources
- Provide parent workshops on vaping awareness, communication, and monitoring strategies.
- Offer family counseling or peer support groups to strengthen family involvement.
7. Collaboration with Healthcare Providers
- Distribute educational pamphlets and referral programs through clinics and pharmacies.
- Encourage pediatricians and family doctors to screen for vaping behaviors during visits.
8. Community Coalitions
- Form coalitions with schools, healthcare providers, law enforcement, parents, and youth.
- Share data on local vaping trends to design targeted prevention programs.
In summary, community prevention efforts work best when they combine education, youth engagement, support services, policy advocacy, and family involvement. By uniting resources at every level, communities can create environments that discourage vaping and protect young people from long-term nicotine addiction.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some common questions:
Question: Do a side-by-side comparison of old cigarette marketing vs. modern vaping marketing?
Answer: Side-by-side comparison showing how old cigarette marketing strategies are being mirrored in modern vaping marketing—just updated for today’s youth culture:
🚬 Old Cigarette Marketing vs. 💨 Modern Vaping Marketing
| Teens and young adults, despite age restrictions, ads and social media reach under-21 audiences. | Old Cigarette Marketing | Modern Vaping Marketing |
|---|---|---|
| Flavors | Mostly tobacco & menthol, but candy-flavored cigars/cigarettes were briefly marketed. | Sweet & fruity flavors (mango, cotton candy, gummy bear) that directly appeal to teens. |
| Packaging | Sleek packs with bright colors and luxury designs. | Disposable vapes in flashy, candy-like packaging or disguised as pens/USBs. |
| Lifestyle Branding | Cigarettes = glamour, rebellion, freedom, masculinity/femininity (e.g., Marlboro Man, Virginia Slims). | Vapes = trendy, techy, fun, rebellious, often linked with youth culture, fashion, or gaming. |
| Celebrities/Influencers | Movie stars, athletes, and cultural icons promoted smoking. | TikTok/Instagram influencers post vape tricks, challenges, and “aesthetic” content. |
| Events & Music | Sponsored concerts, sports, and Hollywood films. | Vape brands linked to music festivals, EDM events, and youth nightlife. |
| Health Messaging | Marketed as “doctor recommended” or “safer” than other tobacco. | Marketed as “safer than smoking”, “just water vapor,” or “clean nicotine.” |
| Target Audience | Young adults and new smokers, despite claiming to be “for adults.” | Teens and young adults, despite age restrictions—ads and social media reach under-21 audiences. |
| Price Promotions | Coupons, discounts, and free samples to encourage trial. | Cheap disposables, multipacks, discounts, making them affordable for youth. |
| Addiction Hook | High nicotine + cultural normalization. | Nicotine salts = stronger, smoother hits + social media normalization. |
✅ Summary:
Cigarette companies once hooked generations through flavors, glamorized advertising, celebrity appeal, and “safer” claims—and vaping companies are now repeating the same playbook, but with modern tools like social media, influencers, and candy-like products.
Question: Provide a comparison chart between vaping addiction and cigarette addiction.
Answer: Comparison chart showing the similarities and differences between vaping addiction and cigarette addiction:
💨 Vaping Addiction vs. 🚬 Cigarette Addiction
| Hard to quit due to stealth use, frequent hits, and high nicotine exposure. | Vaping Addiction | Cigarette Addiction |
|---|---|---|
| Nicotine Content | Often higher nicotine levels due to nicotine salts (smooth, fast-absorbing). A single pod/disposable can equal 1–2 packs of cigarettes. | High nicotine, but harsher smoke limits intake compared to modern vape devices. |
| Delivery Method | Vaporized liquid (nicotine salts or freebase nicotine). Less harsh, easier for beginners. | Burning tobacco, producing smoke, tar, and carcinogens. |
| Onset of Addiction | Rapid, especially in youth due to brain sensitivity + high nicotine doses. | Rapid as well, but sometimes slower due to harsher inhalation. |
| Health Risks | Still under study. Known risks: nicotine addiction, lung injury (EVALI), heart strain, oral health issues. Long-term cancer risks less certain but likely. | Well-documented: cancer (lung, throat, mouth), COPD, heart disease, stroke, premature death. |
| Social Perception | Seen by many youth as “safer,” trendier, cleaner”, often socially acceptable. | Now socially stigmatized in many countries, banned in most public places. |
| Marketing Tactics | Flavors, influencers, social media, tech-like designs. | Celebrities, glamour, masculinity/femininity, doctor endorsements (historic). |
| Cost | Initially cheaper (disposables, refill pods), but can add up with frequent use. | Pack-a-day habit can be more expensive long-term. |
| Quitting Challenges | Hard to quit due to stealth use, frequent hits, high nicotine exposure. | Hard to quit due to strong nicotine dependence + behavioral habits (coffee, stress). |
| Youth Appeal | Very high—flavors, discreet devices, peer use. | Historically high, but now less appealing to youth due to stigma and restrictions. |
✅ Summary:
Both vaping and cigarettes are highly addictive due to nicotine, but vaping often delivers more nicotine, more discreetly, and in youth-friendly ways, making it especially concerning for younger populations. Cigarettes, however, have more well-established long-term deadly health risks like cancer and COPD, while the full long-term risks of vaping are still emerging.
