Addictive behaviors, including substance abuse and behavioral addictions, are closely tied to cultural influences and the accessibility of substances or activities. Cultural norms shape societal attitudes towards addictive behaviors, influencing their prevalence, while the availability of these stimuli significantly affects individual engagement. Recognizing this interplay is essential for effective prevention efforts. This introduction examines the impact of culture and availability on addictive behaviors, laying the groundwork for a comprehensive prevention approach. Additionally, we will explore self-management strategies, family support, and community resources to address addictive behaviors within diverse cultural contexts.
Understanding the Most Common Addictive Behaviors
Identifying the single “most common addictive behavior” can be challenging because addiction manifests in various forms, each affecting individuals differently. However, two of the most prevalent and widely recognized addictions are nicotine addiction and alcohol addiction, which significantly impact public health globally.
Nicotine Addiction
- Prevalence: Nicotine addiction, primarily linked to tobacco use, is one of the most widespread behavioral addictions. Millions of people worldwide struggle with dependence on nicotine, making smoking a critical public health issue.
- Reasons for Addiction:
- Nicotine stimulates the release of dopamine, a neurotransmitter associated with pleasure, in the brain’s reward system.
- The immediate, pleasurable sensation reinforces the behavior, leading to habitual use and dependence.
- Over time, tolerance develops, requiring increasing amounts to achieve the same effect, deepening the addiction.
Alcohol Addiction
- Prevalence: Alcohol use disorder is another common addiction, affecting millions globally. Its widespread social acceptance often masks the severity of the problem.
- Reasons for Addiction:
- Alcohol impacts neurotransmitters in the brain, promoting the release of dopamine and creating pleasurable sensations.
- Continued exposure leads to tolerance, requiring higher consumption for the same effects, which contributes to dependency.
- Emotional and social triggers often play a significant role in perpetuating alcohol addiction.
Behavioral Addictions
Beyond substance addiction, other behaviors such as gambling, gaming, and compulsive eating can become addictive. These behaviors also engage the brain’s reward system, creating cycles of reinforcement and dependence.
Complexity of Addiction
Addiction is multifaceted, with genetic, psychological, and environmental factors contributing to its development. The prevalence of specific addictions often varies based on cultural, regional, and demographic differences:
- In some cultures, alcohol may be the predominant issue.
- In others, behaviors like gambling or gaming may be more prevalent.
Addressing Addiction
Addressing any form of addiction requires a holistic approach:
- Recognizing the unique factors influencing an individual’s addictive behavior.
- Tailoring interventions, whether for nicotine, alcohol, or behavioral addictions, to their specific circumstances.
- Seeking professional help, such as counseling, therapy, or medical interventions, is critical for effective recovery.
Understanding the dynamics of addiction and addressing it with empathy and evidence-based strategies can significantly improve outcomes, helping individuals regain control of their lives.
The Impact of Culture on Addictive Behaviors
Culture significantly influences the prevalence and manifestation of addictive behaviors. Societal norms, values, and attitudes toward substances or activities shape patterns of addiction, creating distinct dynamics across different communities. Here’s how cultural factors affect the most common addictive behaviors:
1. Cultural Attitudes Toward Substance Use
- Example: In some cultures, alcohol and tobacco use are widely accepted, even encouraged, while other cultures stigmatize or strictly prohibit these substances.
- Impact:
- Acceptance of substance use can normalize behaviors, potentially increasing addiction rates.
- Conversely, stigma may deter open conversations and lead to hidden, untreated addiction issues.
2. Cultural Practices and Rituals
- Example: Certain communities use psychoactive substances in religious or ceremonial practices, such as ayahuasca rituals or kava ceremonies.
- Impact:
- Ritualistic or traditional use can influence individuals’ attitudes toward substances.
- It may also blur the line between cultural practice and misuse, leading to patterns of addiction.
3. Societal Stressors and Coping Mechanisms
- Example: Societies under economic strain, political instability, or other stressors may experience higher rates of substance use as coping mechanisms.
- Impact:
- Cultural responses to stress shape how individuals manage emotions, contributing to maladaptive behaviors and addiction prevalence.
4. Cultural Perceptions of Mental Health
- Example: In cultures where mental health issues are stigmatized, individuals may avoid seeking help for addiction-related problems.
- Impact:
- Stigma discourages open acknowledgment of addiction, leading to underreporting and barriers to treatment.
- This can perpetuate cycles of untreated addiction within a community.
5. Economic and Social Factors
- Example: In communities with economic disparities, access to substances or gambling opportunities may influence addiction trends.
- Impact:
- Limited resources and inequality may push individuals toward substances or behaviors as coping tools.
- Wealthy cultures may have higher rates of behavioral addictions like shopping or gaming due to increased accessibility.
6. Cultural Norms in Behavioral Addictions
- Example: Societies that prioritize productivity or celebrate success may inadvertently foster workaholism, while others may normalize gambling or excessive gaming.
- Impact:
- Cultural expectations shape the boundaries between acceptable and excessive behaviors.
- Norms around technology and leisure activities can lead to an increase in behavioral addictions.
Tailoring Interventions for Cultural Sensitivity
Understanding the cultural context is vital for addressing addiction effectively. Interventions must be:
- Culturally sensitive: Respecting and incorporating local traditions and values.
- Inclusive: Recognizing the diversity of beliefs and practices within communities.
- Tailored: Addressing specific societal stressors, stigmas, and norms that influence addiction.
Culture deeply impacts addictive behaviors, shaping their manifestation and prevalence in diverse ways. Recognizing these cultural influences allows for the development of more effective, inclusive prevention and treatment strategies. By integrating cultural awareness into addiction recovery efforts, we can create solutions that resonate with individuals and communities worldwide.
How Availability Shapes Addictive Behaviors
The availability of substances or opportunities to engage in certain behaviors significantly influences the development and prevalence of addictive behaviors. Accessibility impacts experimentation, regular use, and the potential progression to addiction. Here are key ways in which availability plays a role:
1. Substance Availability
- Example: Communities with easy access to alcohol, tobacco, or illicit drugs often see higher rates of substance use disorders.
- Impact:
- Greater availability increases experimentation and regular use.
- Limited access, through regulation or enforcement, can reduce prevalence.
2. Technological and Behavioral Opportunities
- Example: The widespread availability of technology enables activities like gaming, online gambling, and excessive social media use.
- Impact:
- Increased access to these platforms fosters excessive engagement.
- Over time, this can develop into behavioral addictions, especially among vulnerable populations.
3. Prescription Medications
- Example: Overprescription of opioids or other medications with abuse potential has contributed to widespread prescription drug addiction.
- Impact:
- High availability, through overprescribing or diversion, elevates misuse.
- Stricter prescribing guidelines and monitoring can mitigate this risk.
4. Cultural and Social Availability
- Example: Social environments where alcohol consumption or gambling is normalized.
- Impact:
- Behaviors perceived as socially acceptable are more likely to be adopted.
- Cultural influences shape patterns of use, impacting the prevalence of addiction.
5. Economic Factors
- Example: Low-cost alcohol or easily accessible gaming platforms.
- Impact:
- Affordability can lead to higher usage rates.
- Economic disparities may influence the types of addictions prevalent in different socioeconomic groups.
6. Peer Influence
- Example: Peer groups where substance use or certain behaviors are common.
- Impact:
- Availability within social circles can encourage initiation and habitual use.
- Social normalization within peer groups amplifies risk factors for addiction.
7. Marketing and Advertising
- Example: Alcohol or gambling companies targeting specific demographics through aggressive advertising.
- Impact:
- Advertising increases visibility and desirability, leading to higher usage rates.
- Marketing strategies that normalize consumption exacerbate addiction risks.
8. Legal and Regulatory Frameworks
- Example: Legalization of cannabis or deregulation of certain gambling activities.
- Impact:
- Legal availability shapes patterns of use and societal attitudes.
- Striking a balance between accessibility and regulation is critical to mitigating harm.
Balancing Availability with Prevention
The interplay between availability and addiction is multifaceted. High accessibility often increases the risk of addiction, while societal demand perpetuates the cycle of availability.
Key Strategies for Mitigation:
- Regulation: Implementing stricter controls on substances and platforms with addiction potential.
- Education: Promoting awareness of the risks associated with readily available substances or behaviors.
- Harm Reduction: Ensuring that those with addiction have access to support and treatment services.
By addressing the role of availability in addiction, communities and policymakers can create environments that minimize risks and foster healthier behaviors.