Question: Provide a global comparison chart showing how different countries (U.S., Canada, UK, Australia, EU, etc.) are handling youth vaping
Answer: Global comparison chart showing how major regions are addressing youth vaping:
🌍 Global Strategies to Prevent Youth Vaping
| Heated tobacco products have essentially replaced Vaping | Age Limit | Flavor Regulations | Advertising Restrictions | Retail/Online Sales | Other Key Policies |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| United States 🇺🇸 | 21+ | Flavored cartridge ban (except tobacco & menthol), but disposable flavors still widely available | Ban on youth-targeted ads; crackdown on influencers & online marketing | Online sales require age verification; FDA raids illegal sellers | FDA authorization required for products; enforcement against non-compliant brands |
| Canada 🇨🇦 | 18+ (19 in some provinces) | Ban on dessert & candy flavors; only tobacco, mint, menthol allowed in many regions | Strict restrictions; no youth-focused marketing | Restricted sales in convenience stores near schools; online sales with age verification | Health warnings on labels; nicotine cap (20 mg/mL) |
| United Kingdom 🇬🇧 | 18+ | Flavors allowed but under review; proposed ban on disposable flavored vapes (2025) | Strict limits on advertising; no youth media or sponsorships | Disposable vapes to be banned; online age verification required | Nicotine cap (20 mg/mL); plain packaging proposed |
| European Union (EU) 🇪🇺 | 18+ | Flavors restricted in some member states; nicotine-containing e-liquids capped | Ban on cross-border youth marketing; packaging rules | Online sales regulated by member states with ID checks | EU Tobacco Products Directive caps nicotine at 20 mg/mL |
| Australia 🇦🇺 | 18+ | All nicotine vapes prescription-only (since 2021); flavored vapes banned unless medically prescribed | Complete ban on consumer marketing | No retail sales without prescription; customs seizures for illegal imports | Prescription model only—seen as one of the strictest frameworks |
| New Zealand 🇳🇿 | 18+ | Ban on candy & fruity flavors except at specialist vape shops | Ban on youth-targeted ads; restrictions on sponsorships | Limited retail outlets; online sales with verification | Nicotine cap; strong school-based prevention programs |
| Singapore 🇸🇬 | N/A (total ban) | All vaping products banned regardless of nicotine | Total ban on promotion | Illegal to sell or possess | Very strict—possession punishable by fines or jail |
| Japan 🇯🇵 | 20+ | Nicotine-containing e-liquids banned; only heat-not-burn tobacco legal | Restrictions similar to tobacco | Sales limited to licensed outlets | Vaping essentially replaced by heated tobacco products |
🔑 Key Takeaways
Unique approaches: 🇯🇵 Japan bans nicotine e-liquids but allows heat-not-burn tobacco instead.
Strictest: 🇦🇺 Australia (prescription-only model) & 🇸🇬 Singapore (total ban).
Moderate: 🇨🇦 Canada & 🇬🇧 UK (flavor restrictions, nicotine caps, disposable bans).
Laxest (until recently): 🇺🇸 United States, where loopholes allowed flavored disposables to flourish.
Conclusion
Vaping addiction poses serious risks for young people, driven by nicotine’s addictive effects, appealing flavors, and targeted marketing. While vaping is often seen as safer than cigarettes, it can deliver higher nicotine doses and foster dependence more quickly. Governments in the U.S. and worldwide are responding with age restrictions, flavor bans, advertising limits, and education programs, but continued vigilance and combined efforts from families, schools, and communities are essential to protect youth from this growing epidemic.
Video: Top 5 Signs You’re Addicted to Vaping