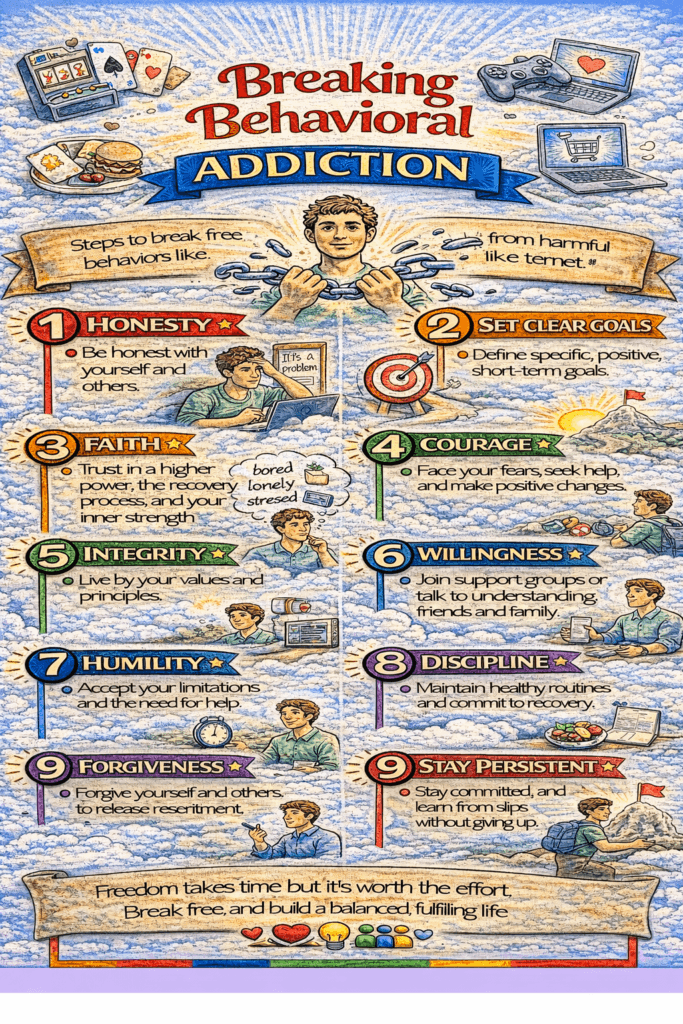
Proactive Self-Management Strategies to Prevent Addictive Behaviors
Preventing addictive behaviors requires intentional self-management strategies that foster resilience, well-being, and informed decision-making. These strategies empower individuals to develop habits and skills that reduce vulnerability to addiction while supporting overall mental and physical health. Here are key self-management strategies for preventing addictive behaviors:
1. Set Clear Boundaries
- Strategy: Define personal limits on behaviors such as substance use, screen time, or other potentially addictive activities.
- Implementation: Establish clear rules for yourself and commit to adhering to them to avoid excessive engagement.
2. Develop Healthy Habits
- Strategy: Build positive routines around nutrition, exercise, and sleep.
- Implementation: Focus on a balanced diet, regular physical activity, and sufficient rest to enhance mental and physical resilience.
3. Stress Management
- Strategy: Practice techniques that help alleviate stress constructively.
- Implementation: Use mindfulness, yoga, deep breathing, or physical exercise to cope with stress instead of turning to addictive behaviors.
4. Enhance Coping Skills
- Strategy: Cultivate healthy ways to address life’s challenges.
- Implementation: Learn problem-solving techniques, seek support from friends or family, and explore creative outlets to manage stress effectively.
5. Self-Reflection
- Strategy: Regularly evaluate your values, goals, and overall well-being.
- Implementation: Spend time journaling or meditating to assess whether your actions align with your long-term aspirations and personal principles.
6. Time Management
- Strategy: Balance daily activities to avoid overindulgence in any single behavior.
- Implementation: Plan a schedule that prioritizes work, leisure, and self-care to ensure a healthy mix of activities.
7. Seek Social Support
- Strategy: Surround yourself with positive influences.
- Implementation: Cultivate relationships with people who encourage healthy behaviors and provide a supportive environment.
8. Educate Yourself
- Strategy: Stay informed about the risks associated with addictive behaviors.
- Implementation: Learn about the potential harms of substances or activities to strengthen your ability to make conscious, informed choices.
9. Mindful Decision-Making
- Strategy: Pause and evaluate the consequences of your actions.
- Implementation: Before engaging in any potentially harmful behavior, take a moment to consider its impact on your well-being and goals.
10. Goal Setting
- Strategy: Establish meaningful personal and professional objectives.
- Implementation: Define realistic, achievable goals that provide a sense of purpose and direction, minimizing the allure of detrimental behaviors.
11. Regular Self-Assessment
- Strategy: Periodically examine your habits and behaviors.
- Implementation: Reflect on your actions to identify any patterns that might signal emerging addictive tendencies, allowing for early intervention.
Proactive self-management fosters resilience and prevents the development of addictive behaviors. By cultivating healthy habits, managing stress, and maintaining alignment with personal goals, individuals can create a solid foundation for long-term well-being.
If concerns about addictive tendencies arise, seeking professional support can provide valuable insights and personalized strategies to address specific challenges. With a proactive and mindful approach, individuals can sustain a life aligned with their values and aspirations.
The Role of Family Support in Preventing Addictive Behaviors
Family support is a cornerstone in preventing addictive behaviors, as it fosters a nurturing environment where healthy habits and resilience thrive. By cultivating trust, open communication, and mutual support, families can proactively address risks and strengthen their bond. Here are key strategies for leveraging family support to prevent addictive behaviors:
1. Open Communication
- Strategy: Promote honest, non-judgmental conversations within the family.
- Implementation: Create a safe space for expressing thoughts and concerns to reinforce trust and understanding.
2. Education and Awareness
- Strategy: Equip family members with knowledge about the risks and consequences of addiction.
- Implementation: Share resources and information on substance abuse and behavioral addictions to foster awareness and informed decision-making.
3. Healthy Role Modeling
- Strategy: Lead by example with positive behaviors and habits.
- Implementation: Practice healthy coping mechanisms, manage stress constructively, and make sound decisions to inspire similar behavior in others.
4. Establish Family Values
- Strategy: Define shared values that discourage addiction and promote well-being.
- Implementation: Clearly communicate and uphold values emphasizing health, mutual respect, and positive choices.
5. Participate in Family Activities
- Strategy: Strengthen bonds through shared experiences.
- Implementation: Engage in regular activities, such as game nights, outdoor adventures, or cooking together, to promote connection and support.
6. Encourage Hobbies and Interests
- Strategy: Support individual pursuits and passions.
- Implementation: Foster an environment where family members can explore hobbies, reducing reliance on harmful behaviors for fulfillment.
7. Set Clear Expectations
- Strategy: Communicate rules and boundaries within the family.
- Implementation: Define expectations regarding behavior and establish consequences for risky actions to encourage accountability.
8. Provide Emotional Support
- Strategy: Be present for family members during challenging times.
- Implementation: Offer empathy, understanding, and encouragement to create a supportive network that promotes resilience.
9. Address Underlying Issues
- Strategy: Identify and resolve family stressors or conflicts.
- Implementation: Use open dialogue or seek professional help to tackle issues that may increase vulnerability to addictive behaviors.
10. Stay Connected
- Strategy: Foster strong relationships among family members.
- Implementation: Regularly check in with each other, spend quality time together, and emphasize the importance of mutual support.
11. Family Counseling or Therapy
- Strategy: Seek professional guidance if concerns arise.
- Implementation: Engage in family counseling to address underlying challenges and develop tailored prevention strategies.
By implementing these family support strategies, families can build a resilient and cohesive unit that actively works to prevent addictive behaviors. A foundation of trust, shared values, and open communication ensures that every family member feels supported and empowered to make positive choices. Together, families can create an environment where well-being and mutual support thrive.
Community Resource Strategies for Preventing Addictive Behaviors
Community resource strategies play a pivotal role in addressing and preventing addictive behaviors by fostering support, education, and intervention at a collective level. A well-equipped community can create an environment where individuals are empowered to make healthier choices and access the resources they need. Here are key community resource strategies that contribute to addiction prevention:
1. Community Education Programs
- Strategy: Conduct educational initiatives on substance abuse and behavioral addictions.
- Implementation: Host workshops, seminars, or community events to increase awareness of addiction risks and promote informed decision-making.
2. Access to Treatment Services
- Strategy: Ensure treatment services are readily available and accessible.
- Implementation: Advocate for local addiction treatment centers, counseling services, and helplines to assist individuals in need.
3. Youth Prevention Programs
- Strategy: Target youth with prevention initiatives.
- Implementation: Develop school-based and community center programs to educate young individuals on the risks of addiction and provide healthy coping skills.
4. Community Support Groups
- Strategy: Establish support groups for individuals and families affected by addiction.
- Implementation: Facilitate regular meetings where members can share experiences, seek guidance, and build a support network.
5. Crisis Intervention Services
- Strategy: Offer immediate assistance to individuals in crisis.
- Implementation: Create helplines and deploy crisis intervention teams to address substance abuse or addiction emergencies.
6. Community Policing and Enforcement
- Strategy: Collaborate with law enforcement to address illegal substance use.
- Implementation: Support community policing efforts that focus on preventing drug trafficking and other activities contributing to addiction.
7. Community-Based Mental Health Services
- Strategy: Provide accessible mental health resources.
- Implementation: Advocate for mental health clinics and counseling services to address issues contributing to addictive behaviors.
8. Recreational and Youth Centers
- Strategy: Offer alternatives to potentially addictive behaviors.
- Implementation: Establish recreational facilities and youth centers that provide safe, engaging activities and opportunities for connection.
9. Community Awareness Campaigns
- Strategy: Launch campaigns to promote addiction prevention.
- Implementation: Use social media, local media outlets, and public events to disseminate information on addiction risks, prevention strategies, and available resources.
10. Parenting Programs
- Strategy: Equip parents with tools to prevent addiction in their children.
- Implementation: Provide workshops that focus on effective communication, setting boundaries, and recognizing early signs of addiction.
11. Employment Assistance Programs
- Strategy: Support employment initiatives for those in recovery.
- Implementation: Facilitate job training, placement, and career support programs to promote stability, a key protective factor against addiction.
12. Policy Advocacy
- Strategy: Advocate for local and regional policies supporting addiction prevention and treatment.
- Implementation: Work with policymakers to enhance treatment accessibility, enforce harm reduction strategies, and fund prevention programs.
Community resource strategies create a collaborative framework that empowers individuals while addressing environmental factors contributing to addictive behaviors. By focusing on education, prevention, treatment, and policy advocacy, communities can foster a culture of resilience and support, reducing the prevalence of addiction and enhancing overall well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some common questions:
(Behavioral addictions include gambling, gaming, social media use, shopping, pornography, compulsive eating, or work addiction.)
1. What is a behavioral addiction?
A behavioral addiction occurs when a person repeatedly engages in a behavior despite negative consequences, loss of control, and emotional distress — similar to substance addiction but without drugs or alcohol.
2. How is behavioral addiction different from a bad habit?
A habit is a routine choice. An addiction involves compulsive behavior, cravings, withdrawal-like symptoms, and interference with daily life or relationships.
3. Why do behavioral addictions form?
They develop when behaviors trigger dopamine release in the brain’s reward system. Over time, the brain begins to crave the behavior for relief, pleasure, or escape.
4. Can behavioral addictions change brain function?
Yes. Research shows behavioral addictions activate the same neural reward pathways as substance use disorders, reinforcing compulsive repetition.
5. What are common signs of behavioral addiction?
- Loss of control
- Increasing time spent on the behavior
- Failed attempts to stop
- Neglect of responsibilities
- Irritability or anxiety when unable to engage
- Continued behavior despite harm
6. Why is it hard to stop behavioral addictions?
Triggers are often part of daily life (phones, money, internet). Avoidance is difficult, making structured coping strategies essential.
7. Do behavioral addictions involve withdrawal?
Yes. People may experience restlessness, irritability, anxiety, low mood, or cravings when the behavior is stopped.
8. How are behavioral addictions treated?
Effective treatments include:
- Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT)
- Mindfulness-based relapse prevention
- Impulse-control training
- Support groups
- Trigger management plans
9. Can medication help?
Sometimes. Certain medications may reduce compulsive urges or treat co-occurring anxiety or depression, under medical supervision.
10. How do triggers affect behavioral addiction?
Triggers may include boredom, stress, loneliness, excitement, or environmental cues (notifications, stores, websites).
11. What are healthy replacement behaviors?
- Exercise
- Creative hobbies
- Social connection
- Meditation or journaling
- Structured daily routines
12. Can someone fully recover from behavioral addiction?
Yes. Recovery means regaining control, reducing compulsive urges, and restoring balance — not necessarily engaging in the behavior again, but doing so safely if appropriate.
13. How long does recovery take?
It varies. Many people notice improvement within weeks of structured treatment, with continued progress over months.
14. How can families support someone with behavioral addiction?
- Avoid shaming
- Encourage treatment
- Set clear boundaries
- Participate in family therapy
- Celebrate progress
15. What is the biggest key to breaking behavioral addiction?
Awareness + coping skills + consistent support. Recovery is about learning new ways to meet emotional needs without compulsive behavior.
Conclusion
The multifaceted nature of addictive behaviors underscores the importance of addressing cultural influences and the availability of addictive stimuli in prevention efforts. The dynamic interplay between culture and accessibility shapes individuals’ susceptibility to engaging in addictive behaviors. Adopting a holistic approach is paramount, and self-management strategies offer individuals the tools to make informed choices. Equally crucial are the roles of family support and community resources, providing a foundation for prevention that extends beyond individual efforts. By recognizing the cultural nuances and enhancing accessibility to supportive resources, communities can foster resilience, reduce the prevalence of addictive behaviors, and ultimately contribute to the well-being of individuals and society as a whole.
Video: